Arabella Sinclair
Do Language Models Exhibit Human-like Structural Priming Effects?
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:We explore which linguistic factors -- at the sentence and token level -- play an important role in influencing language model predictions, and investigate whether these are reflective of results found in humans and human corpora (Gries and Kootstra, 2017). We make use of the structural priming paradigm, where recent exposure to a structure facilitates processing of the same structure. We don't only investigate whether, but also where priming effects occur, and what factors predict them. We show that these effects can be explained via the inverse frequency effect, known in human priming, where rarer elements within a prime increase priming effects, as well as lexical dependence between prime and target. Our results provide an important piece in the puzzle of understanding how properties within their context affect structural prediction in language models.
Attribution and Alignment: Effects of Local Context Repetition on Utterance Production and Comprehension in Dialogue
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Language models are often used as the backbone of modern dialogue systems. These models are pre-trained on large amounts of written fluent language. Repetition is typically penalised when evaluating language model generations. However, it is a key component of dialogue. Humans use local and partner specific repetitions; these are preferred by human users and lead to more successful communication in dialogue. In this study, we evaluate (a) whether language models produce human-like levels of repetition in dialogue, and (b) what are the processing mechanisms related to lexical re-use they use during comprehension. We believe that such joint analysis of model production and comprehension behaviour can inform the development of cognitively inspired dialogue generation systems.
Construction Repetition Reduces Information Rate in Dialogue
Oct 15, 2022



Abstract:Speakers repeat constructions frequently in dialogue. Due to their peculiar information-theoretic properties, repetitions can be thought of as a strategy for cost-effective communication. In this study, we focus on the repetition of lexicalised constructions -- i.e., recurring multi-word units -- in English open-domain spoken dialogues. We hypothesise that speakers use construction repetition to mitigate information rate, leading to an overall decrease in utterance information content over the course of a dialogue. We conduct a quantitative analysis, measuring the information content of constructions and that of their containing utterances, estimating information content with an adaptive neural language model. We observe that construction usage lowers the information content of utterances. This facilitating effect (i) increases throughout dialogues, (ii) is boosted by repetition, (iii) grows as a function of repetition frequency and density, and (iv) is stronger for repetitions of referential constructions.
State-of-the-art generalisation research in NLP: a taxonomy and review
Oct 10, 2022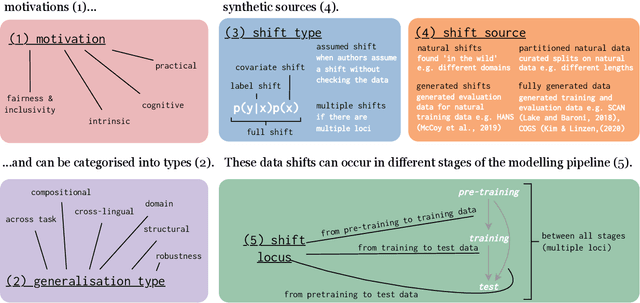
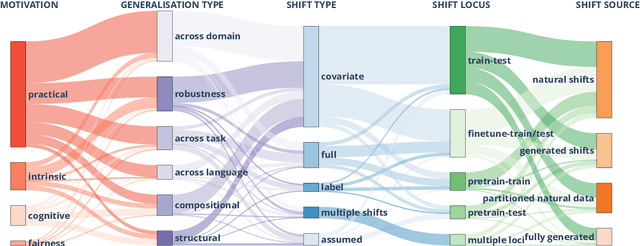
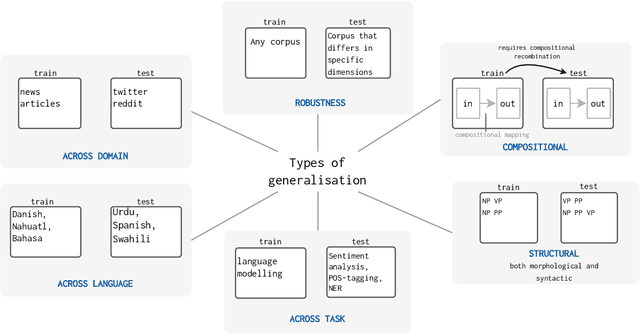

Abstract:The ability to generalise well is one of the primary desiderata of natural language processing (NLP). Yet, what `good generalisation' entails and how it should be evaluated is not well understood, nor are there any common standards to evaluate it. In this paper, we aim to lay the ground-work to improve both of these issues. We present a taxonomy for characterising and understanding generalisation research in NLP, we use that taxonomy to present a comprehensive map of published generalisation studies, and we make recommendations for which areas might deserve attention in the future. Our taxonomy is based on an extensive literature review of generalisation research, and contains five axes along which studies can differ: their main motivation, the type of generalisation they aim to solve, the type of data shift they consider, the source by which this data shift is obtained, and the locus of the shift within the modelling pipeline. We use our taxonomy to classify over 400 previous papers that test generalisation, for a total of more than 600 individual experiments. Considering the results of this review, we present an in-depth analysis of the current state of generalisation research in NLP, and make recommendations for the future. Along with this paper, we release a webpage where the results of our review can be dynamically explored, and which we intend to up-date as new NLP generalisation studies are published. With this work, we aim to make steps towards making state-of-the-art generalisation testing the new status quo in NLP.
Syntactic Persistence in Language Models: Priming as a Window into Abstract Language Representations
Sep 30, 2021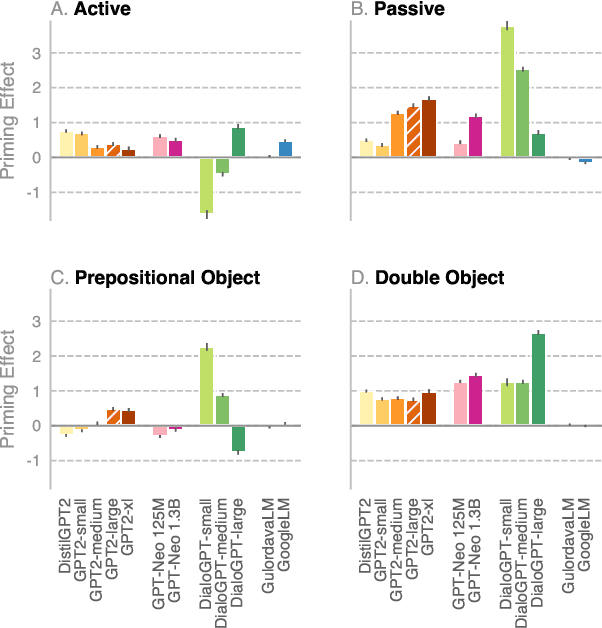
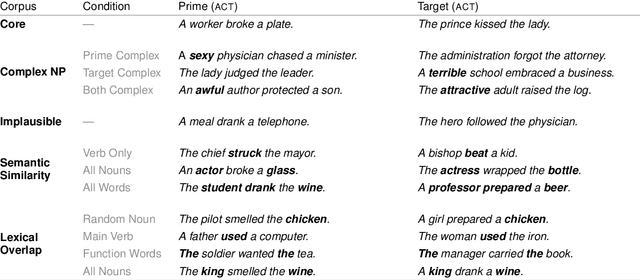
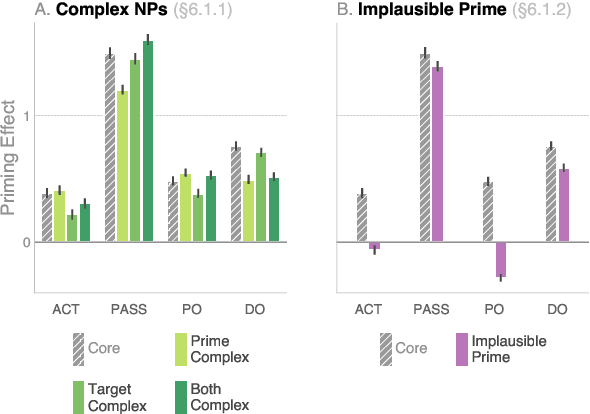
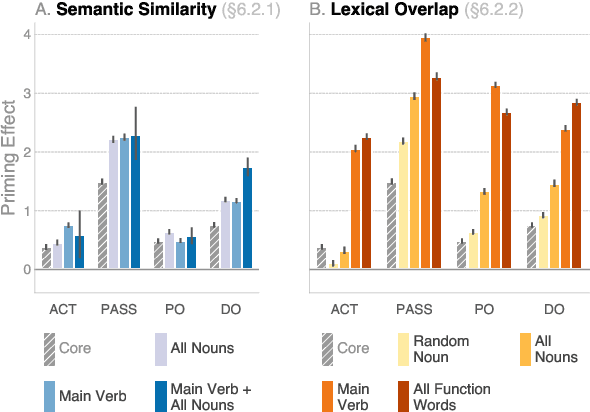
Abstract:We investigate the extent to which modern, neural language models are susceptible to syntactic priming, the phenomenon where the syntactic structure of a sentence makes the same structure more probable in a follow-up sentence. We explore how priming can be used to study the nature of the syntactic knowledge acquired by these models. We introduce a novel metric and release Prime-LM, a large corpus where we control for various linguistic factors which interact with priming strength. We find that recent large Transformer models indeed show evidence of syntactic priming, but also that the syntactic generalisations learned by these models are to some extent modulated by semantic information. We report surprisingly strong priming effects when priming with multiple sentences, each with different words and meaning but with identical syntactic structure. We conclude that the syntactic priming paradigm is a highly useful, additional tool for gaining insights into the capacities of language models.
Refer, Reuse, Reduce: Generating Subsequent References in Visual and Conversational Contexts
Nov 09, 2020

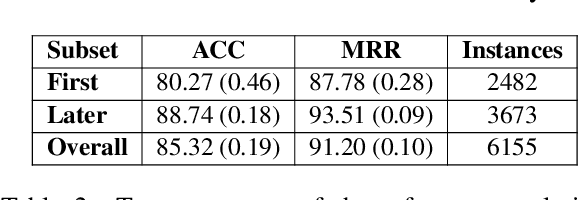
Abstract:Dialogue participants often refer to entities or situations repeatedly within a conversation, which contributes to its cohesiveness. Subsequent references exploit the common ground accumulated by the interlocutors and hence have several interesting properties, namely, they tend to be shorter and reuse expressions that were effective in previous mentions. In this paper, we tackle the generation of first and subsequent references in visually grounded dialogue. We propose a generation model that produces referring utterances grounded in both the visual and the conversational context. To assess the referring effectiveness of its output, we also implement a reference resolution system. Our experiments and analyses show that the model produces better, more effective referring utterances than a model not grounded in the dialogue context, and generates subsequent references that exhibit linguistic patterns akin to humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge