Alexander Gelbukh
Irony Detection in Urdu Text: A Comparative Study Using Machine Learning Models and Large Language Models
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:Ironic identification is a challenging task in Natural Language Processing, particularly when dealing with languages that differ in syntax and cultural context. In this work, we aim to detect irony in Urdu by translating an English Ironic Corpus into the Urdu language. We evaluate ten state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms using GloVe and Word2Vec embeddings, and compare their performance with classical methods. Additionally, we fine-tune advanced transformer-based models, including BERT, RoBERTa, LLaMA 2 (7B), LLaMA 3 (8B), and Mistral, to assess the effectiveness of large-scale models in irony detection. Among machine learning models, Gradient Boosting achieved the best performance with an F1-score of 89.18%. Among transformer-based models, LLaMA 3 (8B) achieved the highest performance with an F1-score of 94.61%. These results demonstrate that combining transliteration techniques with modern NLP models enables robust irony detection in Urdu, a historically low-resource language.
Hybrid Extractive Abstractive Summarization for Multilingual Sentiment Analysis
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:We propose a hybrid approach for multilingual sentiment analysis that combines extractive and abstractive summarization to address the limitations of standalone methods. The model integrates TF-IDF-based extraction with a fine-tuned XLM-R abstractive module, enhanced by dynamic thresholding and cultural adaptation. Experiments across 10 languages show significant improvements over baselines, achieving 0.90 accuracy for English and 0.84 for low-resource languages. The approach also demonstrates 22% greater computational efficiency than traditional methods. Practical applications include real-time brand monitoring and cross-cultural discourse analysis. Future work will focus on optimization for low-resource languages via 8-bit quantization.
EDU-NER-2025: Named Entity Recognition in Urdu Educational Texts using XLM-RoBERTa with X (formerly Twitter)
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Named Entity Recognition (NER) plays a pivotal role in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks by identifying and classifying named entities (NEs) from unstructured data into predefined categories such as person, organization, location, date, and time. While extensive research exists for high-resource languages and general domains, NER in Urdu particularly within domain-specific contexts like education remains significantly underexplored. This is Due to lack of annotated datasets for educational content which limits the ability of existing models to accurately identify entities such as academic roles, course names, and institutional terms, underscoring the urgent need for targeted resources in this domain. To the best of our knowledge, no dataset exists in the domain of the Urdu language for this purpose. To achieve this objective this study makes three key contributions. Firstly, we created a manually annotated dataset in the education domain, named EDU-NER-2025, which contains 13 unique most important entities related to education domain. Second, we describe our annotation process and guidelines in detail and discuss the challenges of labelling EDU-NER-2025 dataset. Third, we addressed and analyzed key linguistic challenges, such as morphological complexity and ambiguity, which are prevalent in formal Urdu texts.
Multilingual Sentiment Analysis of Summarized Texts: A Cross-Language Study of Text Shortening Effects
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Summarization significantly impacts sentiment analysis across languages with diverse morphologies. This study examines extractive and abstractive summarization effects on sentiment classification in English, German, French, Spanish, Italian, Finnish, Hungarian, and Arabic. We assess sentiment shifts post-summarization using multilingual transformers (mBERT, XLM-RoBERTa, T5, and BART) and language-specific models (FinBERT, AraBERT). Results show extractive summarization better preserves sentiment, especially in morphologically complex languages, while abstractive summarization improves readability but introduces sentiment distortion, affecting sentiment accuracy. Languages with rich inflectional morphology, such as Finnish, Hungarian, and Arabic, experience greater accuracy drops than English or German. Findings emphasize the need for language-specific adaptations in sentiment analysis and propose a hybrid summarization approach balancing readability and sentiment preservation. These insights benefit multilingual sentiment applications, including social media monitoring, market analysis, and cross-lingual opinion mining.
Advancing Sentiment Analysis in Tamil-English Code-Mixed Texts: Challenges and Transformer-Based Solutions
Mar 30, 2025
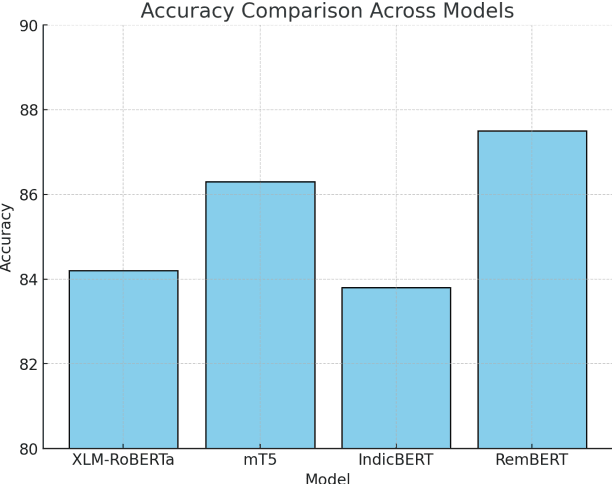
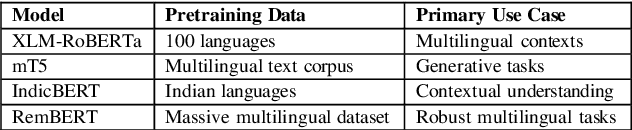

Abstract:The sentiment analysis task in Tamil-English code-mixed texts has been explored using advanced transformer-based models. Challenges from grammatical inconsistencies, orthographic variations, and phonetic ambiguities have been addressed. The limitations of existing datasets and annotation gaps have been examined, emphasizing the need for larger and more diverse corpora. Transformer architectures, including XLM-RoBERTa, mT5, IndicBERT, and RemBERT, have been evaluated in low-resource, code-mixed environments. Performance metrics have been analyzed, highlighting the effectiveness of specific models in handling multilingual sentiment classification. The findings suggest that further advancements in data augmentation, phonetic normalization, and hybrid modeling approaches are required to enhance accuracy. Future research directions for improving sentiment analysis in code-mixed texts have been proposed.
PRKAN: Parameter-Reduced Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) represent an innovation in neural network architectures, offering a compelling alternative to Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) in models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Transformers. By advancing network design, KANs are driving groundbreaking research and enabling transformative applications across various scientific domains involving neural networks. However, existing KANs often require significantly more parameters in their network layers compared to MLPs. To address this limitation, this paper introduces PRKANs (\textbf{P}arameter-\textbf{R}educed \textbf{K}olmogorov-\textbf{A}rnold \textbf{N}etworks), which employ several methods to reduce the parameter count in KAN layers, making them comparable to MLP layers. Experimental results on the MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets demonstrate that PRKANs with attention mechanisms outperform several existing KANs and rival the performance of MLPs, albeit with slightly longer training times. Furthermore, the study highlights the advantages of Gaussian Radial Basis Functions (GRBFs) and layer normalization in KAN designs. The repository for this work is available at: \url{https://github.com/hoangthangta/All-KAN}.
Synthetic Time Series Data Generation for Healthcare Applications: A PCG Case Study
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:The generation of high-quality medical time series data is essential for advancing healthcare diagnostics and safeguarding patient privacy. Specifically, synthesizing realistic phonocardiogram (PCG) signals offers significant potential as a cost-effective and efficient tool for cardiac disease pre-screening. Despite its potential, the synthesis of PCG signals for this specific application received limited attention in research. In this study, we employ and compare three state-of-the-art generative models from different categories - WaveNet, DoppelGANger, and DiffWave - to generate high-quality PCG data. We use data from the George B. Moody PhysioNet Challenge 2022. Our methods are evaluated using various metrics widely used in the previous literature in the domain of time series data generation, such as mean absolute error and maximum mean discrepancy. Our results demonstrate that the generated PCG data closely resembles the original datasets, indicating the effectiveness of our generative models in producing realistic synthetic PCG data. In our future work, we plan to incorporate this method into a data augmentation pipeline to synthesize abnormal PCG signals with heart murmurs, in order to address the current scarcity of abnormal data. We hope to improve the robustness and accuracy of diagnostic tools in cardiology, enhancing their effectiveness in detecting heart murmurs.
Social Support Detection from Social Media Texts
Nov 04, 2024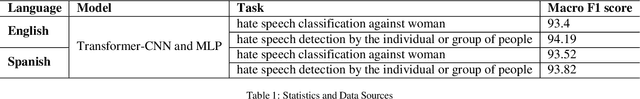
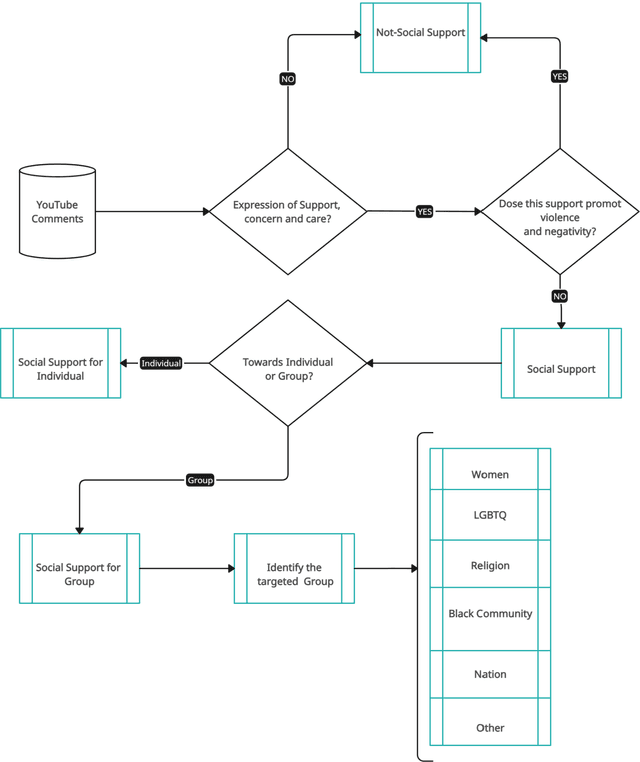
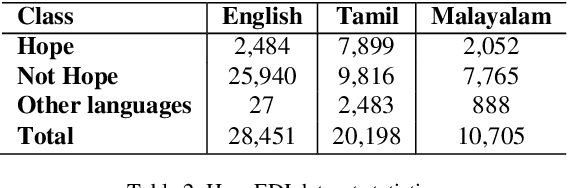
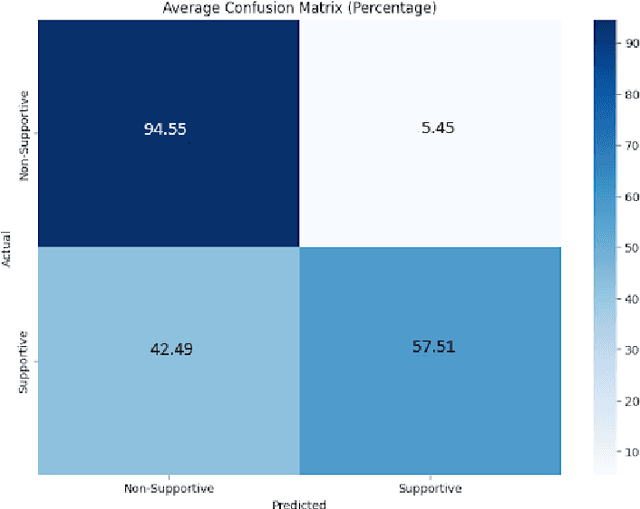
Abstract:Social support, conveyed through a multitude of interactions and platforms such as social media, plays a pivotal role in fostering a sense of belonging, aiding resilience in the face of challenges, and enhancing overall well-being. This paper introduces Social Support Detection (SSD) as a Natural language processing (NLP) task aimed at identifying supportive interactions within online communities. The study presents the task of Social Support Detection (SSD) in three subtasks: two binary classification tasks and one multiclass task, with labels detailed in the dataset section. We conducted experiments on a dataset comprising 10,000 YouTube comments. Traditional machine learning models were employed, utilizing various feature combinations that encompass linguistic, psycholinguistic, emotional, and sentiment information. Additionally, we experimented with neural network-based models using various word embeddings to enhance the performance of our models across these subtasks.The results reveal a prevalence of group-oriented support in online dialogues, reflecting broader societal patterns. The findings demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating psycholinguistic, emotional, and sentiment features with n-grams in detecting social support and distinguishing whether it is directed toward an individual or a group. The best results for different subtasks across all experiments range from 0.72 to 0.82.
Ethio-Fake: Cutting-Edge Approaches to Combat Fake News in Under-Resourced Languages Using Explainable AI
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:The proliferation of fake news has emerged as a significant threat to the integrity of information dissemination, particularly on social media platforms. Misinformation can spread quickly due to the ease of creating and disseminating content, affecting public opinion and sociopolitical events. Identifying false information is therefore essential to reducing its negative consequences and maintaining the reliability of online news sources. Traditional approaches to fake news detection often rely solely on content-based features, overlooking the crucial role of social context in shaping the perception and propagation of news articles. In this paper, we propose a comprehensive approach that integrates social context-based features with news content features to enhance the accuracy of fake news detection in under-resourced languages. We perform several experiments utilizing a variety of methodologies, including traditional machine learning, neural networks, ensemble learning, and transfer learning. Assessment of the outcomes of the experiments shows that the ensemble learning approach has the highest accuracy, achieving a 0.99 F1 score. Additionally, when compared with monolingual models, the fine-tuned model with the target language outperformed others, achieving a 0.94 F1 score. We analyze the functioning of the models, considering the important features that contribute to model performance, using explainable AI techniques.
FC-KAN: Function Combinations in Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce FC-KAN, a Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) that leverages combinations of popular mathematical functions such as B-splines, wavelets, and radial basis functions on low-dimensional data through element-wise operations. We explore several methods for combining the outputs of these functions, including sum, element-wise product, the addition of sum and element-wise product, quadratic function representation, and concatenation. In our experiments, we compare FC-KAN with multi-layer perceptron network (MLP) and other existing KANs, such as BSRBF-KAN, EfficientKAN, FastKAN, and FasterKAN, on the MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets. A variant of FC-KAN, which uses a combination of outputs from B-splines and Difference of Gaussians (DoG) in the form of a quadratic function, outperformed all other models on the average of 5 independent training runs. We expect that FC-KAN can leverage function combinations to design future KANs. Our repository is publicly available at: https://github.com/hoangthangta/FC_KAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge