Andreas Meuleman
Splat and Replace: 3D Reconstruction with Repetitive Elements
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We leverage repetitive elements in 3D scenes to improve novel view synthesis. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have greatly improved novel view synthesis but renderings of unseen and occluded parts remain low-quality if the training views are not exhaustive enough. Our key observation is that our environment is often full of repetitive elements. We propose to leverage those repetitions to improve the reconstruction of low-quality parts of the scene due to poor coverage and occlusions. We propose a method that segments each repeated instance in a 3DGS reconstruction, registers them together, and allows information to be shared among instances. Our method improves the geometry while also accounting for appearance variations across instances. We demonstrate our method on a variety of synthetic and real scenes with typical repetitive elements, leading to a substantial improvement in the quality of novel view synthesis.
On-the-fly Reconstruction for Large-Scale Novel View Synthesis from Unposed Images
Jun 05, 2025
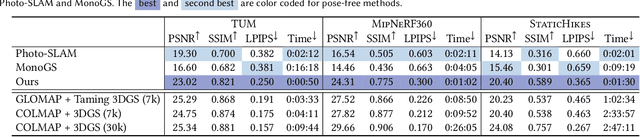
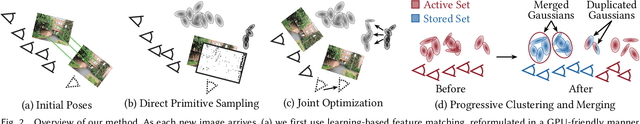
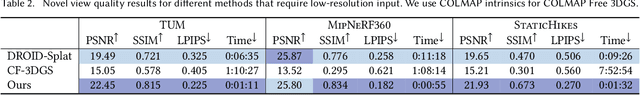
Abstract:Radiance field methods such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) allow easy reconstruction from photos, enabling free-viewpoint navigation. Nonetheless, pose estimation using Structure from Motion and 3DGS optimization can still each take between minutes and hours of computation after capture is complete. SLAM methods combined with 3DGS are fast but struggle with wide camera baselines and large scenes. We present an on-the-fly method to produce camera poses and a trained 3DGS immediately after capture. Our method can handle dense and wide-baseline captures of ordered photo sequences and large-scale scenes. To do this, we first introduce fast initial pose estimation, exploiting learned features and a GPU-friendly mini bundle adjustment. We then introduce direct sampling of Gaussian primitive positions and shapes, incrementally spawning primitives where required, significantly accelerating training. These two efficient steps allow fast and robust joint optimization of poses and Gaussian primitives. Our incremental approach handles large-scale scenes by introducing scalable radiance field construction, progressively clustering 3DGS primitives, storing them in anchors, and offloading them from the GPU. Clustered primitives are progressively merged, keeping the required scale of 3DGS at any viewpoint. We evaluate our solution on a variety of datasets and show that our solution can provide on-the-fly processing of all the capture scenarios and scene sizes we target while remaining competitive with other methods that only handle specific capture styles or scene sizes in speed, image quality, or both.
OmniSDF: Scene Reconstruction using Omnidirectional Signed Distance Functions and Adaptive Binoctrees
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:We present a method to reconstruct indoor and outdoor static scene geometry and appearance from an omnidirectional video moving in a small circular sweep. This setting is challenging because of the small baseline and large depth ranges, making it difficult to find ray crossings. To better constrain the optimization, we estimate geometry as a signed distance field within a spherical binoctree data structure and use a complementary efficient tree traversal strategy based on a breadth-first search for sampling. Unlike regular grids or trees, the shape of this structure well-matches the camera setting, creating a better memory-quality trade-off. From an initial depth estimate, the binoctree is adaptively subdivided throughout the optimization; previous methods use a fixed depth that leaves the scene undersampled. In comparison with three neural optimization methods and two non-neural methods, ours shows decreased geometry error on average, especially in a detailed scene, while significantly reducing the required number of voxels to represent such details.
Polarimetric iToF: Measuring High-Fidelity Depth through Scattering Media
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Indirect time-of-flight (iToF) imaging allows us to capture dense depth information at a low cost. However, iToF imaging often suffers from multipath interference (MPI) artifacts in the presence of scattering media, resulting in severe depth-accuracy degradation. For instance, iToF cameras cannot measure depth accurately through fog because ToF active illumination scatters back to the sensor before reaching the farther target surface. In this work, we propose a polarimetric iToF imaging method that can capture depth information robustly through scattering media. Our observations on the principle of indirect ToF imaging and polarization of light allow us to formulate a novel computational model of scattering-aware polarimetric phase measurements that enables us to correct MPI errors. We first devise a scattering-aware polarimetric iToF model that can estimate the phase of unpolarized backscattered light. We then combine the optical filtering of polarization and our computational modeling of unpolarized backscattered light via scattering analysis of phase and amplitude. This allows us to tackle the MPI problem by estimating the scattering energy through the participating media. We validate our method on an experimental setup using a customized off-the-shelf iToF camera. Our method outperforms baseline methods by a significant margin by means of our scattering model and polarimetric phase measurements.
Progressively Optimized Local Radiance Fields for Robust View Synthesis
Mar 24, 2023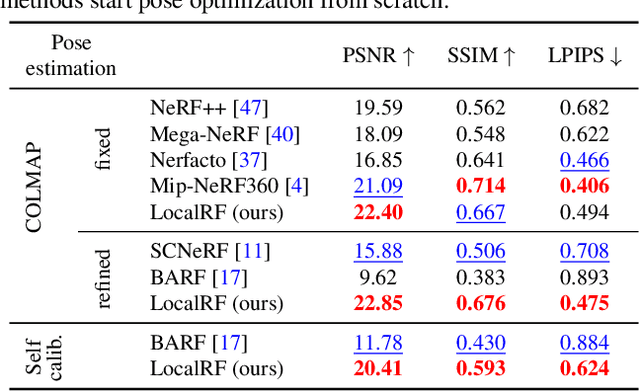
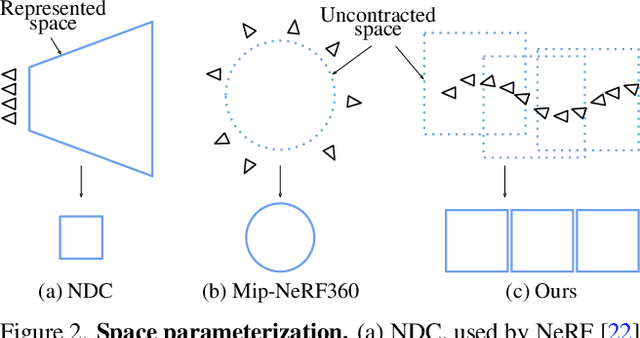
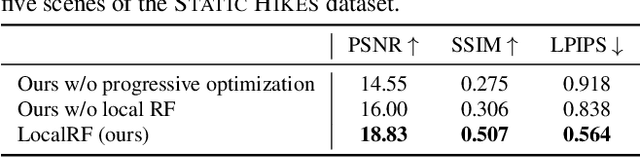
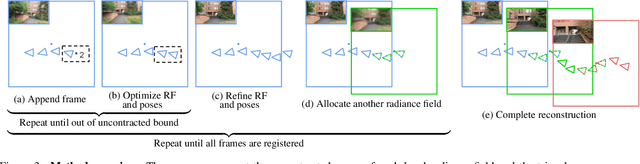
Abstract:We present an algorithm for reconstructing the radiance field of a large-scale scene from a single casually captured video. The task poses two core challenges. First, most existing radiance field reconstruction approaches rely on accurate pre-estimated camera poses from Structure-from-Motion algorithms, which frequently fail on in-the-wild videos. Second, using a single, global radiance field with finite representational capacity does not scale to longer trajectories in an unbounded scene. For handling unknown poses, we jointly estimate the camera poses with radiance field in a progressive manner. We show that progressive optimization significantly improves the robustness of the reconstruction. For handling large unbounded scenes, we dynamically allocate new local radiance fields trained with frames within a temporal window. This further improves robustness (e.g., performs well even under moderate pose drifts) and allows us to scale to large scenes. Our extensive evaluation on the Tanks and Temples dataset and our collected outdoor dataset, Static Hikes, show that our approach compares favorably with the state-of-the-art.
* Project page: https://localrf.github.io/
Robust Dynamic Radiance Fields
Jan 05, 2023Abstract:Dynamic radiance field reconstruction methods aim to model the time-varying structure and appearance of a dynamic scene. Existing methods, however, assume that accurate camera poses can be reliably estimated by Structure from Motion (SfM) algorithms. These methods, thus, are unreliable as SfM algorithms often fail or produce erroneous poses on challenging videos with highly dynamic objects, poorly textured surfaces, and rotating camera motion. We address this robustness issue by jointly estimating the static and dynamic radiance fields along with the camera parameters (poses and focal length). We demonstrate the robustness of our approach via extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments. Our results show favorable performance over the state-of-the-art dynamic view synthesis methods.
FloatingFusion: Depth from ToF and Image-stabilized Stereo Cameras
Oct 06, 2022Abstract:High-accuracy per-pixel depth is vital for computational photography, so smartphones now have multimodal camera systems with time-of-flight (ToF) depth sensors and multiple color cameras. However, producing accurate high-resolution depth is still challenging due to the low resolution and limited active illumination power of ToF sensors. Fusing RGB stereo and ToF information is a promising direction to overcome these issues, but a key problem remains: to provide high-quality 2D RGB images, the main color sensor's lens is optically stabilized, resulting in an unknown pose for the floating lens that breaks the geometric relationships between the multimodal image sensors. Leveraging ToF depth estimates and a wide-angle RGB camera, we design an automatic calibration technique based on dense 2D/3D matching that can estimate camera extrinsic, intrinsic, and distortion parameters of a stabilized main RGB sensor from a single snapshot. This lets us fuse stereo and ToF cues via a correlation volume. For fusion, we apply deep learning via a real-world training dataset with depth supervision estimated by a neural reconstruction method. For evaluation, we acquire a test dataset using a commercial high-power depth camera and show that our approach achieves higher accuracy than existing baselines.
DeepFormableTag: End-to-end Generation and Recognition of Deformable Fiducial Markers
Jun 16, 2022
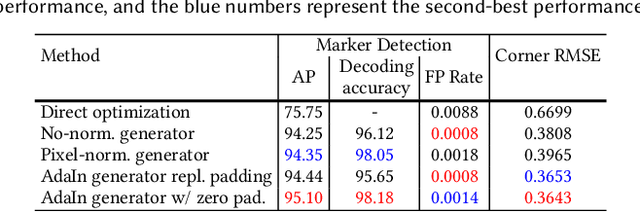
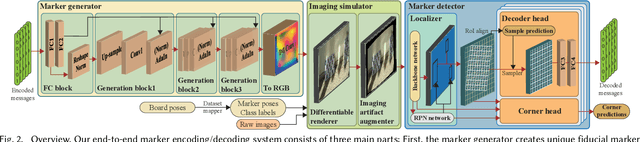
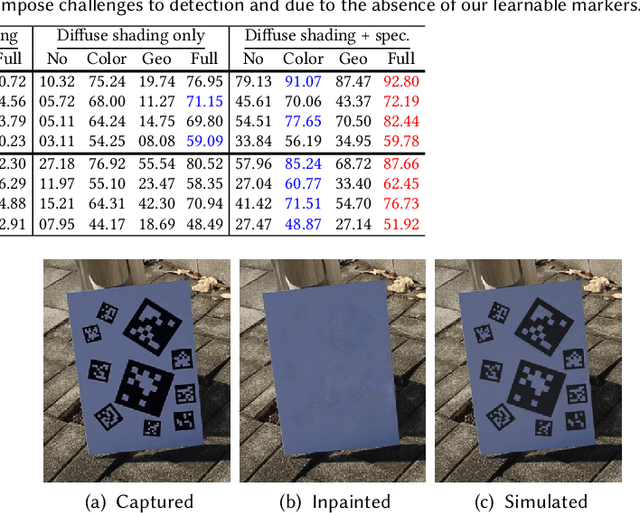
Abstract:Fiducial markers have been broadly used to identify objects or embed messages that can be detected by a camera. Primarily, existing detection methods assume that markers are printed on ideally planar surfaces. Markers often fail to be recognized due to various imaging artifacts of optical/perspective distortion and motion blur. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel deformable fiducial marker system that consists of three main parts: First, a fiducial marker generator creates a set of free-form color patterns to encode significantly large-scale information in unique visual codes. Second, a differentiable image simulator creates a training dataset of photorealistic scene images with the deformed markers, being rendered during optimization in a differentiable manner. The rendered images include realistic shading with specular reflection, optical distortion, defocus and motion blur, color alteration, imaging noise, and shape deformation of markers. Lastly, a trained marker detector seeks the regions of interest and recognizes multiple marker patterns simultaneously via inverse deformation transformation. The deformable marker creator and detector networks are jointly optimized via the differentiable photorealistic renderer in an end-to-end manner, allowing us to robustly recognize a wide range of deformable markers with high accuracy. Our deformable marker system is capable of decoding 36-bit messages successfully at ~29 fps with severe shape deformation. Results validate that our system significantly outperforms the traditional and data-driven marker methods. Our learning-based marker system opens up new interesting applications of fiducial markers, including cost-effective motion capture of the human body, active 3D scanning using our fiducial markers' array as structured light patterns, and robust augmented reality rendering of virtual objects on dynamic surfaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge