Bo Xin
Improving Person Re-identification with Iterative Impression Aggregation
Sep 21, 2020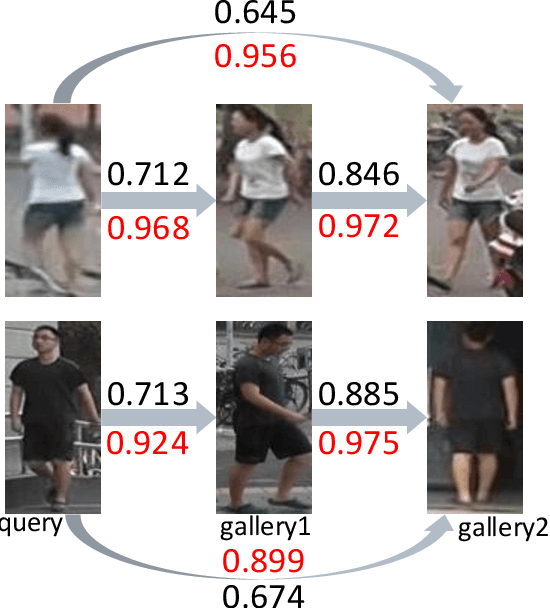
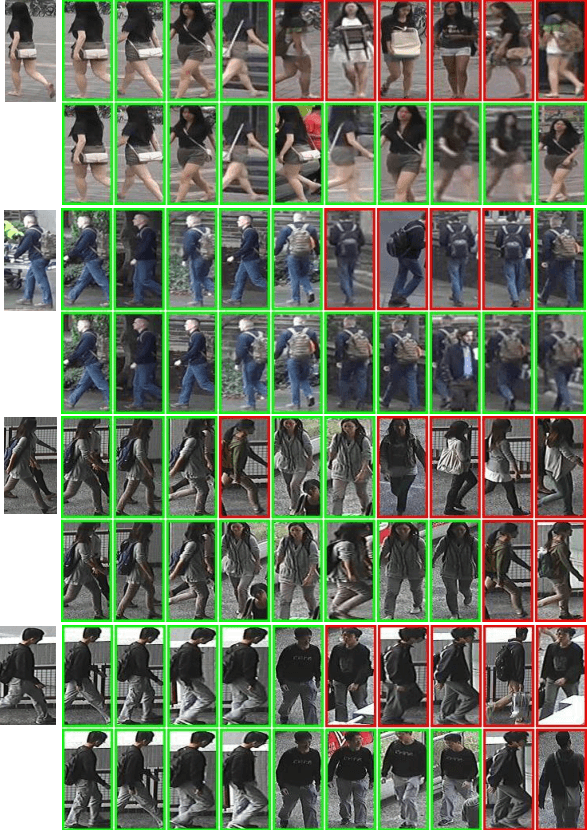

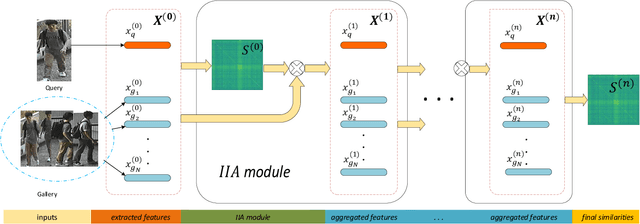

Abstract:Our impression about one person often updates after we see more aspects of him/her and this process keeps iterating given more meetings. We formulate such an intuition into the problem of person re-identification (re-ID), where the representation of a query (probe) image is iteratively updated with new information from the candidates in the gallery. Specifically, we propose a simple attentional aggregation formulation to instantiate this idea and showcase that such a pipeline achieves competitive performance on standard benchmarks including CUHK03, Market-1501 and DukeMTMC. Not only does such a simple method improve the performance of the baseline models, it also achieves comparable performance with latest advanced re-ranking methods. Another advantage of this proposal is its flexibility to incorporate different representations and similarity metrics. By utilizing stronger representations and metrics, we further demonstrate state-of-the-art person re-ID performance, which also validates the general applicability of the proposed method.
Revisiting the Master-Slave Architecture in Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
Dec 20, 2017



Abstract:Many tasks in artificial intelligence require the collaboration of multiple agents. We exam deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent domains. Recent research efforts often take the form of two seemingly conflicting perspectives, the decentralized perspective, where each agent is supposed to have its own controller; and the centralized perspective, where one assumes there is a larger model controlling all agents. In this regard, we revisit the idea of the master-slave architecture by incorporating both perspectives within one framework. Such a hierarchical structure naturally leverages advantages from one another. The idea of combining both perspectives is intuitive and can be well motivated from many real world systems, however, out of a variety of possible realizations, we highlights three key ingredients, i.e. composed action representation, learnable communication and independent reasoning. With network designs to facilitate these explicitly, our proposal consistently outperforms latest competing methods both in synthetic experiments and when applied to challenging StarCraft micromanagement tasks.
From Bayesian Sparsity to Gated Recurrent Nets
Aug 02, 2017



Abstract:The iterations of many first-order algorithms, when applied to minimizing common regularized regression functions, often resemble neural network layers with pre-specified weights. This observation has prompted the development of learning-based approaches that purport to replace these iterations with enhanced surrogates forged as DNN models from available training data. For example, important NP-hard sparse estimation problems have recently benefitted from this genre of upgrade, with simple feedforward or recurrent networks ousting proximal gradient-based iterations. Analogously, this paper demonstrates that more powerful Bayesian algorithms for promoting sparsity, which rely on complex multi-loop majorization-minimization techniques, mirror the structure of more sophisticated long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, or alternative gated feedback networks previously designed for sequence prediction. As part of this development, we examine the parallels between latent variable trajectories operating across multiple time-scales during optimization, and the activations within deep network structures designed to adaptively model such characteristic sequences. The resulting insights lead to a novel sparse estimation system that, when granted training data, can estimate optimal solutions efficiently in regimes where other algorithms fail, including practical direction-of-arrival (DOA) and 3D geometry recovery problems. The underlying principles we expose are also suggestive of a learning process for a richer class of multi-loop algorithms in other domains.
Collaborative Deep Reinforcement Learning for Joint Object Search
Feb 18, 2017



Abstract:We examine the problem of joint top-down active search of multiple objects under interaction, e.g., person riding a bicycle, cups held by the table, etc.. Such objects under interaction often can provide contextual cues to each other to facilitate more efficient search. By treating each detector as an agent, we present the first collaborative multi-agent deep reinforcement learning algorithm to learn the optimal policy for joint active object localization, which effectively exploits such beneficial contextual information. We learn inter-agent communication through cross connections with gates between the Q-networks, which is facilitated by a novel multi-agent deep Q-learning algorithm with joint exploitation sampling. We verify our proposed method on multiple object detection benchmarks. Not only does our model help to improve the performance of state-of-the-art active localization models, it also reveals interesting co-detection patterns that are intuitively interpretable.
Maximal Sparsity with Deep Networks?
May 10, 2016



Abstract:The iterations of many sparse estimation algorithms are comprised of a fixed linear filter cascaded with a thresholding nonlinearity, which collectively resemble a typical neural network layer. Consequently, a lengthy sequence of algorithm iterations can be viewed as a deep network with shared, hand-crafted layer weights. It is therefore quite natural to examine the degree to which a learned network model might act as a viable surrogate for traditional sparse estimation in domains where ample training data is available. While the possibility of a reduced computational budget is readily apparent when a ceiling is imposed on the number of layers, our work primarily focuses on estimation accuracy. In particular, it is well-known that when a signal dictionary has coherent columns, as quantified by a large RIP constant, then most tractable iterative algorithms are unable to find maximally sparse representations. In contrast, we demonstrate both theoretically and empirically the potential for a trained deep network to recover minimal $\ell_0$-norm representations in regimes where existing methods fail. The resulting system is deployed on a practical photometric stereo estimation problem, where the goal is to remove sparse outliers that can disrupt the estimation of surface normals from a 3D scene.
Exploring Algorithmic Limits of Matrix Rank Minimization under Affine Constraints
Jul 01, 2015



Abstract:Many applications require recovering a matrix of minimal rank within an affine constraint set, with matrix completion a notable special case. Because the problem is NP-hard in general, it is common to replace the matrix rank with the nuclear norm, which acts as a convenient convex surrogate. While elegant theoretical conditions elucidate when this replacement is likely to be successful, they are highly restrictive and convex algorithms fail when the ambient rank is too high or when the constraint set is poorly structured. Non-convex alternatives fare somewhat better when carefully tuned; however, convergence to locally optimal solutions remains a continuing source of failure. Against this backdrop we derive a deceptively simple and parameter-free probabilistic PCA-like algorithm that is capable, over a wide battery of empirical tests, of successful recovery even at the theoretical limit where the number of measurements equal the degrees of freedom in the unknown low-rank matrix. Somewhat surprisingly, this is possible even when the affine constraint set is highly ill-conditioned. While proving general recovery guarantees remains evasive for non-convex algorithms, Bayesian-inspired or otherwise, we nonetheless show conditions whereby the underlying cost function has a unique stationary point located at the global optimum; no existing cost function we are aware of satisfies this same property. We conclude with a simple computer vision application involving image rectification and a standard collaborative filtering benchmark.
Background Subtraction via Generalized Fused Lasso Foreground Modeling
Apr 14, 2015



Abstract:Background Subtraction (BS) is one of the key steps in video analysis. Many background models have been proposed and achieved promising performance on public data sets. However, due to challenges such as illumination change, dynamic background etc. the resulted foreground segmentation often consists of holes as well as background noise. In this regard, we consider generalized fused lasso regularization to quest for intact structured foregrounds. Together with certain assumptions about the background, such as the low-rank assumption or the sparse-composition assumption (depending on whether pure background frames are provided), we formulate BS as a matrix decomposition problem using regularization terms for both the foreground and background matrices. Moreover, under the proposed formulation, the two generally distinctive background assumptions can be solved in a unified manner. The optimization was carried out via applying the augmented Lagrange multiplier (ALM) method in such a way that a fast parametric-flow algorithm is used for updating the foreground matrix. Experimental results on several popular BS data sets demonstrate the advantage of the proposed model compared to state-of-the-arts.
Stable Feature Selection from Brain sMRI
Mar 25, 2015



Abstract:Neuroimage analysis usually involves learning thousands or even millions of variables using only a limited number of samples. In this regard, sparse models, e.g. the lasso, are applied to select the optimal features and achieve high diagnosis accuracy. The lasso, however, usually results in independent unstable features. Stability, a manifest of reproducibility of statistical results subject to reasonable perturbations to data and the model, is an important focus in statistics, especially in the analysis of high dimensional data. In this paper, we explore a nonnegative generalized fused lasso model for stable feature selection in the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. In addition to sparsity, our model incorporates two important pathological priors: the spatial cohesion of lesion voxels and the positive correlation between the features and the disease labels. To optimize the model, we propose an efficient algorithm by proving a novel link between total variation and fast network flow algorithms via conic duality. Experiments show that the proposed nonnegative model performs much better in exploring the intrinsic structure of data via selecting stable features compared with other state-of-the-arts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge