Ario Sadafi
Attention Pooling Enhances NCA-based Classification of Microscopy Images
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Neural Cellular Automata (NCA) offer a robust and interpretable approach to image classification, making them a promising choice for microscopy image analysis. However, a performance gap remains between NCA and larger, more complex architectures. We address this challenge by integrating attention pooling with NCA to enhance feature extraction and improve classification accuracy. The attention pooling mechanism refines the focus on the most informative regions, leading to more accurate predictions. We evaluate our method on eight diverse microscopy image datasets and demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing NCA methods while remaining parameter-efficient and explainable. Furthermore, we compare our method with traditional lightweight convolutional neural network and vision transformer architectures, showing improved performance while maintaining a significantly lower parameter count. Our results highlight the potential of NCA-based models an alternative for explainable image classification.
Neural Cellular Automata for Weakly Supervised Segmentation of White Blood Cells
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:The detection and segmentation of white blood cells in blood smear images is a key step in medical diagnostics, supporting various downstream tasks such as automated blood cell counting, morphological analysis, cell classification, and disease diagnosis and monitoring. Training robust and accurate models requires large amounts of labeled data, which is both time-consuming and expensive to acquire. In this work, we propose a novel approach for weakly supervised segmentation using neural cellular automata (NCA-WSS). By leveraging the feature maps generated by NCA during classification, we can extract segmentation masks without the need for retraining with segmentation labels. We evaluate our method on three white blood cell microscopy datasets and demonstrate that NCA-WSS significantly outperforms existing weakly supervised approaches. Our work illustrates the potential of NCA for both classification and segmentation in a weakly supervised framework, providing a scalable and efficient solution for medical image analysis.
Multimodal Analysis of White Blood Cell Differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients using a β-Variational Autoencoder
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Biomedical imaging and RNA sequencing with single-cell resolution improves our understanding of white blood cell diseases like leukemia. By combining morphological and transcriptomic data, we can gain insights into cellular functions and trajectoriess involved in blood cell differentiation. However, existing methodologies struggle with integrating morphological and transcriptomic data, leaving a significant research gap in comprehensively understanding the dynamics of cell differentiation. Here, we introduce an unsupervised method that explores and reconstructs these two modalities and uncovers the relationship between different subtypes of white blood cells from human peripheral blood smears in terms of morphology and their corresponding transcriptome. Our method is based on a beta-variational autoencoder (\beta-VAE) with a customized loss function, incorporating a R-CNN architecture to distinguish single-cell from background and to minimize any interference from artifacts. This implementation of \beta-VAE shows good reconstruction capability along with continuous latent embeddings, while maintaining clear differentiation between single-cell classes. Our novel approach is especially helpful to uncover the correlation of two latent features in complex biological processes such as formation of granules in the cell (granulopoiesis) with gene expression patterns. It thus provides a unique tool to improve the understanding of white blood cell maturation for biomedicine and diagnostics.
Neural Cellular Automata for Lightweight, Robust and Explainable Classification of White Blood Cell Images
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Diagnosis of hematological malignancies depends on accurate identification of white blood cells in peripheral blood smears. Deep learning techniques are emerging as a viable solution to scale and optimize this process by automatic identification of cells in laboratories. However, these techniques face several challenges such as limited generalizability, sensitivity to domain shifts and lack of explainability. Here, we are introducing a novel approach based on neural cellular automata (NCA) for white blood cell classification. We test our approach on three datasets of white blood cell images and show that we achieve competitive performance compared to conventional methods. Our NCA-based method is significantly smaller in terms of parameters and exhibits robustness to domain shifts. Furthermore, the architecture is inherently explainable, providing insights into the decision process for each classification, helping experts understand and validate model predictions. Results demonstrate that NCA not only can be used for image classification, but also address key challenges of conventional methods, indicating a high potential for applicability in clinical practice.
A Continual Learning Approach for Cross-Domain White Blood Cell Classification
Aug 24, 2023



Abstract:Accurate classification of white blood cells in peripheral blood is essential for diagnosing hematological diseases. Due to constantly evolving clinical settings, data sources, and disease classifications, it is necessary to update machine learning classification models regularly for practical real-world use. Such models significantly benefit from sequentially learning from incoming data streams without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. However, models can suffer from catastrophic forgetting, causing a drop in performance on previous tasks when fine-tuned on new data. Here, we propose a rehearsal-based continual learning approach for class incremental and domain incremental scenarios in white blood cell classification. To choose representative samples from previous tasks, we employ exemplar set selection based on the model's predictions. This involves selecting the most confident samples and the most challenging samples identified through uncertainty estimation of the model. We thoroughly evaluated our proposed approach on three white blood cell classification datasets that differ in color, resolution, and class composition, including scenarios where new domains or new classes are introduced to the model with every task. We also test a long class incremental experiment with both new domains and new classes. Our results demonstrate that our approach outperforms established baselines in continual learning, including existing iCaRL and EWC methods for classifying white blood cells in cross-domain environments.
A Study of Age and Sex Bias in Multiple Instance Learning based Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Subtypes
Aug 24, 2023



Abstract:Accurate classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) subtypes is crucial for clinical decision-making and patient care. In this study, we investigate the potential presence of age and sex bias in AML subtype classification using Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) architectures. To that end, we train multiple MIL models using different levels of sex imbalance in the training set and excluding certain age groups. To assess the sex bias, we evaluate the performance of the models on male and female test sets. For age bias, models are tested against underrepresented age groups in the training data. We find a significant effect of sex and age bias on the performance of the model for AML subtype classification. Specifically, we observe that females are more likely to be affected by sex imbalance dataset and certain age groups, such as patients with 72 to 86 years of age with the RUNX1::RUNX1T1 genetic subtype, are significantly affected by an age bias present in the training data. Ensuring inclusivity in the training data is thus essential for generating reliable and equitable outcomes in AML genetic subtype classification, ultimately benefiting diverse patient populations.
Topologically-Regularized Multiple Instance Learning for Red Blood Cell Disease Classification
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Diagnosing rare anemia disorders using microscopic images is challenging for skilled specialists and machine-learning methods alike. Due to thousands of disease-relevant cells in a single blood sample, this constitutes a complex multiple-instance learning (MIL) problem. While the spatial neighborhood of red blood cells is not meaningful per se, the topology, i.e., the geometry of blood samples as a whole, contains informative features to remedy typical MIL issues, such as vanishing gradients and overfitting when training on limited data. We thus develop a topology-based approach that extracts multi-scale topological features from bags of single red blood cell images. The topological features are used to regularize the model, enforcing the preservation of characteristic topological properties of the data. Applied to a dataset of 71 patients suffering from rare anemia disorders with 521 microscopic images of red blood cells, our experiments show that topological regularization is an effective method that leads to more than 3% performance improvements for the automated classification of rare anemia disorders based on single-cell images. This is the first approach that uses topological properties for regularizing the MIL process.
Pixel-Level Explanation of Multiple Instance Learning Models in Biomedical Single Cell Images
Mar 15, 2023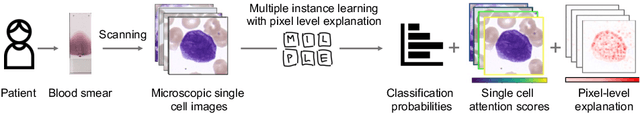
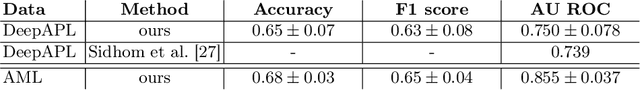
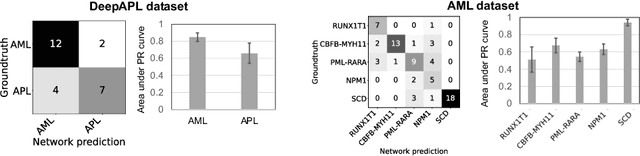
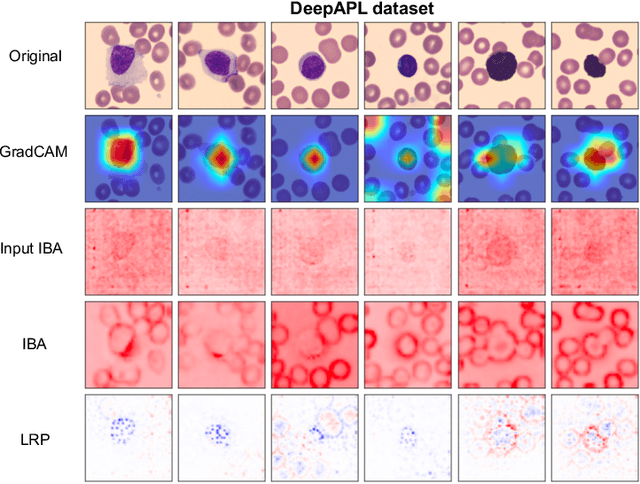
Abstract:Explainability is a key requirement for computer-aided diagnosis systems in clinical decision-making. Multiple instance learning with attention pooling provides instance-level explainability, however for many clinical applications a deeper, pixel-level explanation is desirable, but missing so far. In this work, we investigate the use of four attribution methods to explain a multiple instance learning models: GradCAM, Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation (LRP), Information Bottleneck Attribution (IBA), and InputIBA. With this collection of methods, we can derive pixel-level explanations on for the task of diagnosing blood cancer from patients' blood smears. We study two datasets of acute myeloid leukemia with over 100 000 single cell images and observe how each attribution method performs on the multiple instance learning architecture focusing on different properties of the white blood single cells. Additionally, we compare attribution maps with the annotations of a medical expert to see how the model's decision-making differs from the human standard. Our study addresses the challenge of implementing pixel-level explainability in multiple instance learning models and provides insights for clinicians to better understand and trust decisions from computer-aided diagnosis systems.
BEL: A Bag Embedding Loss for Transformer enhances Multiple Instance Whole Slide Image Classification
Mar 02, 2023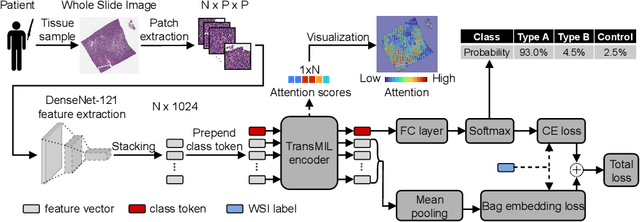


Abstract:Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) has become the predominant approach for classification tasks on gigapixel histopathology whole slide images (WSIs). Within the MIL framework, single WSIs (bags) are decomposed into patches (instances), with only WSI-level annotation available. Recent MIL approaches produce highly informative bag level representations by utilizing the transformer architecture's ability to model the dependencies between instances. However, when applied to high magnification datasets, problems emerge due to the large number of instances and the weak supervisory learning signal. To address this problem, we propose to additionally train transformers with a novel Bag Embedding Loss (BEL). BEL forces the model to learn a discriminative bag-level representation by minimizing the distance between bag embeddings of the same class and maximizing the distance between different classes. We evaluate BEL with the Transformer architecture TransMIL on two publicly available histopathology datasets, BRACS and CAMELYON17. We show that with BEL, TransMIL outperforms the baseline models on both datasets, thus contributing to the clinically highly relevant AI-based tumor classification of histological patient material.
Active Learning Enhances Classification of Histopathology Whole Slide Images with Attention-based Multiple Instance Learning
Mar 02, 2023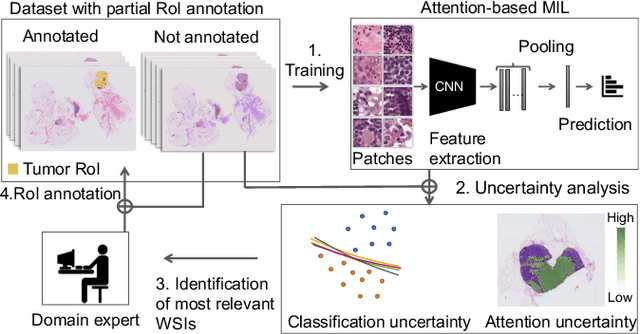
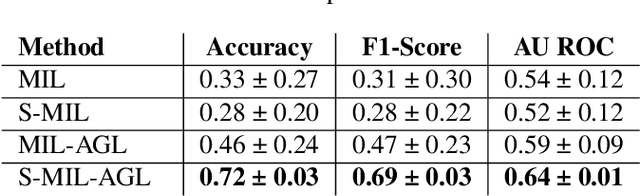
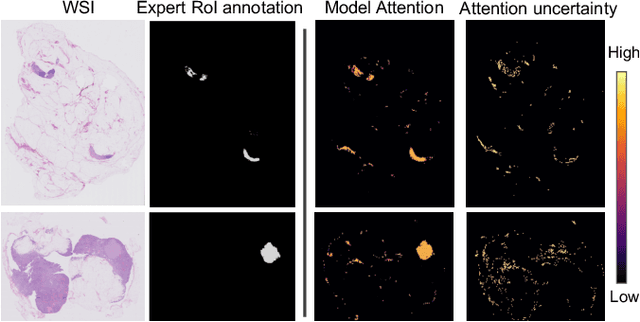
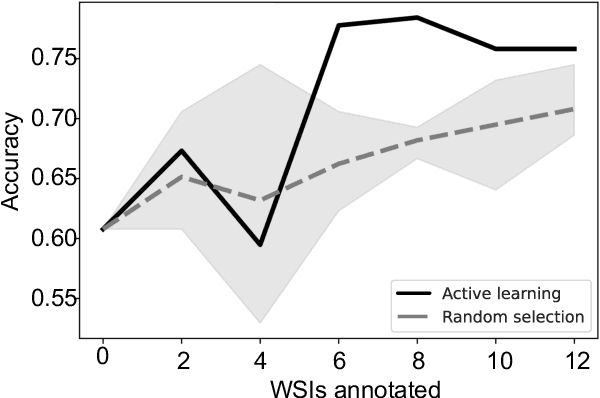
Abstract:In many histopathology tasks, sample classification depends on morphological details in tissue or single cells that are only visible at the highest magnification. For a pathologist, this implies tedious zooming in and out, while for a computational decision support algorithm, it leads to the analysis of a huge number of small image patches per whole slide image (WSI). Attention-based multiple instance learning (MIL), where attention estimation is learned in a weakly supervised manner, has been successfully applied in computational histopathology, but it is challenged by large numbers of irrelevant patches, reducing its accuracy. Here, we present an active learning approach to the problem. Querying the expert to annotate regions of interest in a WSI guides the formation of high-attention regions for MIL. We train an attention-based MIL and calculate a confidence metric for every image in the dataset to select the most uncertain WSIs for expert annotation. We test our approach on the CAMELYON17 dataset classifying metastatic lymph node sections in breast cancer. With a novel attention guiding loss, this leads to an accuracy boost of the trained models with few regions annotated for each class. Active learning thus improves WSIs classification accuracy, leads to faster and more robust convergence, and speeds up the annotation process. It may in the future serve as an important contribution to train MIL models in the clinically relevant context of cancer classification in histopathology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge