Abu Bakar Siddiqur Rahman
FC-KAN: Function Combinations in Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce FC-KAN, a Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) that leverages combinations of popular mathematical functions such as B-splines, wavelets, and radial basis functions on low-dimensional data through element-wise operations. We explore several methods for combining the outputs of these functions, including sum, element-wise product, the addition of sum and element-wise product, quadratic function representation, and concatenation. In our experiments, we compare FC-KAN with multi-layer perceptron network (MLP) and other existing KANs, such as BSRBF-KAN, EfficientKAN, FastKAN, and FasterKAN, on the MNIST and Fashion-MNIST datasets. A variant of FC-KAN, which uses a combination of outputs from B-splines and Difference of Gaussians (DoG) in the form of a quadratic function, outperformed all other models on the average of 5 independent training runs. We expect that FC-KAN can leverage function combinations to design future KANs. Our repository is publicly available at: https://github.com/hoangthangta/FC_KAN.
ThangDLU at #SMM4H 2024: Encoder-decoder models for classifying text data on social disorders in children and adolescents
Apr 30, 2024

Abstract:This paper describes our participation in Task 3 and Task 5 of the #SMM4H (Social Media Mining for Health) 2024 Workshop, explicitly targeting the classification challenges within tweet data. Task 3 is a multi-class classification task centered on tweets discussing the impact of outdoor environments on symptoms of social anxiety. Task 5 involves a binary classification task focusing on tweets reporting medical disorders in children. We applied transfer learning from pre-trained encoder-decoder models such as BART-base and T5-small to identify the labels of a set of given tweets. We also presented some data augmentation methods to see their impact on the model performance. Finally, the systems obtained the best F1 score of 0.627 in Task 3 and the best F1 score of 0.841 in Task 5.
DepressionEmo: A novel dataset for multilabel classification of depression emotions
Jan 09, 2024Abstract:Emotions are integral to human social interactions, with diverse responses elicited by various situational contexts. Particularly, the prevalence of negative emotional states has been correlated with negative outcomes for mental health, necessitating a comprehensive analysis of their occurrence and impact on individuals. In this paper, we introduce a novel dataset named DepressionEmo designed to detect 8 emotions associated with depression by 6037 examples of long Reddit user posts. This dataset was created through a majority vote over inputs by zero-shot classifications from pre-trained models and validating the quality by annotators and ChatGPT, exhibiting an acceptable level of interrater reliability between annotators. The correlation between emotions, their distribution over time, and linguistic analysis are conducted on DepressionEmo. Besides, we provide several text classification methods classified into two groups: machine learning methods such as SVM, XGBoost, and Light GBM; and deep learning methods such as BERT, GAN-BERT, and BART. The pretrained BART model, bart-base allows us to obtain the highest F1- Macro of 0.76, showing its outperformance compared to other methods evaluated in our analysis. Across all emotions, the highest F1-Macro value is achieved by suicide intent, indicating a certain value of our dataset in identifying emotions in individuals with depression symptoms through text analysis. The curated dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/abuBakarSiddiqurRahman/DepressionEmo.
WikiDes: A Wikipedia-Based Dataset for Generating Short Descriptions from Paragraphs
Sep 27, 2022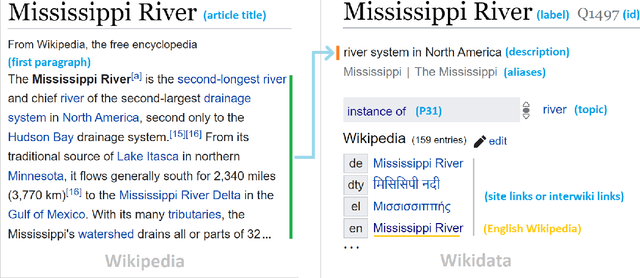
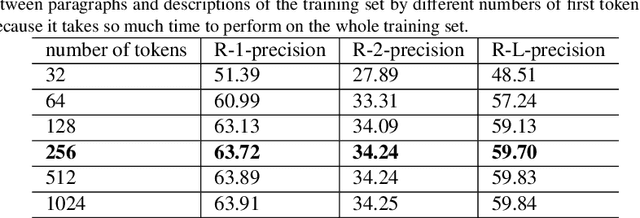
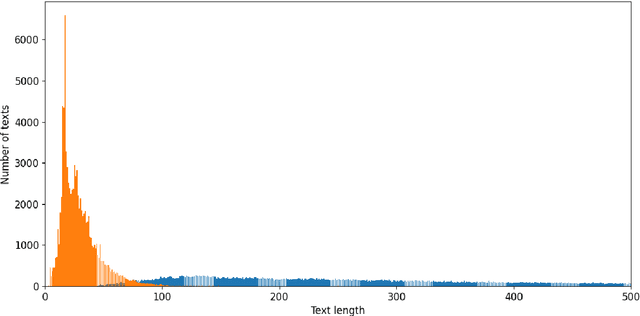
Abstract:As free online encyclopedias with massive volumes of content, Wikipedia and Wikidata are key to many Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, such as information retrieval, knowledge base building, machine translation, text classification, and text summarization. In this paper, we introduce WikiDes, a novel dataset to generate short descriptions of Wikipedia articles for the problem of text summarization. The dataset consists of over 80k English samples on 6987 topics. We set up a two-phase summarization method - description generation (Phase I) and candidate ranking (Phase II) - as a strong approach that relies on transfer and contrastive learning. For description generation, T5 and BART show their superiority compared to other small-scale pre-trained models. By applying contrastive learning with the diverse input from beam search, the metric fusion-based ranking models outperform the direct description generation models significantly up to 22 ROUGE in topic-exclusive split and topic-independent split. Furthermore, the outcome descriptions in Phase II are supported by human evaluation in over 45.33% chosen compared to 23.66% in Phase I against the gold descriptions. In the aspect of sentiment analysis, the generated descriptions cannot effectively capture all sentiment polarities from paragraphs while doing this task better from the gold descriptions. The automatic generation of new descriptions reduces the human efforts in creating them and enriches Wikidata-based knowledge graphs. Our paper shows a practical impact on Wikipedia and Wikidata since there are thousands of missing descriptions. Finally, we expect WikiDes to be a useful dataset for related works in capturing salient information from short paragraphs. The curated dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/declare-lab/WikiDes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge