Alexandre Tkatchenko
Machine learning surrogate models of many-body dispersion interactions in polymer melts
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Accurate prediction of many-body dispersion (MBD) interactions is essential for understanding the van der Waals forces that govern the behavior of many complex molecular systems. However, the high computational cost of MBD calculations limits their direct application in large-scale simulations. In this work, we introduce a machine learning surrogate model specifically designed to predict MBD forces in polymer melts, a system that demands accurate MBD description and offers structural advantages for machine learning approaches. Our model is based on a trimmed SchNet architecture that selectively retains the most relevant atomic connections and incorporates trainable radial basis functions for geometric encoding. We validate our surrogate model on datasets from polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride melts, demonstrating high predictive accuracy and robust generalization across diverse polymer systems. In addition, the model captures key physical features, such as the characteristic decay behavior of MBD interactions, providing valuable insights for optimizing cutoff strategies. Characterized by high computational efficiency, our surrogate model enables practical incorporation of MBD effects into large-scale molecular simulations.
Pretraining Graph Transformers with Atom-in-a-Molecule Quantum Properties for Improved ADMET Modeling
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:We evaluate the impact of pretraining Graph Transformer architectures on atom-level quantum-mechanical features for the modeling of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) properties of drug-like compounds. We compare this pretraining strategy with two others: one based on molecular quantum properties (specifically the HOMO-LUMO gap) and one using a self-supervised atom masking technique. After fine-tuning on Therapeutic Data Commons ADMET datasets, we evaluate the performance improvement in the different models observing that models pretrained with atomic quantum mechanical properties produce in general better results. We then analyse the latent representations and observe that the supervised strategies preserve the pretraining information after finetuning and that different pretrainings produce different trends in latent expressivity across layers. Furthermore, we find that models pretrained on atomic quantum mechanical properties capture more low-frequency laplacian eigenmodes of the input graph via the attention weights and produce better representations of atomic environments within the molecule. Application of the analysis to a much larger non-public dataset for microsomal clearance illustrates generalizability of the studied indicators. In this case the performances of the models are in accordance with the representation analysis and highlight, especially for the case of masking pretraining and atom-level quantum property pretraining, how model types with similar performance on public benchmarks can have different performances on large scale pharmaceutical data.
Constructing Effective Machine Learning Models for the Sciences: A Multidisciplinary Perspective
Nov 21, 2022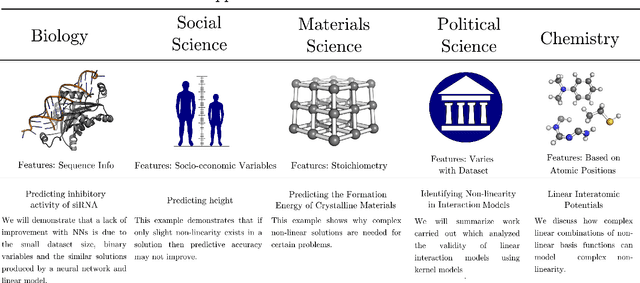
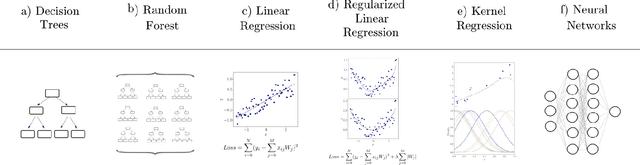
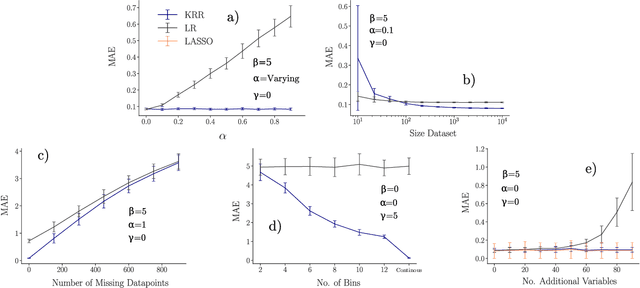
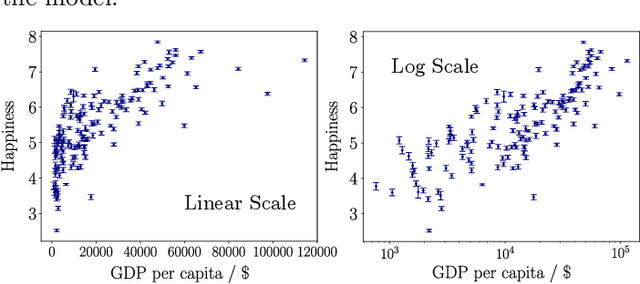
Abstract:Learning from data has led to substantial advances in a multitude of disciplines, including text and multimedia search, speech recognition, and autonomous-vehicle navigation. Can machine learning enable similar leaps in the natural and social sciences? This is certainly the expectation in many scientific fields and recent years have seen a plethora of applications of non-linear models to a wide range of datasets. However, flexible non-linear solutions will not always improve upon manually adding transforms and interactions between variables to linear regression models. We discuss how to recognize this before constructing a data-driven model and how such analysis can help us move to intrinsically interpretable regression models. Furthermore, for a variety of applications in the natural and social sciences we demonstrate why improvements may be seen with more complex regression models and why they may not.
Accurate Machine Learned Quantum-Mechanical Force Fields for Biomolecular Simulations
May 17, 2022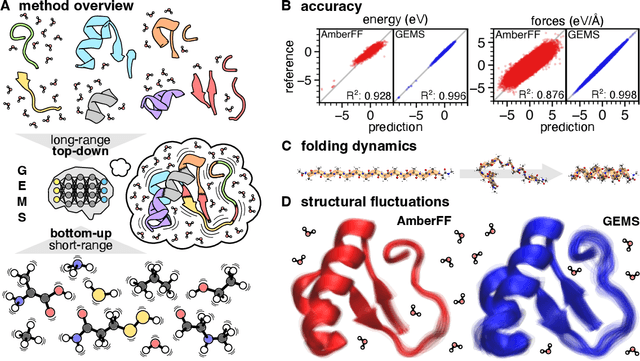
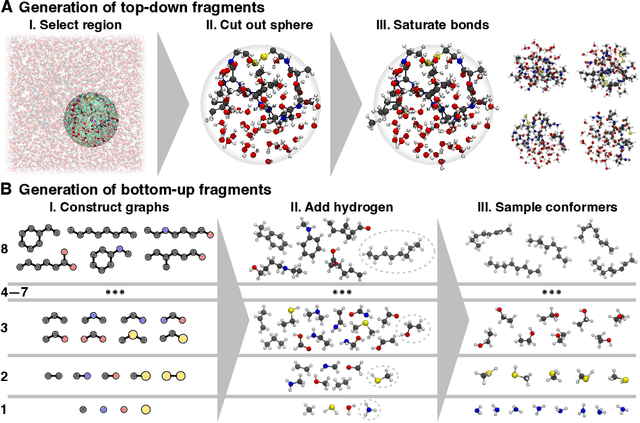
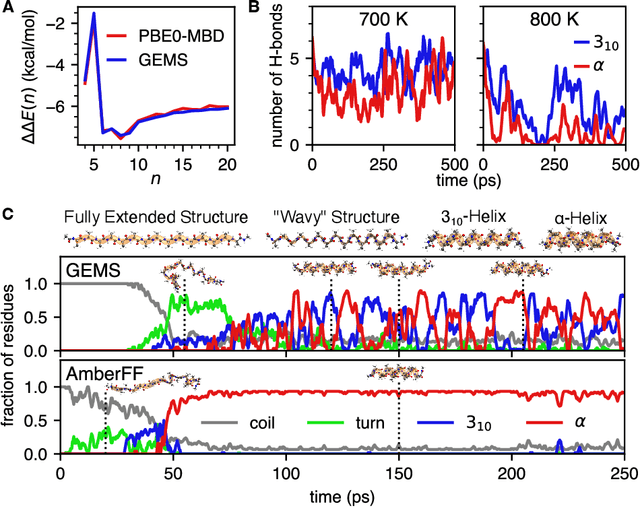
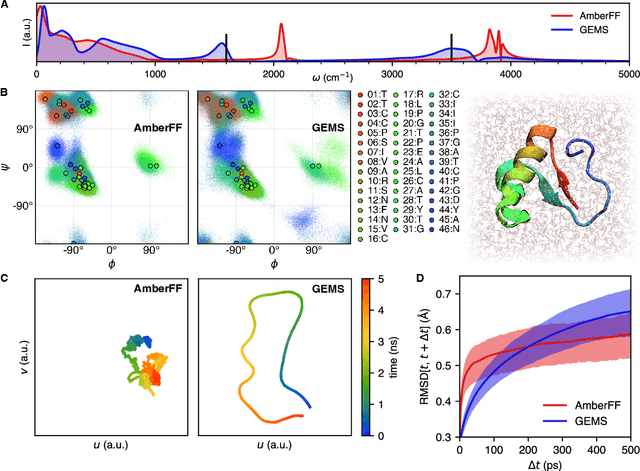
Abstract:Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations allow atomistic insights into chemical and biological processes. Accurate MD simulations require computationally demanding quantum-mechanical calculations, being practically limited to short timescales and few atoms. For larger systems, efficient, but much less reliable empirical force fields are used. Recently, machine learned force fields (MLFFs) emerged as an alternative means to execute MD simulations, offering similar accuracy as ab initio methods at orders-of-magnitude speedup. Until now, MLFFs mainly capture short-range interactions in small molecules or periodic materials, due to the increased complexity of constructing models and obtaining reliable reference data for large molecules, where long-ranged many-body effects become important. This work proposes a general approach to constructing accurate MLFFs for large-scale molecular simulations (GEMS) by training on "bottom-up" and "top-down" molecular fragments of varying size, from which the relevant physicochemical interactions can be learned. GEMS is applied to study the dynamics of alanine-based peptides and the 46-residue protein crambin in aqueous solution, allowing nanosecond-scale MD simulations of >25k atoms at essentially ab initio quality. Our findings suggest that structural motifs in peptides and proteins are more flexible than previously thought, indicating that simulations at ab initio accuracy might be necessary to understand dynamic biomolecular processes such as protein (mis)folding, drug-protein binding, or allosteric regulation.
BIGDML: Towards Exact Machine Learning Force Fields for Materials
Jun 08, 2021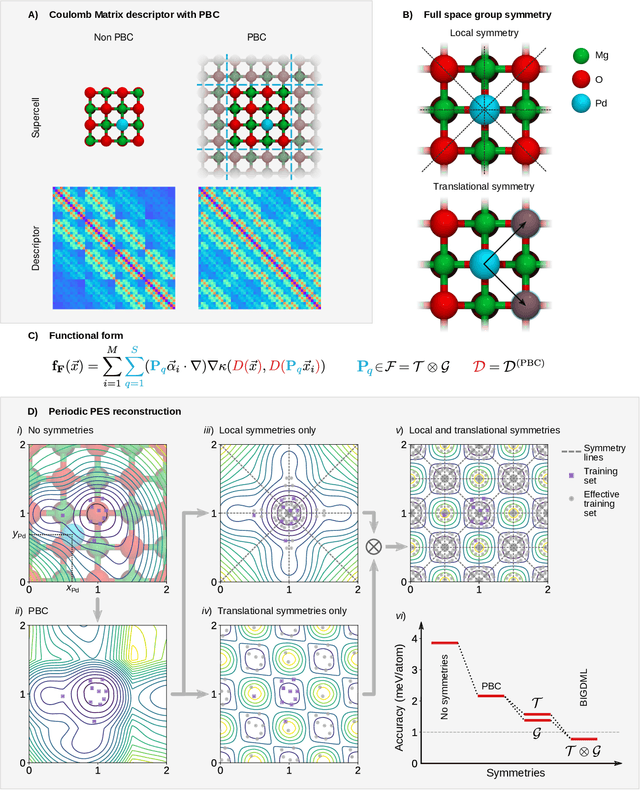
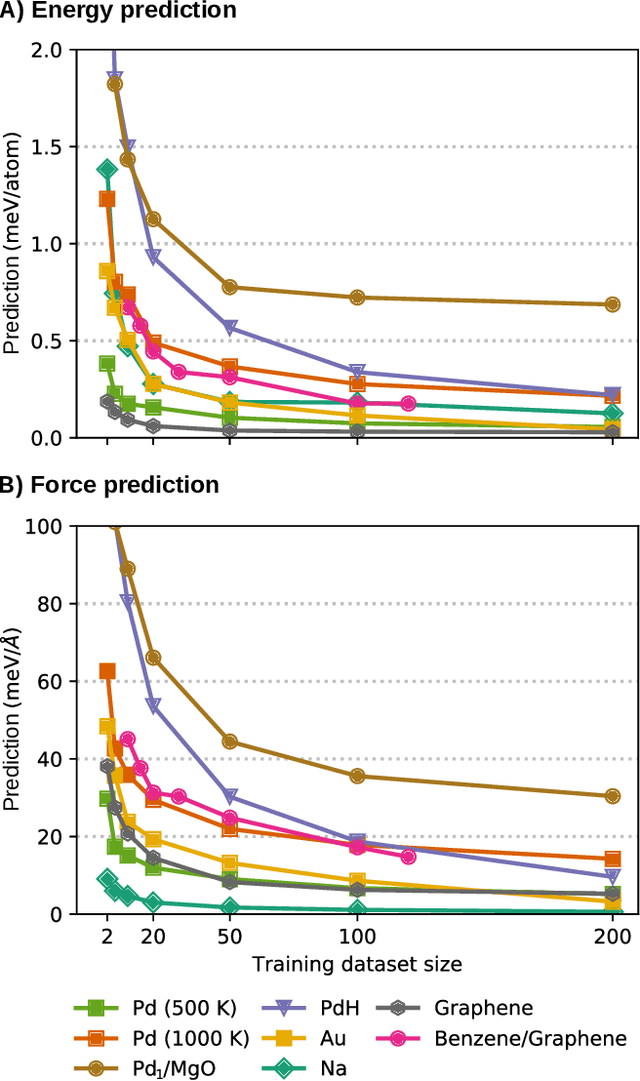
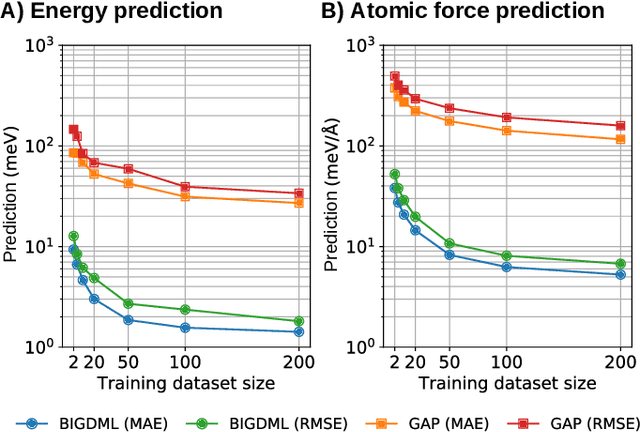
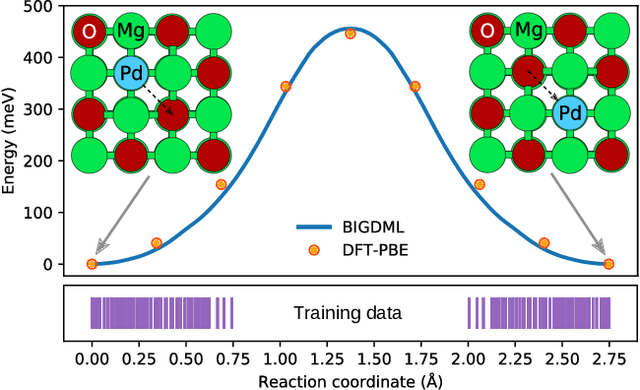
Abstract:Machine-learning force fields (MLFF) should be accurate, computationally and data efficient, and applicable to molecules, materials, and interfaces thereof. Currently, MLFFs often introduce tradeoffs that restrict their practical applicability to small subsets of chemical space or require exhaustive datasets for training. Here, we introduce the Bravais-Inspired Gradient-Domain Machine Learning (BIGDML) approach and demonstrate its ability to construct reliable force fields using a training set with just 10-200 geometries for materials including pristine and defect-containing 2D and 3D semiconductors and metals, as well as chemisorbed and physisorbed atomic and molecular adsorbates on surfaces. The BIGDML model employs the full relevant symmetry group for a given material, does not assume artificial atom types or localization of atomic interactions and exhibits high data efficiency and state-of-the-art energy accuracies (errors substantially below 1 meV per atom) for an extended set of materials. Extensive path-integral molecular dynamics carried out with BIGDML models demonstrate the counterintuitive localization of benzene--graphene dynamics induced by nuclear quantum effects and allow to rationalize the Arrhenius behavior of hydrogen diffusion coefficient in a Pd crystal for a wide range of temperatures.
Machine Learning Force Fields
Oct 14, 2020
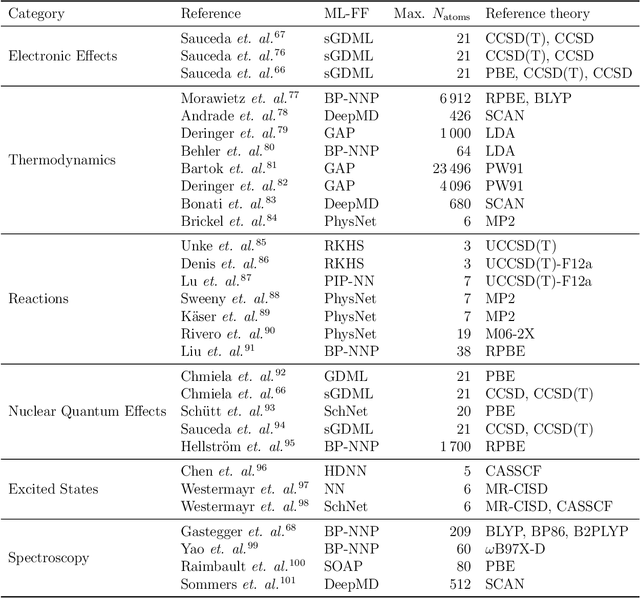
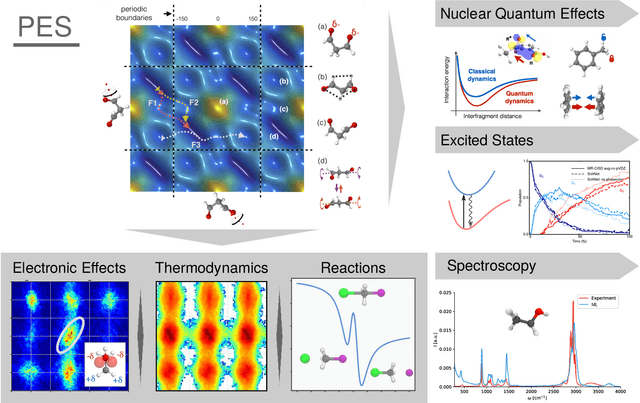

Abstract:In recent years, the use of Machine Learning (ML) in computational chemistry has enabled numerous advances previously out of reach due to the computational complexity of traditional electronic-structure methods. One of the most promising applications is the construction of ML-based force fields (FFs), with the aim to narrow the gap between the accuracy of ab initio methods and the efficiency of classical FFs. The key idea is to learn the statistical relation between chemical structure and potential energy without relying on a preconceived notion of fixed chemical bonds or knowledge about the relevant interactions. Such universal ML approximations are in principle only limited by the quality and quantity of the reference data used to train them. This review gives an overview of applications of ML-FFs and the chemical insights that can be obtained from them. The core concepts underlying ML-FFs are described in detail and a step-by-step guide for constructing and testing them from scratch is given. The text concludes with a discussion of the challenges that remain to be overcome by the next generation of ML-FFs.
Machine learning for molecular simulation
Nov 07, 2019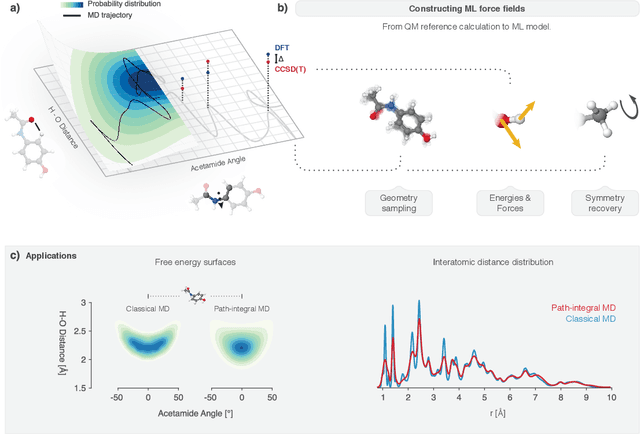
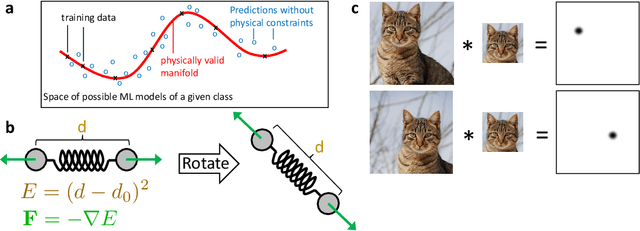
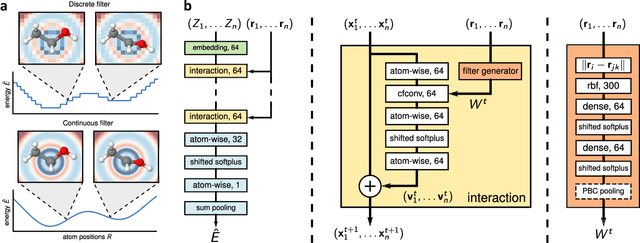
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) is transforming all areas of science. The complex and time-consuming calculations in molecular simulations are particularly suitable for a machine learning revolution and have already been profoundly impacted by the application of existing ML methods. Here we review recent ML methods for molecular simulation, with particular focus on (deep) neural networks for the prediction of quantum-mechanical energies and forces, coarse-grained molecular dynamics, the extraction of free energy surfaces and kinetics and generative network approaches to sample molecular equilibrium structures and compute thermodynamics. To explain these methods and illustrate open methodological problems, we review some important principles of molecular physics and describe how they can be incorporated into machine learning structures. Finally, we identify and describe a list of open challenges for the interface between ML and molecular simulation.
Learning representations of molecules and materials with atomistic neural networks
Dec 11, 2018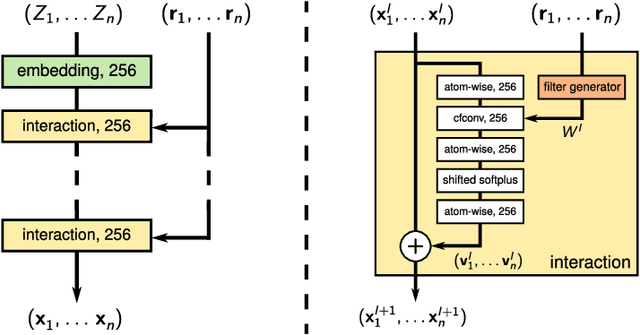
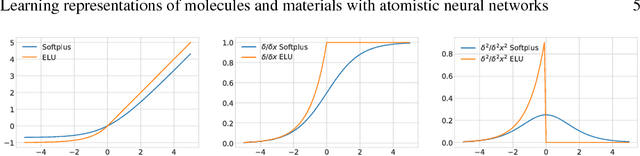
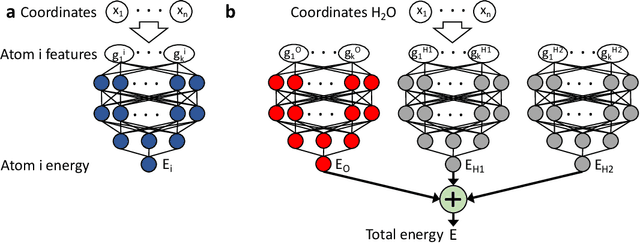
Abstract:Deep Learning has been shown to learn efficient representations for structured data such as image, text or audio. In this chapter, we present neural network architectures that are able to learn efficient representations of molecules and materials. In particular, the continuous-filter convolutional network SchNet accurately predicts chemical properties across compositional and configurational space on a variety of datasets. Beyond that, we analyze the obtained representations to find evidence that their spatial and chemical properties agree with chemical intuition.
Quantum-chemical insights from interpretable atomistic neural networks
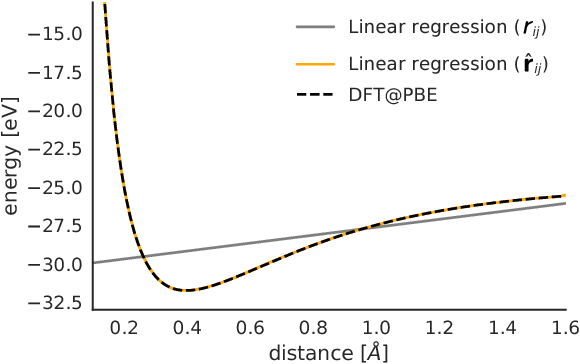
Jun 27, 2018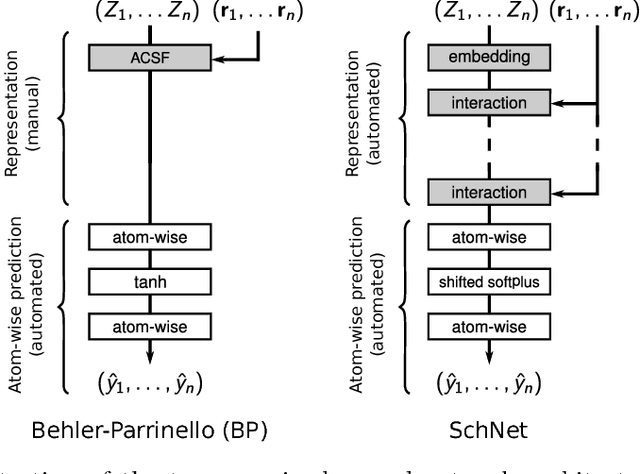

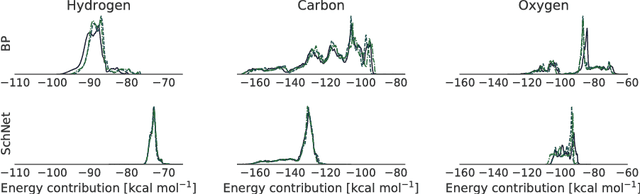
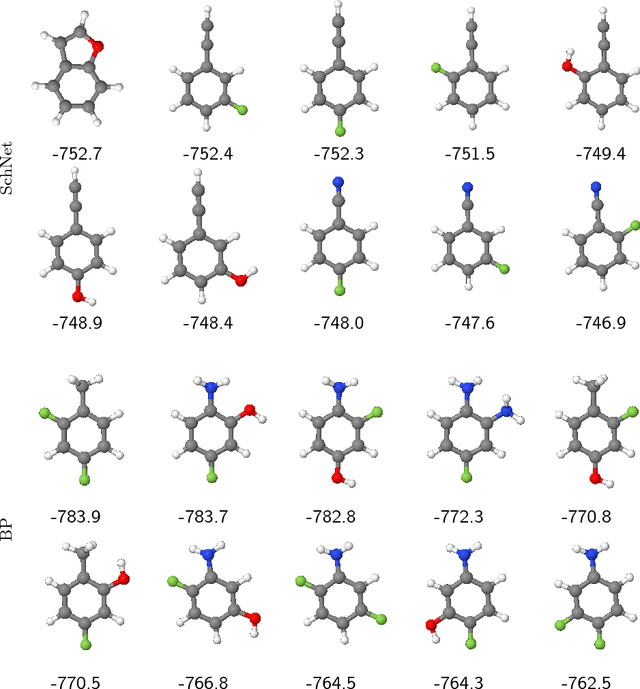
Abstract:With the rise of deep neural networks for quantum chemistry applications, there is a pressing need for architectures that, beyond delivering accurate predictions of chemical properties, are readily interpretable by researchers. Here, we describe interpretation techniques for atomistic neural networks on the example of Behler-Parrinello networks as well as the end-to-end model SchNet. Both models obtain predictions of chemical properties by aggregating atom-wise contributions. These latent variables can serve as local explanations of a prediction and are obtained during training without additional cost. Due to their correspondence to well-known chemical concepts such as atomic energies and partial charges, these atom-wise explanations enable insights not only about the model but more importantly about the underlying quantum-chemical regularities. We generalize from atomistic explanations to 3d space, thus obtaining spatially resolved visualizations which further improve interpretability. Finally, we analyze learned embeddings of chemical elements that exhibit a partial ordering that resembles the order of the periodic table. As the examined neural networks show excellent agreement with chemical knowledge, the presented techniques open up new venues for data-driven research in chemistry, physics and materials science.
SchNet: A continuous-filter convolutional neural network for modeling quantum interactions
Dec 19, 2017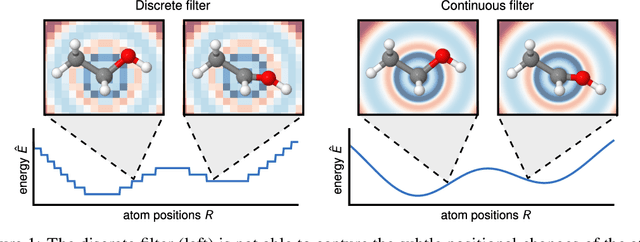

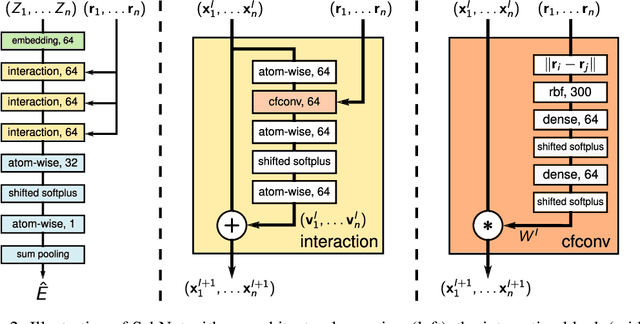
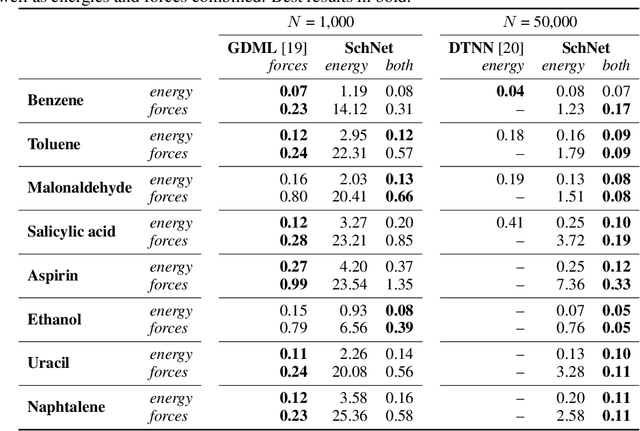
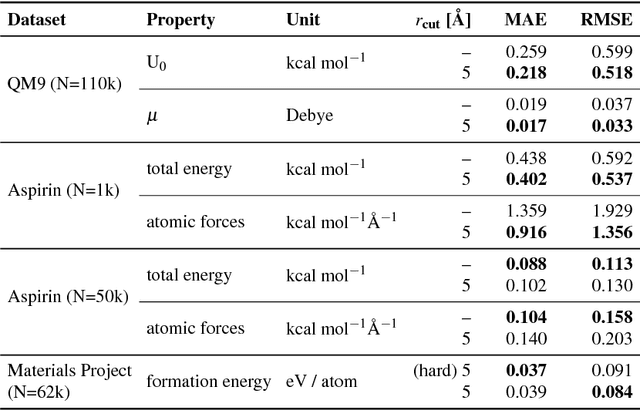
Abstract:Deep learning has the potential to revolutionize quantum chemistry as it is ideally suited to learn representations for structured data and speed up the exploration of chemical space. While convolutional neural networks have proven to be the first choice for images, audio and video data, the atoms in molecules are not restricted to a grid. Instead, their precise locations contain essential physical information, that would get lost if discretized. Thus, we propose to use continuous-filter convolutional layers to be able to model local correlations without requiring the data to lie on a grid. We apply those layers in SchNet: a novel deep learning architecture modeling quantum interactions in molecules. We obtain a joint model for the total energy and interatomic forces that follows fundamental quantum-chemical principles. This includes rotationally invariant energy predictions and a smooth, differentiable potential energy surface. Our architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance for benchmarks of equilibrium molecules and molecular dynamics trajectories. Finally, we introduce a more challenging benchmark with chemical and structural variations that suggests the path for further work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge