Hoang-Thang Ta
AF-KAN: Activation Function-Based Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks for Efficient Representation Learning
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) have inspired numerous works exploring their applications across a wide range of scientific problems, with the potential to replace Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs). While many KANs are designed using basis and polynomial functions, such as B-splines, ReLU-KAN utilizes a combination of ReLU functions to mimic the structure of B-splines and take advantage of ReLU's speed. However, ReLU-KAN is not built for multiple inputs, and its limitations stem from ReLU's handling of negative values, which can restrict feature extraction. To address these issues, we introduce Activation Function-Based Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (AF-KAN), expanding ReLU-KAN with various activations and their function combinations. This novel KAN also incorporates parameter reduction methods, primarily attention mechanisms and data normalization, to enhance performance on image classification datasets. We explore different activation functions, function combinations, grid sizes, and spline orders to validate the effectiveness of AF-KAN and determine its optimal configuration. In the experiments, AF-KAN significantly outperforms MLP, ReLU-KAN, and other KANs with the same parameter count. It also remains competitive even when using fewer than 6 to 10 times the parameters while maintaining the same network structure. However, AF-KAN requires a longer training time and consumes more FLOPs. The repository for this work is available at https://github.com/hoangthangta/All-KAN.
PRKAN: Parameter-Reduced Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) represent an innovation in neural network architectures, offering a compelling alternative to Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) in models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Transformers. By advancing network design, KANs are driving groundbreaking research and enabling transformative applications across various scientific domains involving neural networks. However, existing KANs often require significantly more parameters in their network layers compared to MLPs. To address this limitation, this paper introduces PRKANs (\textbf{P}arameter-\textbf{R}educed \textbf{K}olmogorov-\textbf{A}rnold \textbf{N}etworks), which employ several methods to reduce the parameter count in KAN layers, making them comparable to MLP layers. Experimental results on the MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets demonstrate that PRKANs with attention mechanisms outperform several existing KANs and rival the performance of MLPs, albeit with slightly longer training times. Furthermore, the study highlights the advantages of Gaussian Radial Basis Functions (GRBFs) and layer normalization in KAN designs. The repository for this work is available at: \url{https://github.com/hoangthangta/All-KAN}.
FC-KAN: Function Combinations in Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce FC-KAN, a Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) that leverages combinations of popular mathematical functions such as B-splines, wavelets, and radial basis functions on low-dimensional data through element-wise operations. We explore several methods for combining the outputs of these functions, including sum, element-wise product, the addition of sum and element-wise product, quadratic function representation, and concatenation. In our experiments, we compare FC-KAN with multi-layer perceptron network (MLP) and other existing KANs, such as BSRBF-KAN, EfficientKAN, FastKAN, and FasterKAN, on the MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets. A variant of FC-KAN, which uses a combination of outputs from B-splines and Difference of Gaussians (DoG) in the form of a quadratic function, outperformed all other models on the average of 5 independent training runs. We expect that FC-KAN can leverage function combinations to design future KANs. Our repository is publicly available at: https://github.com/hoangthangta/FC_KAN.
Utilize Transformers for translating Wikipedia category names
Aug 12, 2024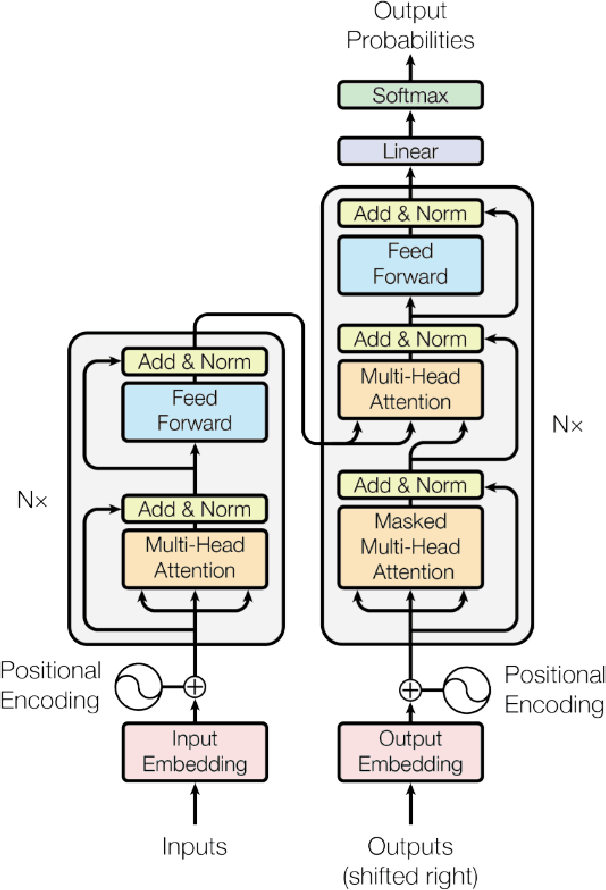
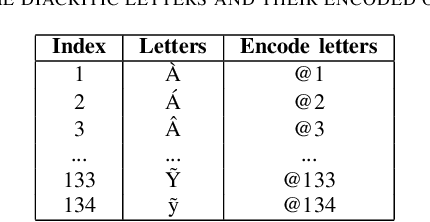
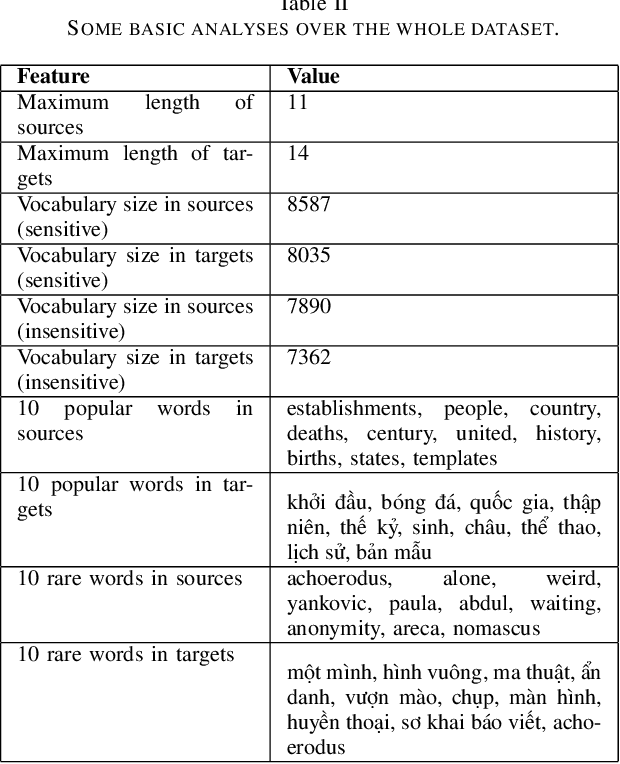
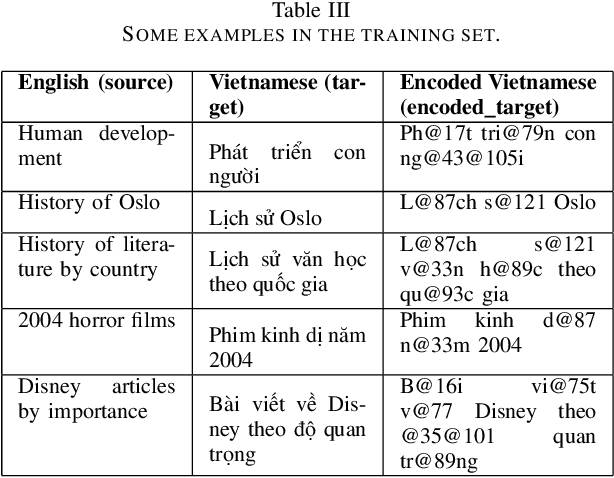
Abstract:On Wikipedia, articles are categorized to aid readers in navigating content efficiently. The manual creation of new categories can be laborious and time-intensive. To tackle this issue, we built language models to translate Wikipedia categories from English to Vietnamese with a dataset containing 15,000 English-Vietnamese category pairs. Subsequently, small to medium-scale Transformer pre-trained models with a sequence-to-sequence architecture were fine-tuned for category translation. The experiments revealed that OPUS-MT-en-vi surpassed other models, attaining the highest performance with a BLEU score of 0.73, despite its smaller model storage. We expect our paper to be an alternative solution for translation tasks with limited computer resources.
BSRBF-KAN: A combination of B-splines and Radial Basic Functions in Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce BSRBF-KAN, a Kolmogorov Arnold Network (KAN) that combines Bsplines and radial basis functions (RBFs) to fit input vectors in data training. We perform experiments with BSRBF-KAN, MLP, and other popular KANs, including EfficientKAN, FastKAN, FasterKAN, and GottliebKAN over the MNIST dataset. BSRBF-KAN shows stability in 5 training times with a competitive average accuracy of 97.55% and obtains convergence better than other networks. We expect BSRBF-KAN can open many combinations of mathematical functions to design KANs. Our repo is publicly available at: https://github.com/hoangthangta/BSRBF-KAN.
ThangDLU at #SMM4H 2024: Encoder-decoder models for classifying text data on social disorders in children and adolescents
Apr 30, 2024

Abstract:This paper describes our participation in Task 3 and Task 5 of the #SMM4H (Social Media Mining for Health) 2024 Workshop, explicitly targeting the classification challenges within tweet data. Task 3 is a multi-class classification task centered on tweets discussing the impact of outdoor environments on symptoms of social anxiety. Task 5 involves a binary classification task focusing on tweets reporting medical disorders in children. We applied transfer learning from pre-trained encoder-decoder models such as BART-base and T5-small to identify the labels of a set of given tweets. We also presented some data augmentation methods to see their impact on the model performance. Finally, the systems obtained the best F1 score of 0.627 in Task 3 and the best F1 score of 0.841 in Task 5.
Self-training from Self-memory in Data-to-text Generation
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel training model, self-training from self-memory (STSM) in data-to-text generation (DTG), allowing the model to self-train on subsets, including self-memory as outputs inferred directly from the trained models and/or the new data. The quality of self-memory is validated by two models, data-to-text (D2T) and text-to-data (T2D), by two pre-defined conditions: (1) the appearance of all source values in the outputs of the D2T model and (2) the ability to convert back to source data in the outputs in the T2D model. We utilize a greedy algorithm to generate shorter D2T outputs if they contain all source values. Subsequently, we use the T2D model to confirm that these outputs can capture input relationships by demonstrating their capacity to convert text back into data. With 30% of the dataset, we can train the D2T model with a competitive performance compared to full training in the same setup. We experiment with our model on two datasets, E2E NLG and DART. STSM offers the D2T model a generalization capability from its subset memory while reducing training data volume. Ultimately, we anticipate that this paper will contribute to continual learning solutions that adapt to new training data, incorporating it as a form of self-memory in DTG tasks. The curated dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/hoangthangta/STSM.
DepressionEmo: A novel dataset for multilabel classification of depression emotions
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Emotions are integral to human social interactions, with diverse responses elicited by various situational contexts. Particularly, the prevalence of negative emotional states has been correlated with negative outcomes for mental health, necessitating a comprehensive analysis of their occurrence and impact on individuals. In this paper, we introduce a novel dataset named DepressionEmo designed to detect 8 emotions associated with depression by 6037 examples of long Reddit user posts. This dataset was created through a majority vote over inputs by zero-shot classifications from pre-trained models and validating the quality by annotators and ChatGPT, exhibiting an acceptable level of interrater reliability between annotators. The correlation between emotions, their distribution over time, and linguistic analysis are conducted on DepressionEmo. Besides, we provide several text classification methods classified into two groups: machine learning methods such as SVM, XGBoost, and Light GBM; and deep learning methods such as BERT, GAN-BERT, and BART. The pretrained BART model, bart-base allows us to obtain the highest F1- Macro of 0.76, showing its outperformance compared to other methods evaluated in our analysis. Across all emotions, the highest F1-Macro value is achieved by suicide intent, indicating a certain value of our dataset in identifying emotions in individuals with depression symptoms through text analysis. The curated dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/abuBakarSiddiqurRahman/DepressionEmo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge