Azaan Rehman
Advancing low-field MRI with a universal denoising imaging transformer: Towards fast and high-quality imaging
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Recent developments in low-field (LF) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems present remarkable opportunities for affordable and widespread MRI access. A robust denoising method to overcome the intrinsic low signal-noise-ratio (SNR) barrier is critical to the success of LF MRI. However, current data-driven MRI denoising methods predominantly handle magnitude images and rely on customized models with constrained data diversity and quantity, which exhibit limited generalizability in clinical applications across diverse MRI systems, pulse sequences, and organs. In this study, we present ImT-MRD: a complex-valued imaging transformer trained on a vast number of clinical MRI scans aiming at universal MR denoising at LF systems. Compared with averaging multiple-repeated scans for higher image SNR, the model obtains better image quality from fewer repetitions, demonstrating its capability for accelerating scans under various clinical settings. Moreover, with its complex-valued image input, the model can denoise intermediate results before advanced post-processing and prepare high-quality data for further MRI research. By delivering universal and accurate denoising across clinical and research tasks, our model holds great promise to expedite the evolution of LF MRI for accessible and equal biomedical applications.
Inline AI: Open-source Deep Learning Inference for Cardiac MR
Apr 03, 2024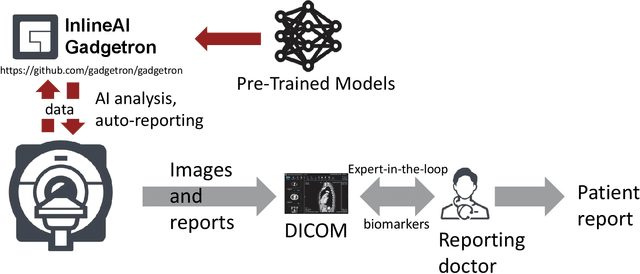
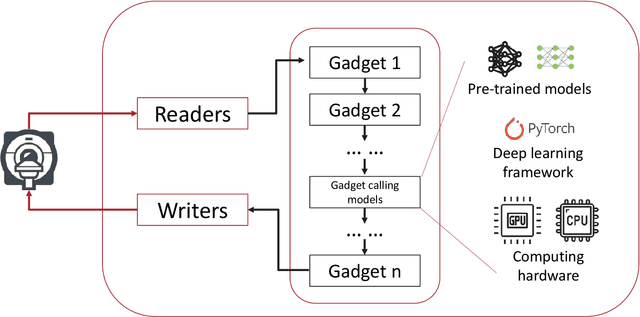
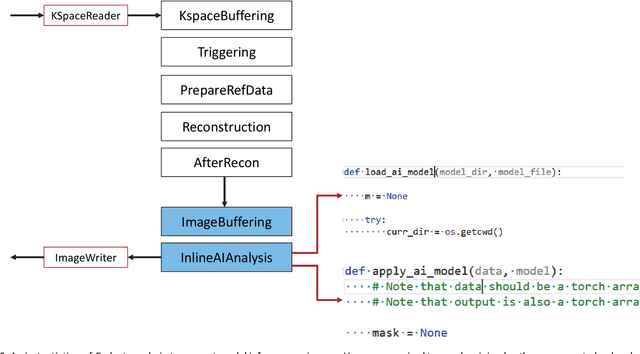
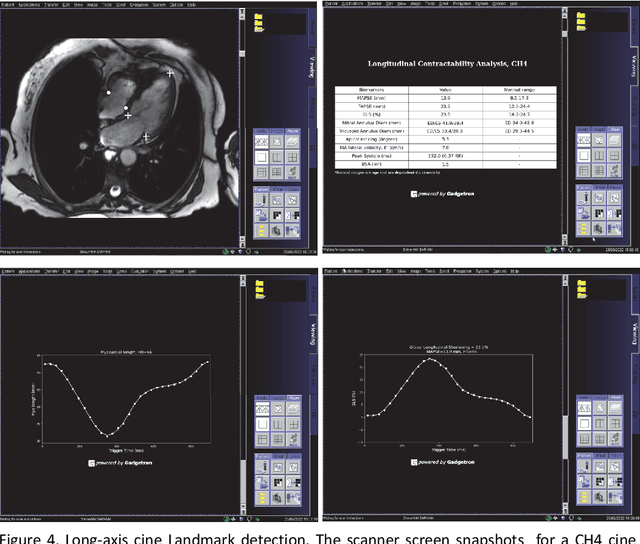
Abstract:Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) is established as a non-invasive imaging technique for evaluation of heart function, anatomy, and myocardial tissue characterization. Quantitative biomarkers are central for diagnosis and management of heart disease. Deep learning (DL) is playing an ever more important role in extracting these quantitative measures from CMR images. While many researchers have reported promising results in training and evaluating models, model deployment into the imaging workflow is less explored. A new imaging AI framework, the InlineAI, was developed and open-sourced. The main innovation is to enable the model inference inline as a part of imaging computation, instead of as an offline post-processing step and to allow users to plug in their models. We demonstrate the system capability on three applications: long-axis CMR cine landmark detection, short-axis CMR cine analysis of function and anatomy, and quantitative perfusion mapping. The InlineAI allowed models to be deployed into imaging workflow in a streaming manner directly on the scanner. The model was loaded and inference on incoming images were performed while the data acquisition was ongoing, and results were sent back to scanner. Several biomarkers were extracted from model outputs in the demonstrated applications and reported as curves and tabular values. All processes are full automated. the model inference was completed within 6-45s after the end of imaging data acquisition.
Imaging transformer for MRI denoising with the SNR unit training: enabling generalization across field-strengths, imaging contrasts, and anatomy
Apr 03, 2024

Abstract:The ability to recover MRI signal from noise is key to achieve fast acquisition, accurate quantification, and high image quality. Past work has shown convolutional neural networks can be used with abundant and paired low and high-SNR images for training. However, for applications where high-SNR data is difficult to produce at scale (e.g. with aggressive acceleration, high resolution, or low field strength), training a new denoising network using a large quantity of high-SNR images can be infeasible. In this study, we overcome this limitation by improving the generalization of denoising models, enabling application to many settings beyond what appears in the training data. Specifically, we a) develop a training scheme that uses complex MRIs reconstructed in the SNR units (i.e., the images have a fixed noise level, SNR unit training) and augments images with realistic noise based on coil g-factor, and b) develop a novel imaging transformer (imformer) to handle 2D, 2D+T, and 3D MRIs in one model architecture. Through empirical evaluation, we show this combination improves performance compared to CNN models and improves generalization, enabling a denoising model to be used across field-strengths, image contrasts, and anatomy.
MTGAT: Multimodal Temporal Graph Attention Networks for Unaligned Human Multimodal Language Sequences
Oct 22, 2020



Abstract:Human communication is multimodal in nature; it is through multiple modalities, i.e., language, voice, and facial expressions, that opinions and emotions are expressed. Data in this domain exhibits complex multi-relational and temporal interactions. Learning from this data is a fundamentally challenging research problem. In this paper, we propose Multimodal Temporal Graph Attention Networks (MTGAT). MTGAT is an interpretable graph-based neural model that provides a suitable framework for analyzing this type of multimodal sequential data. We first introduce a procedure to convert unaligned multimodal sequence data into a graph with heterogeneous nodes and edges that captures the rich interactions between different modalities through time. Then, a novel graph operation, called Multimodal Temporal Graph Attention, along with a dynamic pruning and read-out technique is designed to efficiently process this multimodal temporal graph. By learning to focus only on the important interactions within the graph, our MTGAT is able to achieve state-of-the-art performance on multimodal sentiment analysis and emotion recognition benchmarks including IEMOCAP and CMU-MOSI, while utilizing significantly fewer computations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge