Alexander W. Winkler
Transformer Inertial Poser: Attention-based Real-time Human Motion Reconstruction from Sparse IMUs
Mar 29, 2022
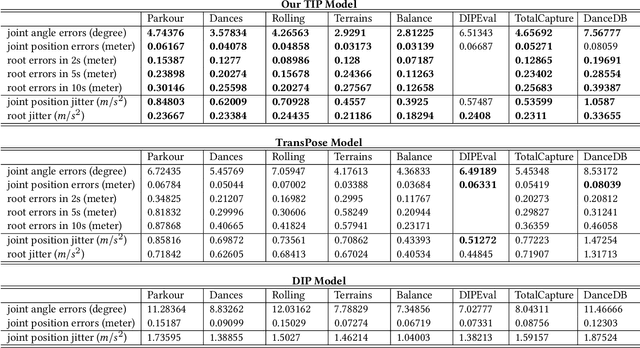
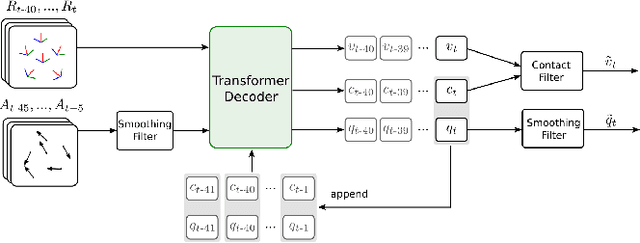
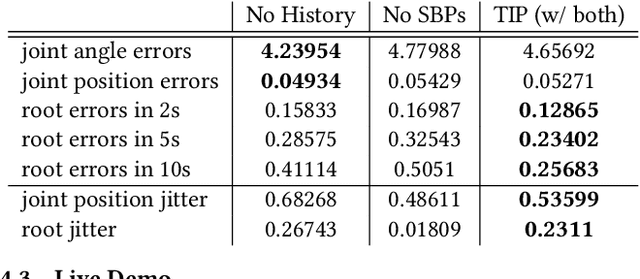
Abstract:Real-time human motion reconstruction from a sparse set of wearable IMUs provides an non-intrusive and economic approach to motion capture. Without the ability to acquire absolute position information using IMUs, many prior works took data-driven approaches that utilize large human motion datasets to tackle the under-determined nature of the problem. Still, challenges such as temporal consistency, global translation estimation, and diverse coverage of motion or terrain types remain. Inspired by recent success of Transformer models in sequence modeling, we propose an attention-based deep learning method to reconstruct full-body motion from six IMU sensors in real-time. Together with a physics-based learning objective to predict "stationary body points", our method achieves new state-of-the-art results both quantitatively and qualitatively, while being simple to implement and smaller in size. We evaluate our method extensively on synthesized and real IMU data, and with real-time live demos.
Planning and Execution of Dynamic Whole-Body Locomotion for a Hydraulic Quadruped on Challenging Terrain
Apr 07, 2019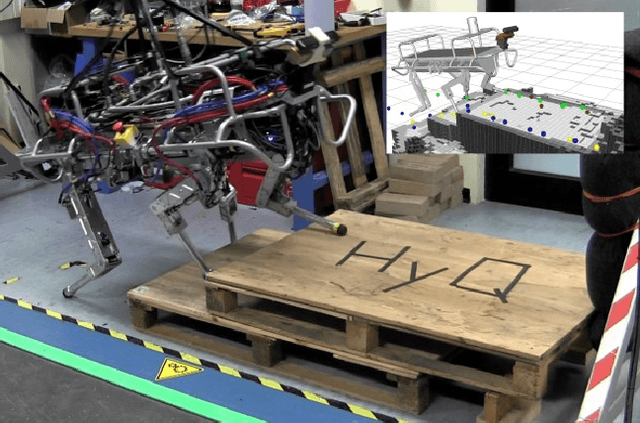
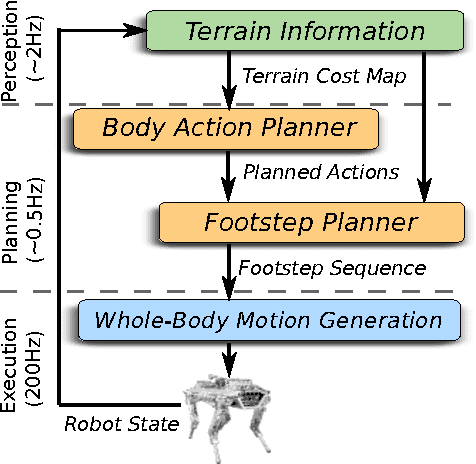
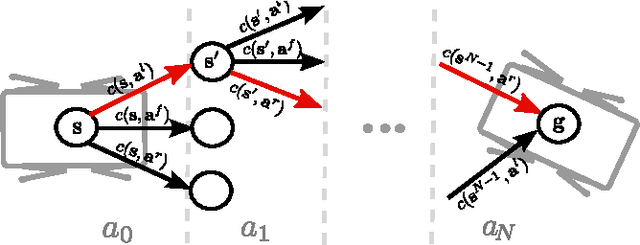
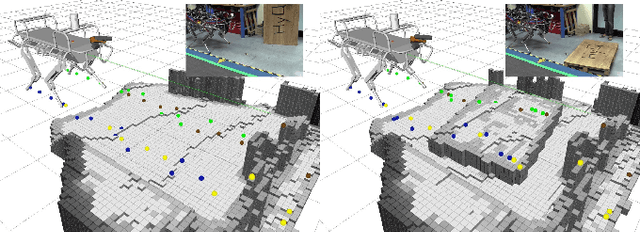
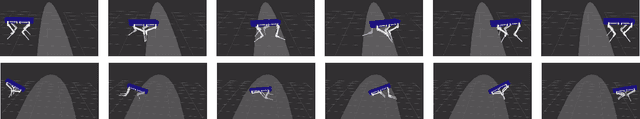
Abstract:We present a framework for dynamic quadrupedal locomotion over challenging terrain, where the choice of appropriate footholds is crucial for the success of the behaviour. We build a model of the environment on-line and on-board using an efficient occupancy grid representation. We use Any-time-Repairing A* (ARA*) to search over a tree of possible actions, choose a rough body path and select the locally-best footholds accordingly. We run a n-step lookahead optimization of the body trajectory using a dynamic stability metric, the Zero Moment Point (ZMP), that generates natural dynamic whole-body motions. A combination of floating-base inverse dynamics and virtual model control accurately executes the desired motions on an actively compliant system. Experimental trials show that this framework allows us to traverse terrains at nearly 6 times the speed of our previous work, evaluated over the same set of trials.
* 7 pages, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation
On-line and on-board planning and perception for quadrupedal locomotion
Apr 07, 2019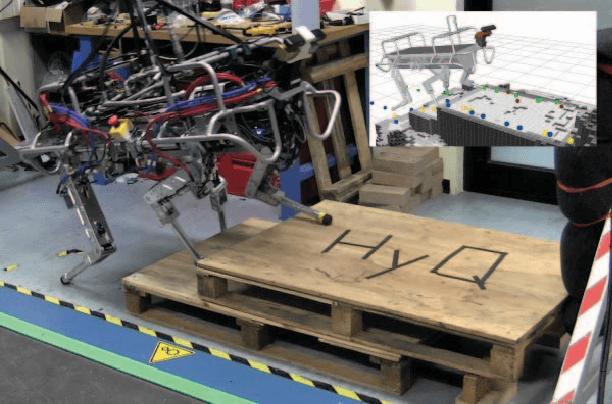
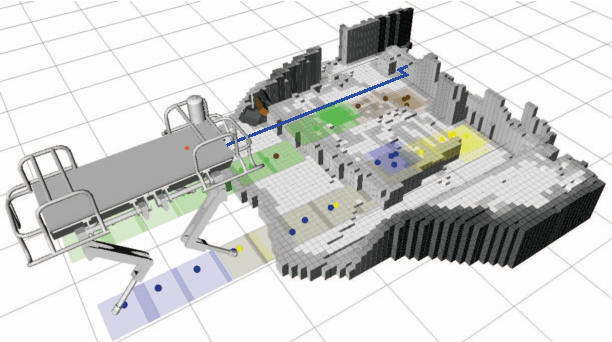
Abstract:We present a legged motion planning approach for quadrupedal locomotion over challenging terrain. We decompose the problem into body action planning and footstep planning. We use a lattice representation together with a set of defined body movement primitives for computing a body action plan. The lattice representation allows us to plan versatile movements that ensure feasibility for every possible plan. To this end, we propose a set of rules that define the footstep search regions and footstep sequence given a body action. We use Anytime Repairing A* (ARA*) search that guarantees bounded suboptimal plans. Our main contribution is a planning approach that generates on-line versatile movements. Experimental trials demonstrate the performance of our planning approach in a set of challenging terrain conditions. The terrain information and plans are computed on-line and on-board.
* 7 pages, International Conference on Technologies for Practical Robot Applications
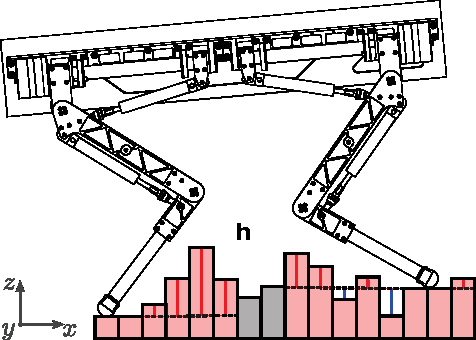
Robust Whole-Body Motion Control of Legged Robots
Mar 07, 2017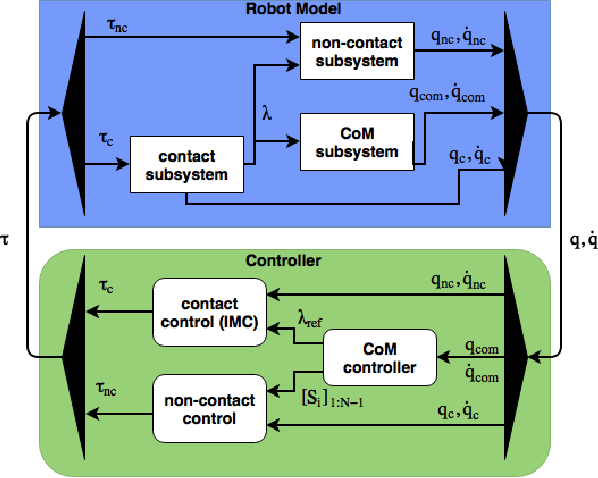
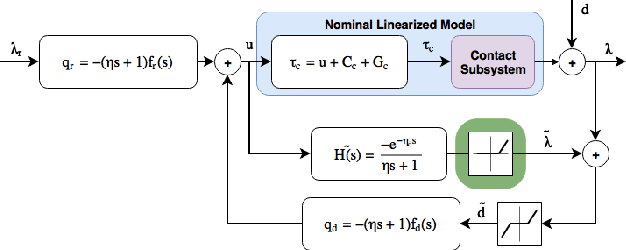
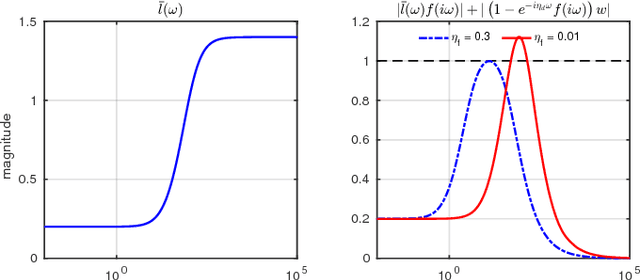
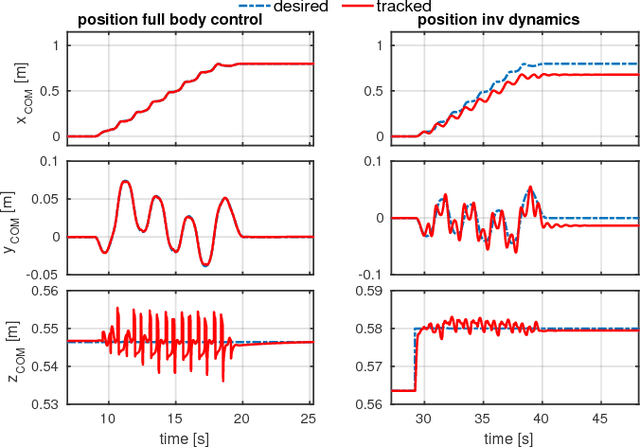
Abstract:We introduce a robust control architecture for the whole-body motion control of torque controlled robots with arms and legs. The method is based on the robust control of contact forces in order to track a planned Center of Mass trajectory. Its appeal lies in the ability to guarantee robust stability and performance despite rigid body model mismatch, actuator dynamics, delays, contact surface stiffness, and unobserved ground profiles. Furthermore, we introduce a task space decomposition approach which removes the coupling effects between contact force controller and the other non-contact controllers. Finally, we verify our control performance on a quadruped robot and compare its performance to a standard inverse dynamics approach on hardware.
An Efficient Optimal Planning and Control Framework For Quadrupedal Locomotion
Mar 04, 2017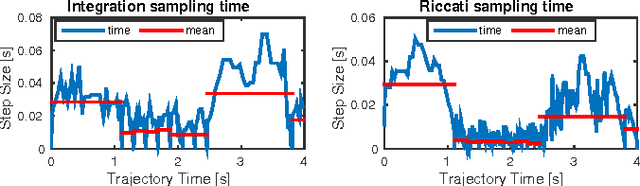
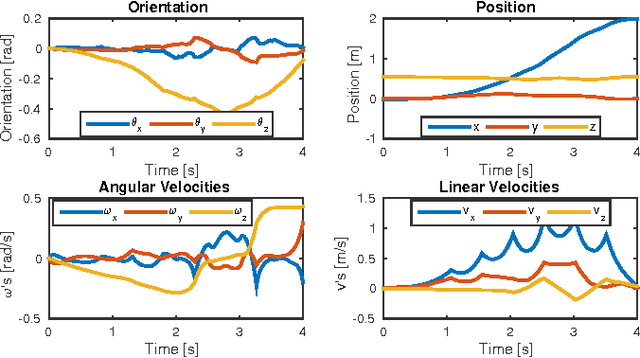
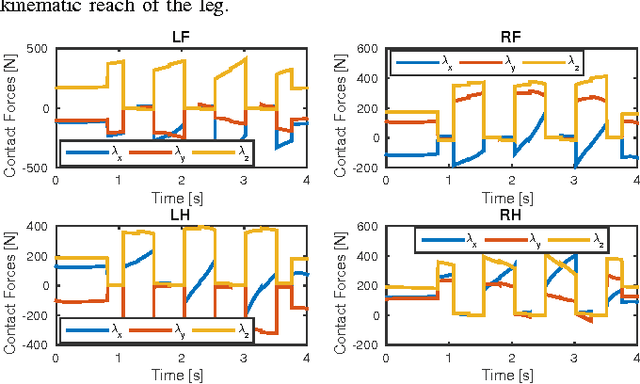
Abstract:In this paper, we present an efficient Dynamic Programing framework for optimal planning and control of legged robots. First we formulate this problem as an optimal control problem for switched systems. Then we propose a multi--level optimization approach to find the optimal switching times and the optimal continuous control inputs. Through this scheme, the decomposed optimization can potentially be done more efficiently than the combined approach. Finally, we present a continuous-time constrained LQR algorithm which simultaneously optimizes the feedforward and feedback controller with $O(n)$ time-complexity. In order to validate our approach, we show the performance of our framework on a quadrupedal robot. We choose the Center of Mass dynamics and the full kinematic formulation as the switched system model where the switching times as well as the contact forces and the joint velocities are optimized for different locomotion tasks such as gap crossing, walking and trotting.
Trajectory Optimization Through Contacts and Automatic Gait Discovery for Quadrupeds
Jul 15, 2016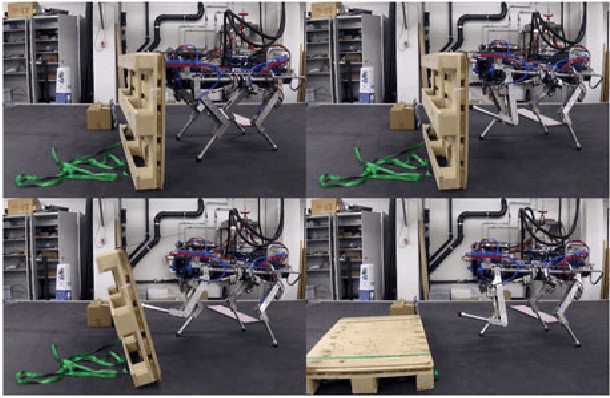
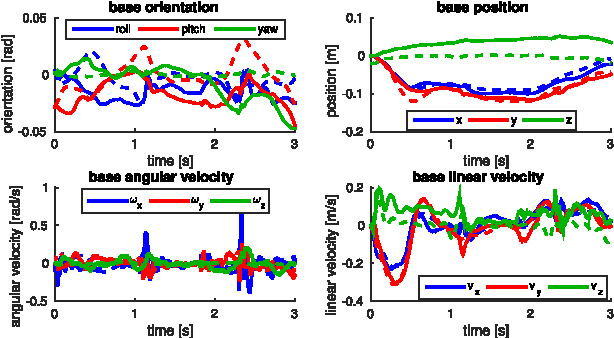
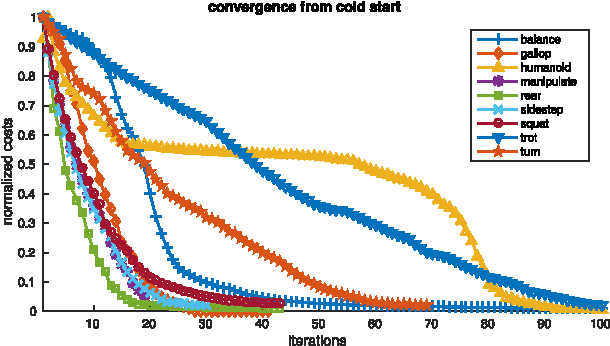
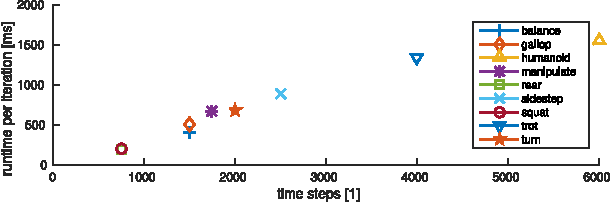
Abstract:In this work we present a trajectory Optimization framework for whole-body motion planning through contacts. We demonstrate how the proposed approach can be applied to automatically discover different gaits and dynamic motions on a quadruped robot. In contrast to most previous methods, we do not pre-specify contact switches, timings, points or gait patterns, but they are a direct outcome of the optimization. Furthermore, we optimize over the entire dynamics of the robot, which enables the optimizer to fully leverage the capabilities of the robot. To illustrate the spectrum of achievable motions, here we show eight different tasks, which would require very different control structures when solved with state-of-the-art methods. Using our trajectory Optimization approach, we are solving each task with a simple, high level cost function and without any changes in the control structure. Furthermore, we fully integrated our approach with the robot's control and estimation framework such that optimization can be run online. By demonstrating a rough manipulation task with multiple dynamic contact switches, we exemplarily show how optimized trajectories and control inputs can be directly applied to hardware.
Evaluating direct transcription and nonlinear optimization methods for robot motion planning
Jan 29, 2016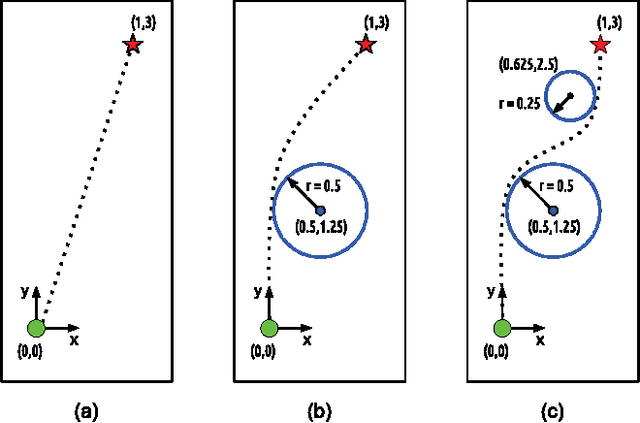
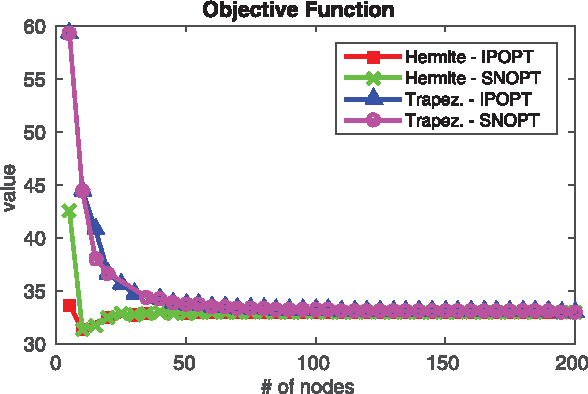

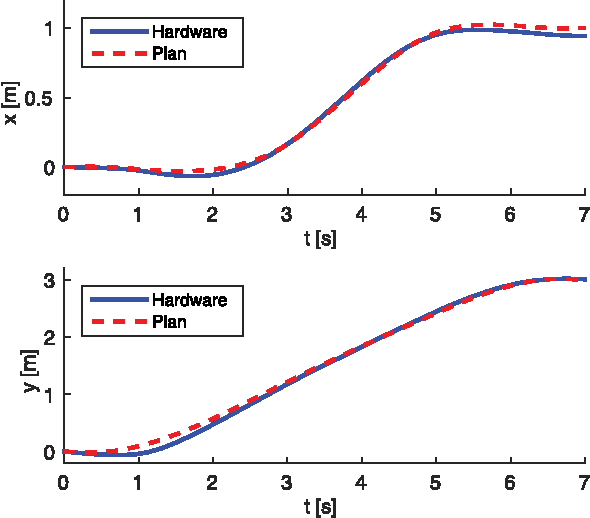
Abstract:This paper studies existing direct transcription methods for trajectory optimization applied to robot motion planning. There are diverse alternatives for the implementation of direct transcription. In this study we analyze the effects of such alternatives when solving a robotics problem. Different parameters such as integration scheme, number of discretization nodes, initialization strategies and complexity of the problem are evaluated. We measure the performance of the methods in terms of computational time, accuracy and quality of the solution. Additionally, we compare two optimization methodologies frequently used to solve the transcribed problem, namely Sequential Quadratic Programming (SQP) and Interior Point Method (IPM). As a benchmark, we solve different motion tasks on an underactuated and non-minimal-phase ball-balancing robot with a 10 dimensional state space and 3 dimensional input space. Additionally, we validate the results on a simulated 3D quadrotor. Finally, as a verification of using direct transcription methods for trajectory optimization on real robots, we present hardware experiments on a motion task including path constraints and actuation limits.
Projection based whole body motion planning for legged robots
Oct 06, 2015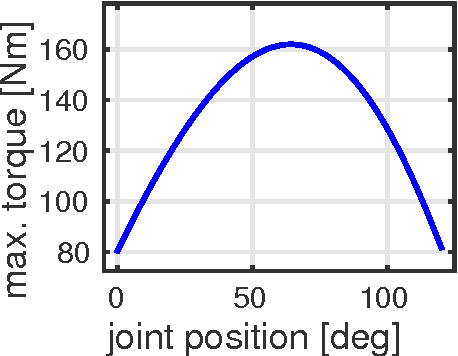
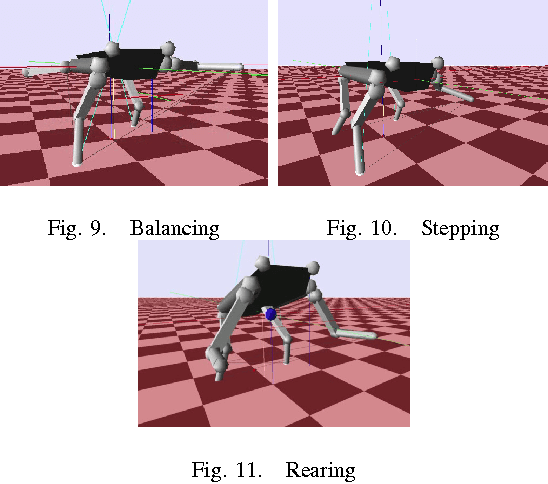
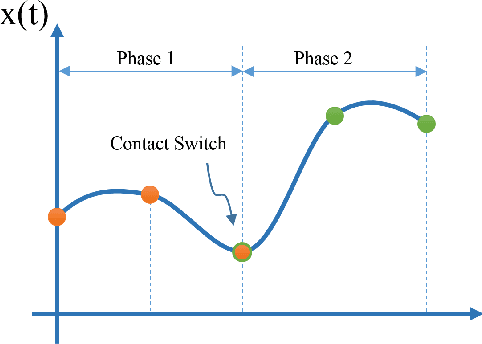
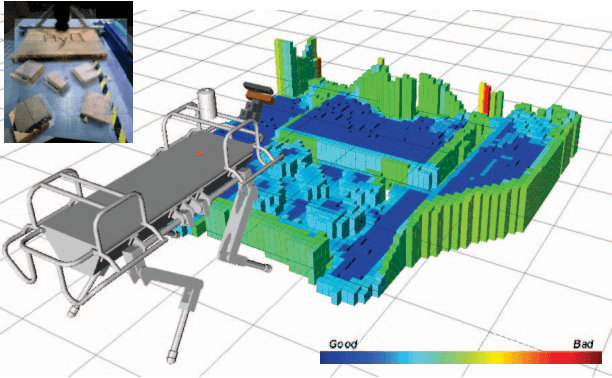
Abstract:In this paper we present a new approach for dynamic motion planning for legged robots. We formulate a trajectory optimization problem based on a compact form of the robot dynamics. Such a form is obtained by projecting the rigid body dynamics onto the null space of the Constraint Jacobian. As consequence of the projection, contact forces are removed from the model but their effects are still taken into account. This approach permits to solve the optimal control problem of a floating base constrained multibody system while avoiding the use of an explicit contact model. We use direct transcription to numerically solve the optimization. As the contact forces are not part of the decision variables the size of the resultant discrete mathematical program is reduced and therefore solutions can be obtained in a tractable time. Using a predefined sequence of contact configurations (phases), our approach solves motions where contact switches occur. Transitions between phases are automatically resolved without using a model for switching dynamics. We present results on a hydraulic quadruped robot (HyQ), including single phase (standing, crouching) as well as multiple phase (rearing, diagonal leg balancing and stepping) dynamic motions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge