Arindam Das
BEVMOSNet: Multimodal Fusion for BEV Moving Object Segmentation
Mar 05, 2025
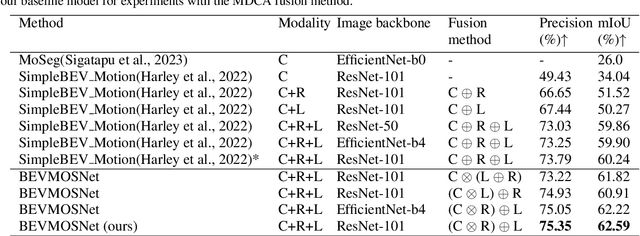
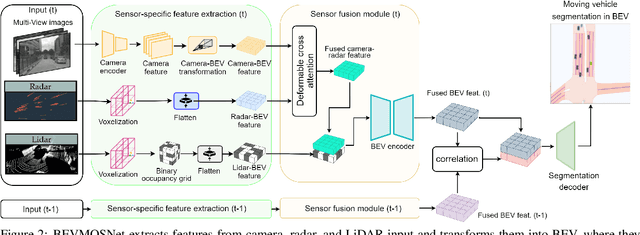
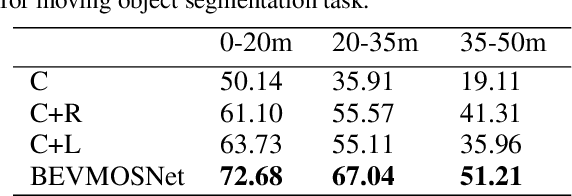
Abstract:Accurate motion understanding of the dynamic objects within the scene in bird's-eye-view (BEV) is critical to ensure a reliable obstacle avoidance system and smooth path planning for autonomous vehicles. However, this task has received relatively limited exploration when compared to object detection and segmentation with only a few recent vision-based approaches presenting preliminary findings that significantly deteriorate in low-light, nighttime, and adverse weather conditions such as rain. Conversely, LiDAR and radar sensors remain almost unaffected in these scenarios, and radar provides key velocity information of the objects. Therefore, we introduce BEVMOSNet, to our knowledge, the first end-to-end multimodal fusion leveraging cameras, LiDAR, and radar to precisely predict the moving objects in BEV. In addition, we perform a deeper analysis to find out the optimal strategy for deformable cross-attention-guided sensor fusion for cross-sensor knowledge sharing in BEV. While evaluating BEVMOSNet on the nuScenes dataset, we show an overall improvement in IoU score of 36.59% compared to the vision-based unimodal baseline BEV-MoSeg (Sigatapu et al., 2023), and 2.35% compared to the multimodel SimpleBEV (Harley et al., 2022), extended for the motion segmentation task, establishing this method as the state-of-the-art in BEV motion segmentation.
Reflective Teacher: Semi-Supervised Multimodal 3D Object Detection in Bird's-Eye-View via Uncertainty Measure
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Applying pseudo labeling techniques has been found to be advantageous in semi-supervised 3D object detection (SSOD) in Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) for autonomous driving, particularly where labeled data is limited. In the literature, Exponential Moving Average (EMA) has been used for adjustments of the weights of teacher network by the student network. However, the same induces catastrophic forgetting in the teacher network. In this work, we address this issue by introducing a novel concept of Reflective Teacher where the student is trained by both labeled and pseudo labeled data while its knowledge is progressively passed to the teacher through a regularizer to ensure retention of previous knowledge. Additionally, we propose Geometry Aware BEV Fusion (GA-BEVFusion) for efficient alignment of multi-modal BEV features, thus reducing the disparity between the modalities - camera and LiDAR. This helps to map the precise geometric information embedded among LiDAR points reliably with the spatial priors for extraction of semantic information from camera images. Our experiments on the nuScenes and Waymo datasets demonstrate: 1) improved performance over state-of-the-art methods in both fully supervised and semi-supervised settings; 2) Reflective Teacher achieves equivalent performance with only 25% and 22% of labeled data for nuScenes and Waymo datasets respectively, in contrast to other fully supervised methods that utilize the full labeled dataset.
MapsTP: HD Map Images Based Multimodal Trajectory Prediction for Automated Vehicles
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Predicting ego vehicle trajectories remains a critical challenge, especially in urban and dense areas due to the unpredictable behaviours of other vehicles and pedestrians. Multimodal trajectory prediction enhances decision-making by considering multiple possible future trajectories based on diverse sources of environmental data. In this approach, we leverage ResNet-50 to extract image features from high-definition map data and use IMU sensor data to calculate speed, acceleration, and yaw rate. A temporal probabilistic network is employed to compute potential trajectories, selecting the most accurate and highly probable trajectory paths. This method integrates HD map data to improve the robustness and reliability of trajectory predictions for autonomous vehicles.
Fisheye Camera and Ultrasonic Sensor Fusion For Near-Field Obstacle Perception in Bird's-Eye-View
Feb 01, 2024Abstract:Accurate obstacle identification represents a fundamental challenge within the scope of near-field perception for autonomous driving. Conventionally, fisheye cameras are frequently employed for comprehensive surround-view perception, including rear-view obstacle localization. However, the performance of such cameras can significantly deteriorate in low-light conditions, during nighttime, or when subjected to intense sun glare. Conversely, cost-effective sensors like ultrasonic sensors remain largely unaffected under these conditions. Therefore, we present, to our knowledge, the first end-to-end multimodal fusion model tailored for efficient obstacle perception in a bird's-eye-view (BEV) perspective, utilizing fisheye cameras and ultrasonic sensors. Initially, ResNeXt-50 is employed as a set of unimodal encoders to extract features specific to each modality. Subsequently, the feature space associated with the visible spectrum undergoes transformation into BEV. The fusion of these two modalities is facilitated via concatenation. At the same time, the ultrasonic spectrum-based unimodal feature maps pass through content-aware dilated convolution, applied to mitigate the sensor misalignment between two sensors in the fused feature space. Finally, the fused features are utilized by a two-stage semantic occupancy decoder to generate grid-wise predictions for precise obstacle perception. We conduct a systematic investigation to determine the optimal strategy for multimodal fusion of both sensors. We provide insights into our dataset creation procedures, annotation guidelines, and perform a thorough data analysis to ensure adequate coverage of all scenarios. When applied to our dataset, the experimental results underscore the robustness and effectiveness of our proposed multimodal fusion approach.
BEVSeg2TP: Surround View Camera Bird's-Eye-View Based Joint Vehicle Segmentation and Ego Vehicle Trajectory Prediction
Dec 20, 2023



Abstract:Trajectory prediction is, naturally, a key task for vehicle autonomy. While the number of traffic rules is limited, the combinations and uncertainties associated with each agent's behaviour in real-world scenarios are nearly impossible to encode. Consequently, there is a growing interest in learning-based trajectory prediction. The proposed method in this paper predicts trajectories by considering perception and trajectory prediction as a unified system. In considering them as unified tasks, we show that there is the potential to improve the performance of perception. To achieve these goals, we present BEVSeg2TP - a surround-view camera bird's-eye-view-based joint vehicle segmentation and ego vehicle trajectory prediction system for autonomous vehicles. The proposed system uses a network trained on multiple camera views. The images are transformed using several deep learning techniques to perform semantic segmentation of objects, including other vehicles, in the scene. The segmentation outputs are fused across the camera views to obtain a comprehensive representation of the surrounding vehicles from the bird's-eye-view perspective. The system further predicts the future trajectory of the ego vehicle using a spatiotemporal probabilistic network (STPN) to optimize trajectory prediction. This network leverages information from encoder-decoder transformers and joint vehicle segmentation.
Navigating Uncertainty: The Role of Short-Term Trajectory Prediction in Autonomous Vehicle Safety
Jul 12, 2023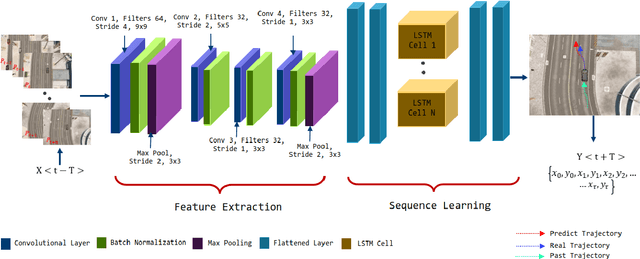
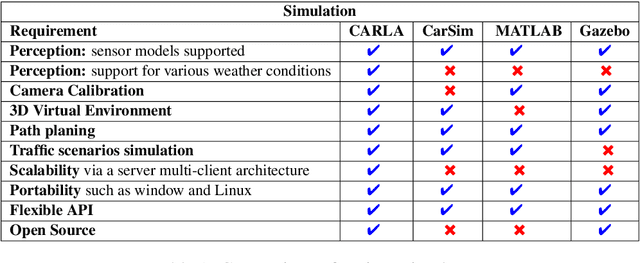
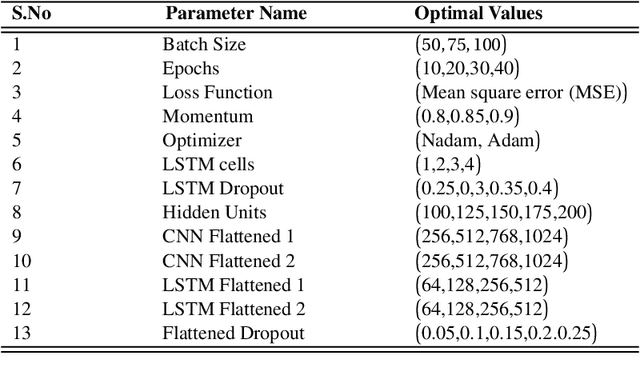
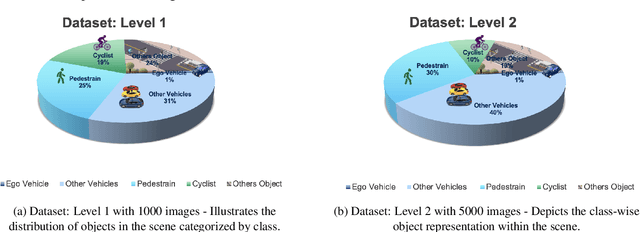
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles require accurate and reliable short-term trajectory predictions for safe and efficient driving. While most commercial automated vehicles currently use state machine-based algorithms for trajectory forecasting, recent efforts have focused on end-to-end data-driven systems. Often, the design of these models is limited by the availability of datasets, which are typically restricted to generic scenarios. To address this limitation, we have developed a synthetic dataset for short-term trajectory prediction tasks using the CARLA simulator. This dataset is extensive and incorporates what is considered complex scenarios - pedestrians crossing the road, vehicles overtaking - and comprises 6000 perspective view images with corresponding IMU and odometry information for each frame. Furthermore, an end-to-end short-term trajectory prediction model using convolutional neural networks (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks has also been developed. This model can handle corner cases, such as slowing down near zebra crossings and stopping when pedestrians cross the road, without the need for explicit encoding of the surrounding environment. In an effort to accelerate this research and assist others, we are releasing our dataset and model to the research community. Our datasets are publicly available on https://github.com/sharmasushil/Navigating-Uncertainty-Trajectory-Prediction .
Revisiting Modality Imbalance In Multimodal Pedestrian Detection
Feb 24, 2023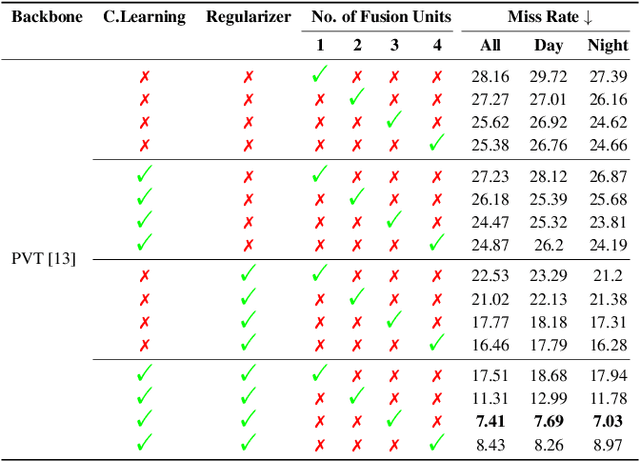
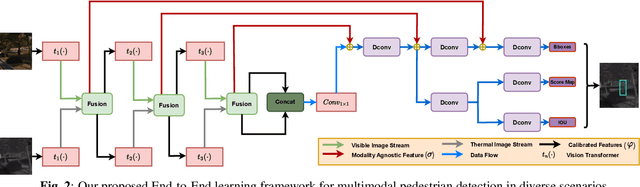
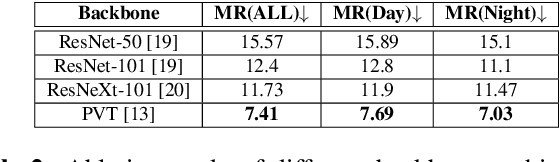

Abstract:Multimodal learning, particularly for pedestrian detection, has recently received emphasis due to its capability to function equally well in several critical autonomous driving scenarios such as low-light, night-time, and adverse weather conditions. However, in most cases, the training distribution largely emphasizes the contribution of one specific input that makes the network biased towards one modality. Hence, the generalization of such models becomes a significant problem where the non-dominant input modality during training could be contributing more to the course of inference. Here, we introduce a novel training setup with regularizer in the multimodal architecture to resolve the problem of this disparity between the modalities. Specifically, our regularizer term helps to make the feature fusion method more robust by considering both the feature extractors equivalently important during the training to extract the multimodal distribution which is referred to as removing the imbalance problem. Furthermore, our decoupling concept of output stream helps the detection task by sharing the spatial sensitive information mutually. Extensive experiments of the proposed method on KAIST and UTokyo datasets shows improvement of the respective state-of-the-art performance.
Deep Multi-Task Networks For Occluded Pedestrian Pose Estimation
Jun 15, 2022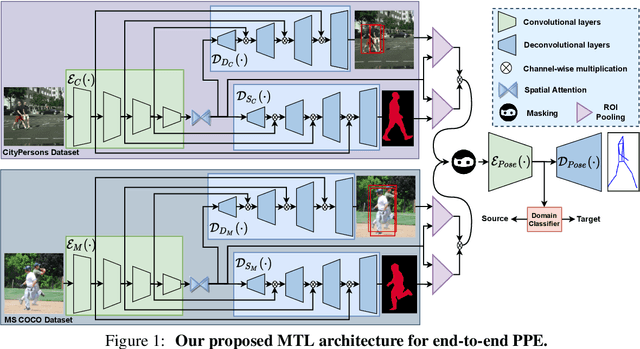
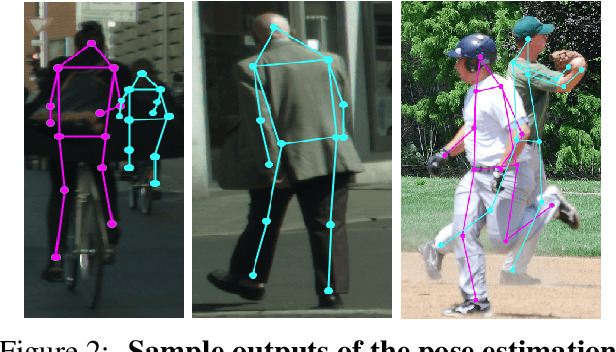
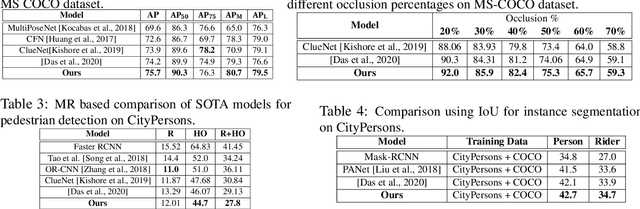
Abstract:Most of the existing works on pedestrian pose estimation do not consider estimating the pose of an occluded pedestrians, as the annotations of the occluded parts are not available in relevant automotive datasets. For example, CityPersons, a well-known dataset for pedestrian detection in automotive scenes does not provide pose annotations, whereas MS-COCO, a non-automotive dataset, contains human pose estimation. In this work, we propose a multi-task framework to extract pedestrian features through detection and instance segmentation tasks performed separately on these two distributions. Thereafter, an encoder learns pose specific features using an unsupervised instance-level domain adaptation method for the pedestrian instances from both distributions. The proposed framework has improved state-of-the-art performances of pose estimation, pedestrian detection, and instance segmentation.
UnShadowNet: Illumination Critic Guided Contrastive Learning For Shadow Removal
Mar 29, 2022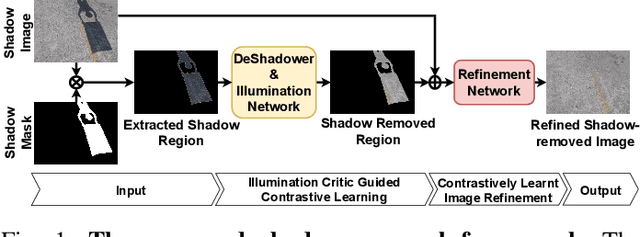

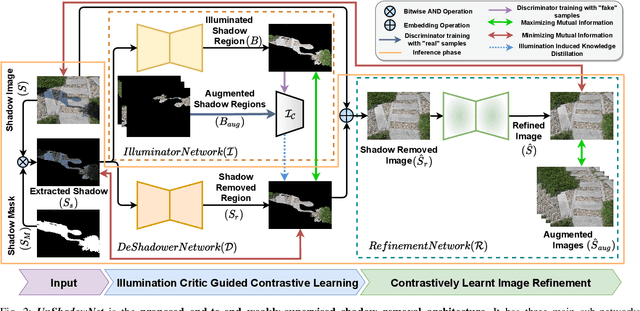

Abstract:Shadows are frequently encountered natural phenomena that significantly hinder the performance of computer vision perception systems in practical settings, e.g., autonomous driving. A solution to this would be to eliminate shadow regions from the images before the processing of the perception system. Yet, training such a solution requires pairs of aligned shadowed and non-shadowed images which are difficult to obtain. We introduce a novel weakly supervised shadow removal framework UnShadowNet trained using contrastive learning. It comprises of a DeShadower network responsible for removal of the extracted shadow under the guidance of an Illumination network which is trained adversarially by the illumination critic and a Refinement network to further remove artifacts. We show that UnShadowNet can also be easily extended to a fully-supervised setup to exploit the ground-truth when available. UnShadowNet outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches on three publicly available shadow datasets (ISTD, adjusted ISTD, SRD) in both the weakly and fully supervised setups.
Spatio-Contextual Deep Network Based Multimodal Pedestrian Detection For Autonomous Driving
May 26, 2021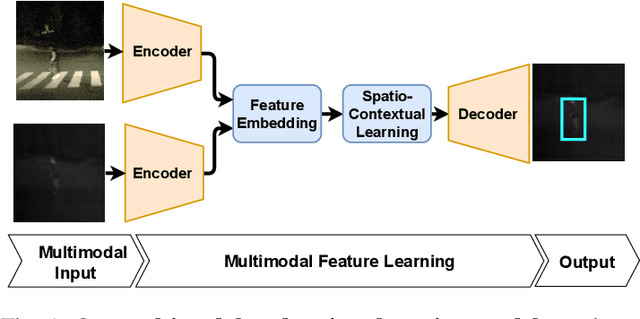
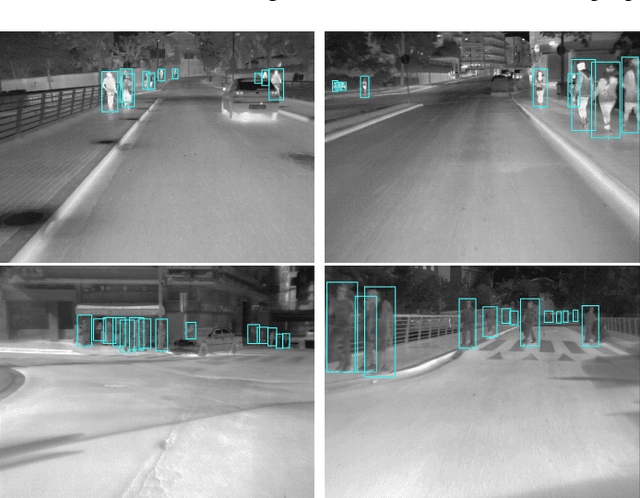
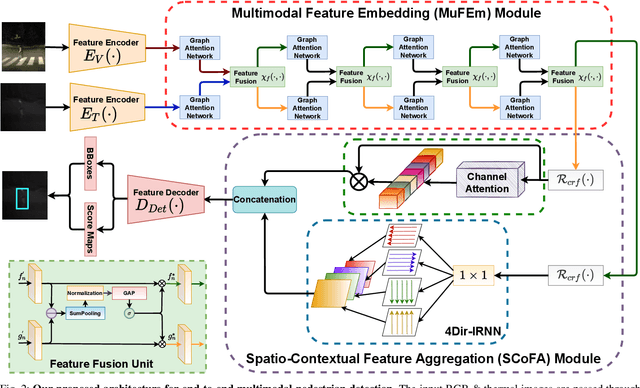
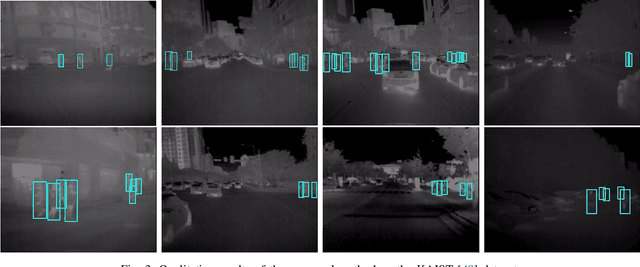

Abstract:Pedestrian Detection is the most critical module of an Autonomous Driving system. Although a camera is commonly used for this purpose, its quality degrades severely in low-light night time driving scenarios. On the other hand, the quality of a thermal camera image remains unaffected in similar conditions. This paper proposes an end-to-end multimodal fusion model for pedestrian detection using RGB and thermal images. Its novel spatio-contextual deep network architecture is capable of exploiting the multimodal input efficiently. It consists of two distinct deformable ResNeXt-50 encoders for feature extraction from the two modalities. Fusion of these two encoded features takes place inside a multimodal feature embedding module (MuFEm) consisting of several groups of a pair of Graph Attention Network and a feature fusion unit. The output of the last feature fusion unit of MuFEm is subsequently passed to two CRFs for their spatial refinement. Further enhancement of the features is achieved by applying channel-wise attention and extraction of contextual information with the help of four RNNs traversing in four different directions. Finally, these feature maps are used by a single-stage decoder to generate the bounding box of each pedestrian and the score map. We have performed extensive experiments of the proposed framework on three publicly available multimodal pedestrian detection benchmark datasets, namely KAIST, CVC-14, and UTokyo. The results on each of them improved the respective state-of-the-art performance. A short video giving an overview of this work along with its qualitative results can be seen at https://youtu.be/FDJdSifuuCs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge