Baldo Faieta
Controlled and Conditional Text to Image Generation with Diffusion Prior
Feb 23, 2023Abstract:Denoising Diffusion models have shown remarkable performance in generating diverse, high quality images from text. Numerous techniques have been proposed on top of or in alignment with models like Stable Diffusion and Imagen that generate images directly from text. A lesser explored approach is DALLE-2's two step process comprising a Diffusion Prior that generates a CLIP image embedding from text and a Diffusion Decoder that generates an image from a CLIP image embedding. We explore the capabilities of the Diffusion Prior and the advantages of an intermediate CLIP representation. We observe that Diffusion Prior can be used in a memory and compute efficient way to constrain the generation to a specific domain without altering the larger Diffusion Decoder. Moreover, we show that the Diffusion Prior can be trained with additional conditional information such as color histogram to further control the generation. We show quantitatively and qualitatively that the proposed approaches perform better than prompt engineering for domain specific generation and existing baselines for color conditioned generation. We believe that our observations and results will instigate further research into the diffusion prior and uncover more of its capabilities.
HyperNST: Hyper-Networks for Neural Style Transfer
Aug 09, 2022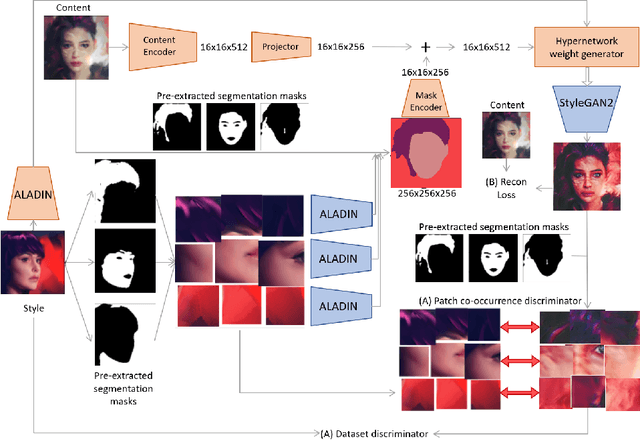
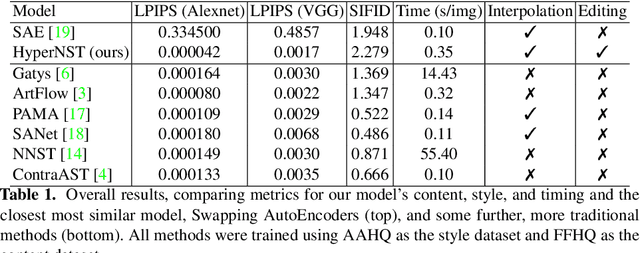
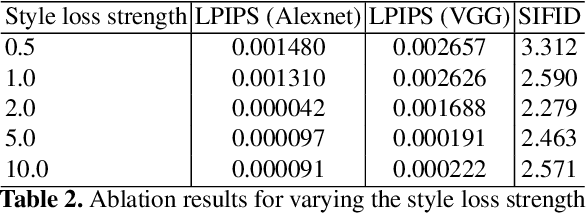
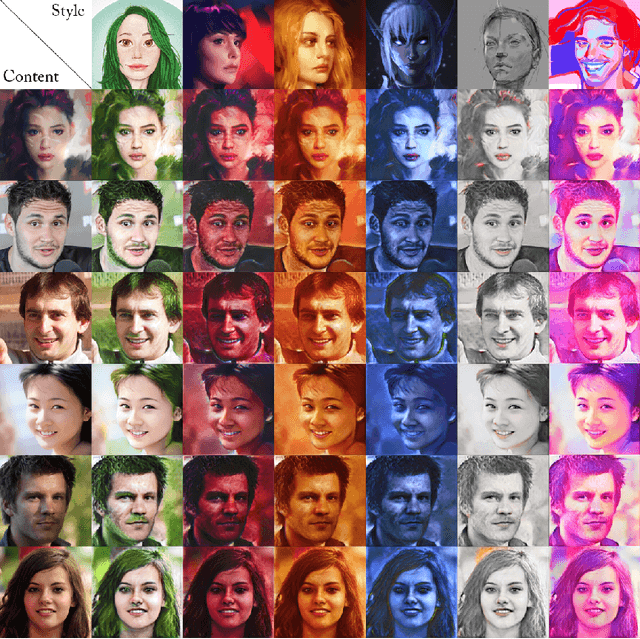
Abstract:We present HyperNST; a neural style transfer (NST) technique for the artistic stylization of images, based on Hyper-networks and the StyleGAN2 architecture. Our contribution is a novel method for inducing style transfer parameterized by a metric space, pre-trained for style-based visual search (SBVS). We show for the first time that such space may be used to drive NST, enabling the application and interpolation of styles from an SBVS system. The technical contribution is a hyper-network that predicts weight updates to a StyleGAN2 pre-trained over a diverse gamut of artistic content (portraits), tailoring the style parameterization on a per-region basis using a semantic map of the facial regions. We show HyperNST to exceed state of the art in content preservation for our stylized content while retaining good style transfer performance.
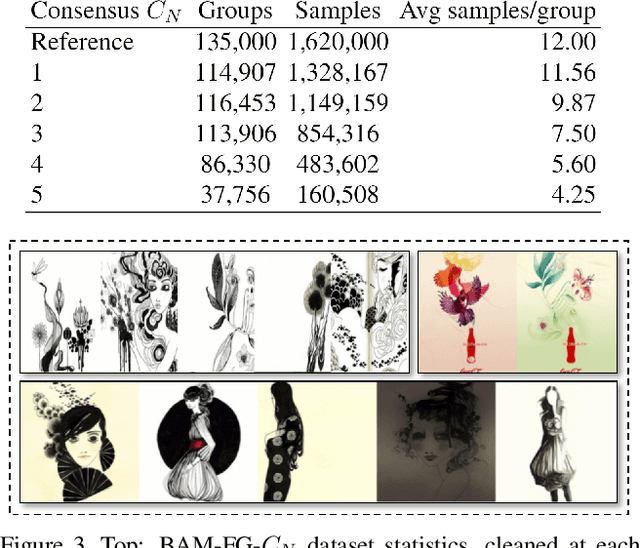
StyleBabel: Artistic Style Tagging and Captioning
Mar 11, 2022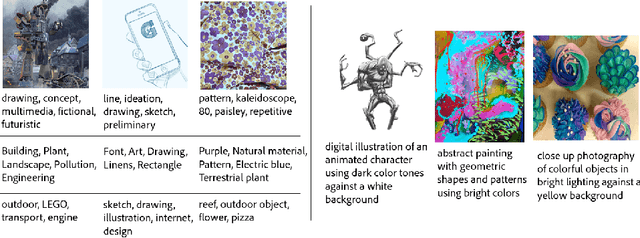
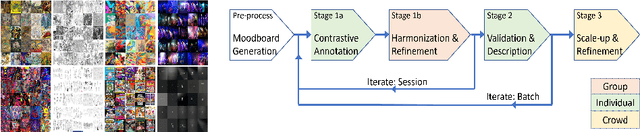
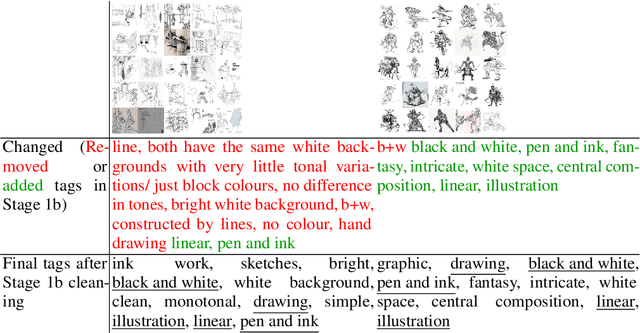
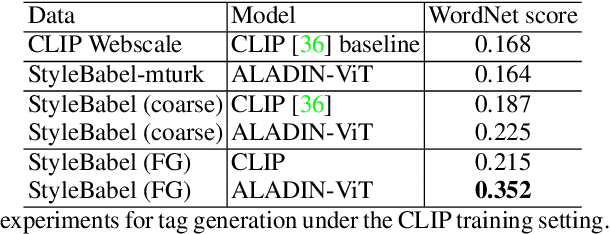
Abstract:We present StyleBabel, a unique open access dataset of natural language captions and free-form tags describing the artistic style of over 135K digital artworks, collected via a novel participatory method from experts studying at specialist art and design schools. StyleBabel was collected via an iterative method, inspired by `Grounded Theory': a qualitative approach that enables annotation while co-evolving a shared language for fine-grained artistic style attribute description. We demonstrate several downstream tasks for StyleBabel, adapting the recent ALADIN architecture for fine-grained style similarity, to train cross-modal embeddings for: 1) free-form tag generation; 2) natural language description of artistic style; 3) fine-grained text search of style. To do so, we extend ALADIN with recent advances in Visual Transformer (ViT) and cross-modal representation learning, achieving a state of the art accuracy in fine-grained style retrieval.
Multimodal Contrastive Training for Visual Representation Learning
Apr 26, 2021



Abstract:We develop an approach to learning visual representations that embraces multimodal data, driven by a combination of intra- and inter-modal similarity preservation objectives. Unlike existing visual pre-training methods, which solve a proxy prediction task in a single domain, our method exploits intrinsic data properties within each modality and semantic information from cross-modal correlation simultaneously, hence improving the quality of learned visual representations. By including multimodal training in a unified framework with different types of contrastive losses, our method can learn more powerful and generic visual features. We first train our model on COCO and evaluate the learned visual representations on various downstream tasks including image classification, object detection, and instance segmentation. For example, the visual representations pre-trained on COCO by our method achieve state-of-the-art top-1 validation accuracy of $55.3\%$ on ImageNet classification, under the common transfer protocol. We also evaluate our method on the large-scale Stock images dataset and show its effectiveness on multi-label image tagging, and cross-modal retrieval tasks.
ALADIN: All Layer Adaptive Instance Normalization for Fine-grained Style Similarity
Mar 17, 2021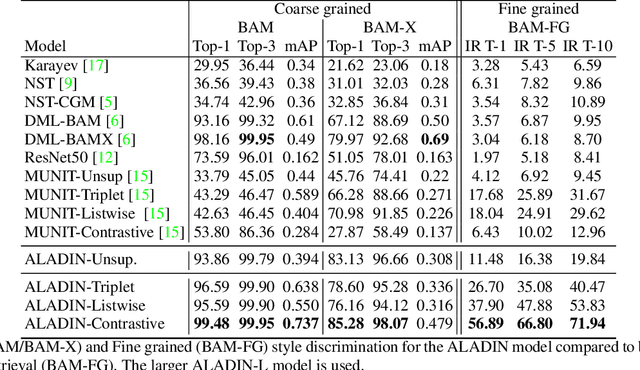
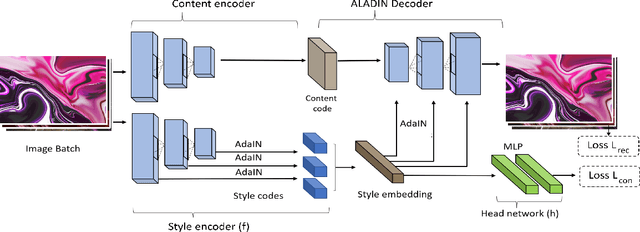
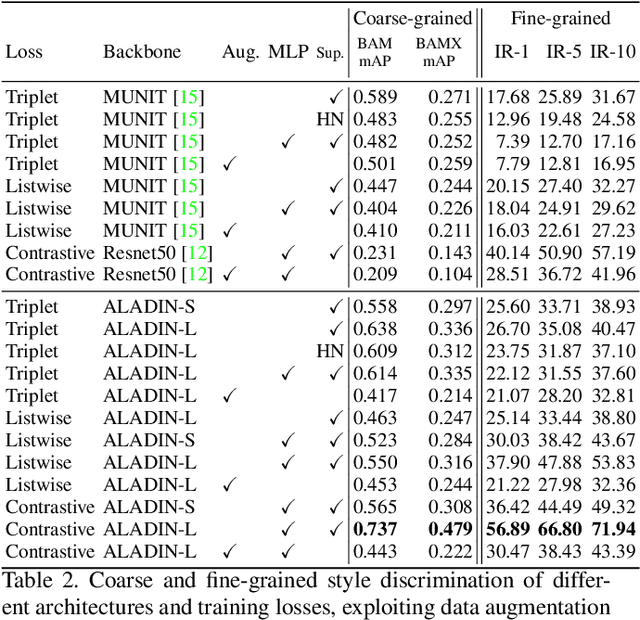
Abstract:We present ALADIN (All Layer AdaIN); a novel architecture for searching images based on the similarity of their artistic style. Representation learning is critical to visual search, where distance in the learned search embedding reflects image similarity. Learning an embedding that discriminates fine-grained variations in style is hard, due to the difficulty of defining and labelling style. ALADIN takes a weakly supervised approach to learning a representation for fine-grained style similarity of digital artworks, leveraging BAM-FG, a novel large-scale dataset of user generated content groupings gathered from the web. ALADIN sets a new state of the art accuracy for style-based visual search over both coarse labelled style data (BAM) and BAM-FG; a new 2.62 million image dataset of 310,000 fine-grained style groupings also contributed by this work.
Multitask Text-to-Visual Embedding with Titles and Clickthrough Data
May 30, 2019



Abstract:Text-visual (or called semantic-visual) embedding is a central problem in vision-language research. It typically involves mapping of an image and a text description to a common feature space through a CNN image encoder and a RNN language encoder. In this paper, we propose a new method for learning text-visual embedding using both image titles and click-through data from an image search engine. We also propose a new triplet loss function by modeling positive awareness of the embedding, and introduce a novel mini-batch-based hard negative sampling approach for better data efficiency in the learning process. Experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms existing methods, and is also effective for real-world text-to-visual retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge