Andrew Janowczyk
Case Western Reserve University, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Cleveland OH, USA, Lausanne University Hospital, Precision Oncology Center, Vaud, Switzerland
CohortFinder: an open-source tool for data-driven partitioning of biomedical image cohorts to yield robust machine learning models
Jul 17, 2023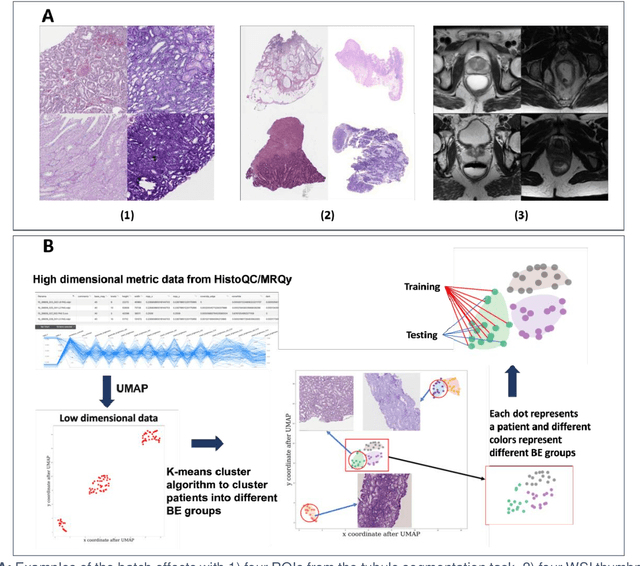

Abstract:Batch effects (BEs) refer to systematic technical differences in data collection unrelated to biological variations whose noise is shown to negatively impact machine learning (ML) model generalizability. Here we release CohortFinder, an open-source tool aimed at mitigating BEs via data-driven cohort partitioning. We demonstrate CohortFinder improves ML model performance in downstream medical image processing tasks. CohortFinder is freely available for download at cohortfinder.com.
PatchSorter: A High Throughput Deep Learning Digital Pathology Tool for Object Labeling
Jul 13, 2023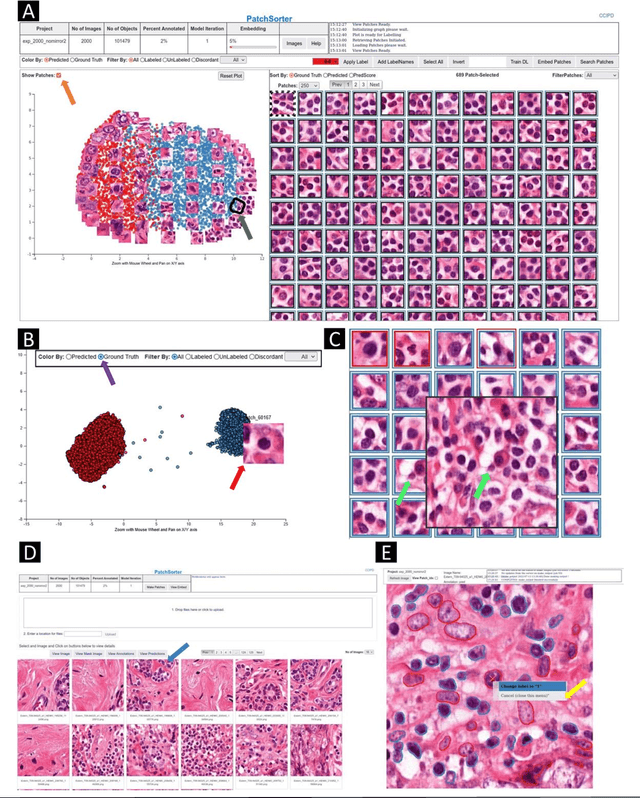
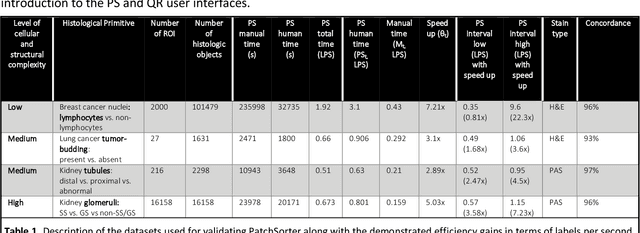
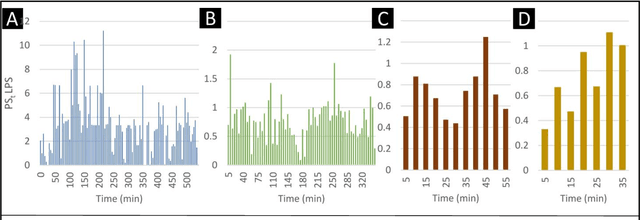
Abstract:The discovery of patterns associated with diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy response in digital pathology images often requires intractable labeling of large quantities of histological objects. Here we release an open-source labeling tool, PatchSorter, which integrates deep learning with an intuitive web interface. Using >100,000 objects, we demonstrate a >7x improvement in labels per second over unaided labeling, with minimal impact on labeling accuracy, thus enabling high-throughput labeling of large datasets.
Panoptic segmentation with highly imbalanced semantic labels
Apr 02, 2022



Abstract:This manuscript describes the panoptic segmentation method we devised for our submission to the CONIC challenge at ISBI 2022. Key features of our method are a weighted loss that we specifically engineered for semantic segmentation of highly imbalanced cell types, and an existing state-of-the art nuclei instance segmentation model, which we combine in a Hovernet-like architecture.
Quick Annotator: an open-source digital pathology based rapid image annotation tool
Jan 06, 2021



Abstract:Image based biomarker discovery typically requires an accurate segmentation of histologic structures (e.g., cell nuclei, tubules, epithelial regions) in digital pathology Whole Slide Images (WSI). Unfortunately, annotating each structure of interest is laborious and often intractable even in moderately sized cohorts. Here, we present an open-source tool, Quick Annotator (QA), designed to improve annotation efficiency of histologic structures by orders of magnitude. While the user annotates regions of interest (ROI) via an intuitive web interface, a deep learning (DL) model is concurrently optimized using these annotations and applied to the ROI. The user iteratively reviews DL results to either (a) accept accurately annotated regions, or (b) correct erroneously segmented structures to improve subsequent model suggestions, before transitioning to other ROIs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of QA over comparable manual efforts via three use cases. These include annotating (a) 337,386 nuclei in 5 pancreatic WSIs, (b) 5,692 tubules in 10 colorectal WSIs, and (c) 14,187 regions of epithelium in 10 breast WSIs. Efficiency gains in terms of annotations per second of 102x, 9x, and 39x were respectively witnessed while retaining f-scores >.95, suggesting QA may be a valuable tool for efficiently fully annotating WSIs employed in downstream biomarker studies.
MRQy: An Open-Source Tool for Quality Control of MR Imaging Data
Apr 13, 2020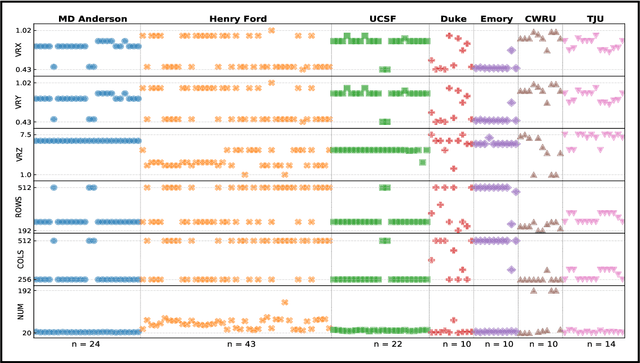
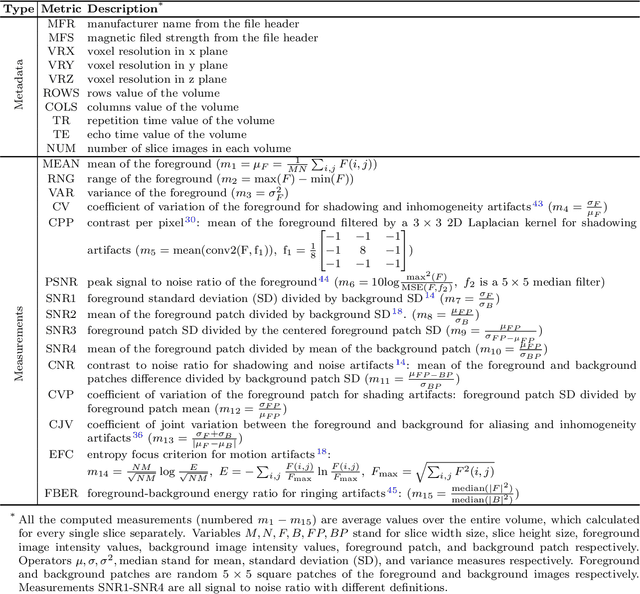
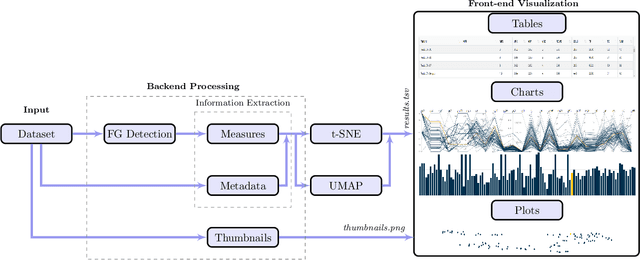
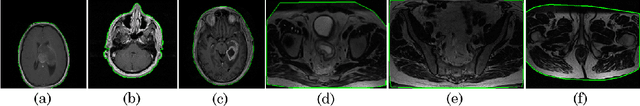
Abstract:Even as public data repositories such as The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) have enabled development of new radiomics and machine learning schemes, a key concern remains the generalizability of these methods to unseen datasets. For MRI datasets, model performance could be impacted by (a) site- or scanner-specific variations in image resolution, field-of-view, or image contrast, or (b) presence of imaging artifacts such as noise, motion, inhomogeneity, ringing, or aliasing; which can adversely affect relative image quality between data cohorts. This indicates a need for a quantitative tool to quickly determine relative differences in MRI volumes both within and between large data cohorts. We present MRQy, a new open-source quality control tool to (a) interrogate MRI cohorts for site- or equipment-based differences, and (b) quantify the impact of MRI artifacts on relative image quality; to help determine how to correct for these variations prior to model development. MRQy extracts a series of quality measures (e.g. noise ratios, variation metrics, entropy and energy criteria) and MR image metadata (e.g. voxel resolution, image dimensions) for subsequent interrogation via a specialized HTML5 based front-end designed for real-time filtering and trend visualization. MRQy is designed to be a standalone, unsupervised tool that can be efficiently run on a standard desktop computer. It has been made freely accessible at http://github.com/ccipd/MRQy for wider community use and feedback. MRQy was used to evaluate (a) n=133 brain MRIs from TCIA (7 sites), and (b) n=104 rectal MRIs (3 local sites). MRQy measures revealed significant site-specific variations in both cohorts, indicating potential batch effects. Marked differences in specific MRQy measures were also able to identify MRI datasets that needed to be corrected for common MR imaging artifacts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge