Boyang Liang
Unfolding Once is Enough: A Deployment-Friendly Transformer Unit for Super-Resolution
Aug 05, 2023



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed a few attempts of vision transformers for single image super-resolution (SISR). Since the high resolution of intermediate features in SISR models increases memory and computational requirements, efficient SISR transformers are more favored. Based on some popular transformer backbone, many methods have explored reasonable schemes to reduce the computational complexity of the self-attention module while achieving impressive performance. However, these methods only focus on the performance on the training platform (e.g., Pytorch/Tensorflow) without further optimization for the deployment platform (e.g., TensorRT). Therefore, they inevitably contain some redundant operators, posing challenges for subsequent deployment in real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a deployment-friendly transformer unit, namely UFONE (i.e., UnFolding ONce is Enough), to alleviate these problems. In each UFONE, we introduce an Inner-patch Transformer Layer (ITL) to efficiently reconstruct the local structural information from patches and a Spatial-Aware Layer (SAL) to exploit the long-range dependencies between patches. Based on UFONE, we propose a Deployment-friendly Inner-patch Transformer Network (DITN) for the SISR task, which can achieve favorable performance with low latency and memory usage on both training and deployment platforms. Furthermore, to further boost the deployment efficiency of the proposed DITN on TensorRT, we also provide an efficient substitution for layer normalization and propose a fusion optimization strategy for specific operators. Extensive experiments show that our models can achieve competitive results in terms of qualitative and quantitative performance with high deployment efficiency. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/yongliuy/DITN}.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and Results
Apr 25, 2022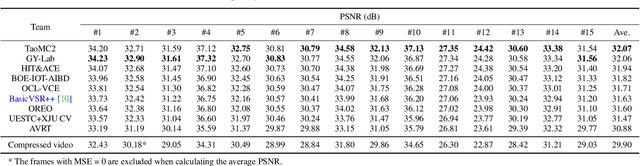
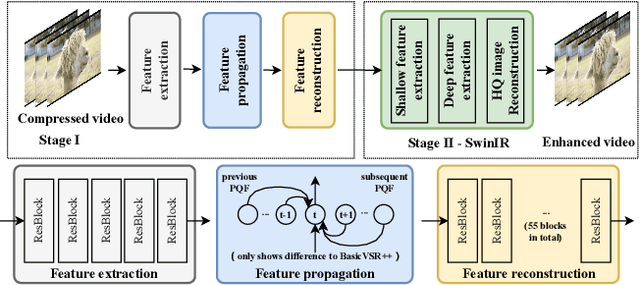
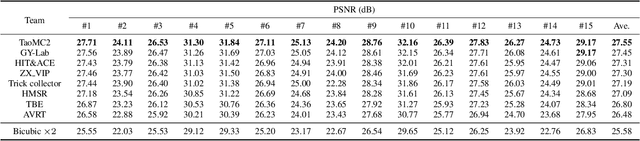
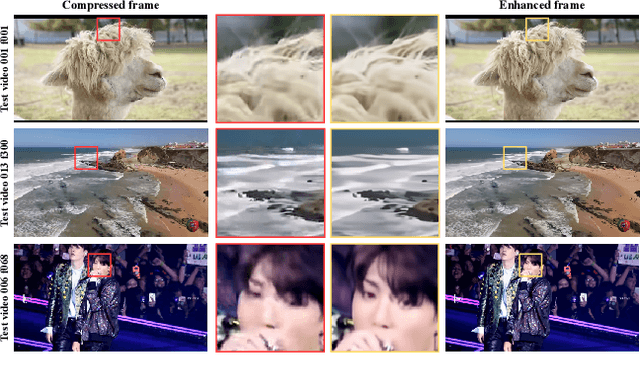
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video. In this challenge, we proposed the LDV 2.0 dataset, which includes the LDV dataset (240 videos) and 95 additional videos. This challenge includes three tracks. Track 1 aims at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP. Track 2 and Track 3 target both the super-resolution and quality enhancement of HEVC compressed video. They require x2 and x4 super-resolution, respectively. The three tracks totally attract more than 600 registrations. In the test phase, 8 teams, 8 teams and 12 teams submitted the final results to Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of super-resolution and quality enhancement of compressed video. The proposed LDV 2.0 dataset is available at https://github.com/RenYang-home/LDV_dataset. The homepage of this challenge (including open-sourced codes) is at https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE22_VEnh_SR.
Deep Recurrent Neural Network with Multi-scale Bi-directional Propagation for Video Deblurring
Dec 09, 2021



Abstract:The success of the state-of-the-art video deblurring methods stems mainly from implicit or explicit estimation of alignment among the adjacent frames for latent video restoration. However, due to the influence of the blur effect, estimating the alignment information from the blurry adjacent frames is not a trivial task. Inaccurate estimations will interfere the following frame restoration. Instead of estimating alignment information, we propose a simple and effective deep Recurrent Neural Network with Multi-scale Bi-directional Propagation (RNN-MBP) to effectively propagate and gather the information from unaligned neighboring frames for better video deblurring. Specifically, we build a Multi-scale Bi-directional Propagation~(MBP) module with two U-Net RNN cells which can directly exploit the inter-frame information from unaligned neighboring hidden states by integrating them in different scales. Moreover, to better evaluate the proposed algorithm and existing state-of-the-art methods on real-world blurry scenes, we also create a Real-World Blurry Video Dataset (RBVD) by a well-designed Digital Video Acquisition System (DVAS) and use it as the training and evaluation dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RBVD dataset effectively improves the performance of existing algorithms on real-world blurry videos, and the proposed algorithm performs favorably against the state-of-the-art methods on three typical benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/XJTU-CVLAB-LOWLEVEL/RNN-MBP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge