Newton Howard
Dynamical Systems Analysis Reveals Functional Regimes in Large Language Models
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Large language models perform text generation through high-dimensional internal dynamics, yet the temporal organisation of these dynamics remains poorly understood. Most interpretability approaches emphasise static representations or causal interventions, leaving temporal structure largely unexplored. Drawing on neuroscience, where temporal integration and metastability are core markers of neural organisation, we adapt these concepts to transformer models and discuss a composite dynamical metric, computed from activation time-series during autoregressive generation. We evaluate this metric in GPT-2-medium across five conditions: structured reasoning, forced repetition, high-temperature noisy sampling, attention-head pruning, and weight-noise injection. Structured reasoning consistently exhibits elevated metric relative to repetitive, noisy, and perturbed regimes, with statistically significant differences confirmed by one-way ANOVA and large effect sizes in key comparisons. These results are robust to layer selection, channel subsampling, and random seeds. Our findings demonstrate that neuroscience-inspired dynamical metrics can reliably characterise differences in computational organisation across functional regimes in large language models. We stress that the proposed metric captures formal dynamical properties and does not imply subjective experience.
Advancing Neuromorphic Computing: Mixed-Signal Design Techniques Leveraging Brain Code Units and Fundamental Code Units
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a groundbreaking digital neuromorphic architecture that innovatively integrates Brain Code Unit (BCU) and Fundamental Code Unit (FCU) using mixedsignal design methodologies. Leveraging open-source datasets and the latest advances in materials science, our research focuses on enhancing the computational efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability of neuromorphic systems. The core of our approach lies in harmonizing the precision and scalability of digital systems with the robustness and energy efficiency of analog processing. Through experimentation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our system across various metrics. The BCU achieved an accuracy of 88.0% and a power efficiency of 20.0 GOP/s/W, while the FCU recorded an accuracy of 86.5% and a power efficiency of 18.5 GOP/s/W. Our mixed-signal design approach significantly improved latency and throughput, achieving a latency as low as 0.75 ms and throughput up to 213 TOP/s. These results firmly establish the potential of our architecture in neuromorphic computing, providing a solid foundation for future developments in this domain. Our study underscores the feasibility of mixedsignal neuromorphic systems and their promise in advancing the field, particularly in applications requiring high efficiency and adaptability
WikiDes: A Wikipedia-Based Dataset for Generating Short Descriptions from Paragraphs
Sep 27, 2022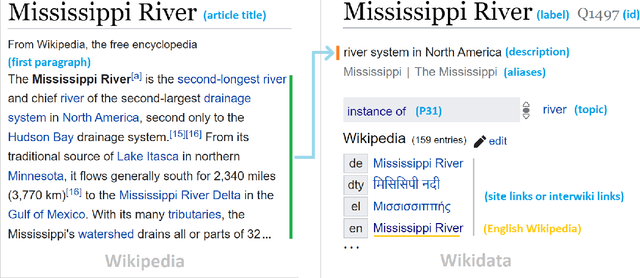
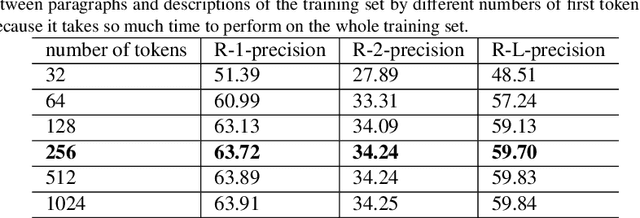
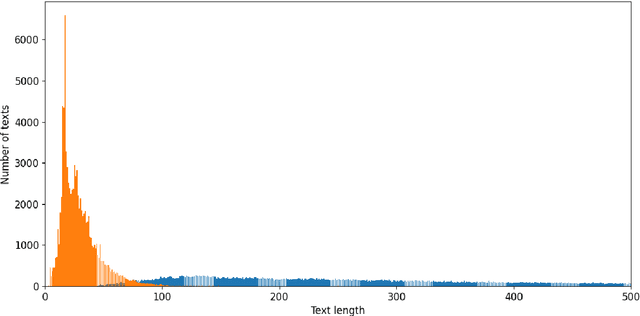
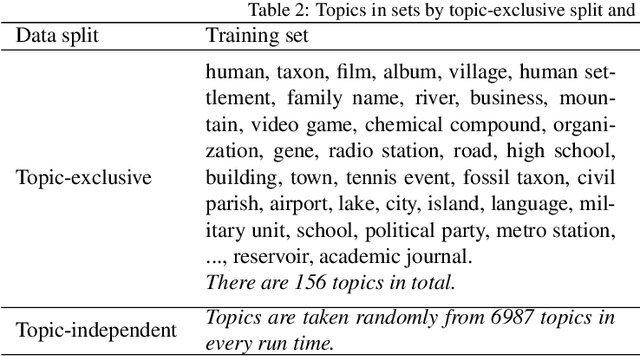
Abstract:As free online encyclopedias with massive volumes of content, Wikipedia and Wikidata are key to many Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, such as information retrieval, knowledge base building, machine translation, text classification, and text summarization. In this paper, we introduce WikiDes, a novel dataset to generate short descriptions of Wikipedia articles for the problem of text summarization. The dataset consists of over 80k English samples on 6987 topics. We set up a two-phase summarization method - description generation (Phase I) and candidate ranking (Phase II) - as a strong approach that relies on transfer and contrastive learning. For description generation, T5 and BART show their superiority compared to other small-scale pre-trained models. By applying contrastive learning with the diverse input from beam search, the metric fusion-based ranking models outperform the direct description generation models significantly up to 22 ROUGE in topic-exclusive split and topic-independent split. Furthermore, the outcome descriptions in Phase II are supported by human evaluation in over 45.33% chosen compared to 23.66% in Phase I against the gold descriptions. In the aspect of sentiment analysis, the generated descriptions cannot effectively capture all sentiment polarities from paragraphs while doing this task better from the gold descriptions. The automatic generation of new descriptions reduces the human efforts in creating them and enriches Wikidata-based knowledge graphs. Our paper shows a practical impact on Wikipedia and Wikidata since there are thousands of missing descriptions. Finally, we expect WikiDes to be a useful dataset for related works in capturing salient information from short paragraphs. The curated dataset is publicly available at: https://github.com/declare-lab/WikiDes.
Deep clustering of longitudinal data
Feb 09, 2018



Abstract:Deep neural networks are a family of computational models that have led to a dramatical improvement of the state of the art in several domains such as image, voice or text analysis. These methods provide a framework to model complex, non-linear interactions in large datasets, and are naturally suited to the analysis of hierarchical data such as, for instance, longitudinal data with the use of recurrent neural networks. In the other hand, cohort studies have become a tool of importance in the research field of epidemiology. In such studies, variables are measured repeatedly over time, to allow the practitioner to study their temporal evolution as trajectories, and, as such, as longitudinal data. This paper investigates the application of the advanced modelling techniques provided by the deep learning framework in the analysis of the longitudinal data provided by cohort studies. Methods: A method for visualizing and clustering longitudinal dataset is proposed, and compared to other widely used approaches to the problem on both real and simulated datasets. Results: The proposed method is shown to be coherent with the preexisting procedures on simple tasks, and to outperform them on more complex tasks such as the partitioning of longitudinal datasets into non-spherical clusters. Conclusion: Deep artificial neural networks can be used to visualize longitudinal data in a low dimensional manifold that is much simpler to interpret than traditional longitudinal plots are. Consequently, practitioners should start considering the use of deep artificial neural networks for the analysis of their longitudinal data in studies to come.
A new recurrent neural network based predictive model for Faecal Calprotectin analysis: A retrospective study
Dec 17, 2016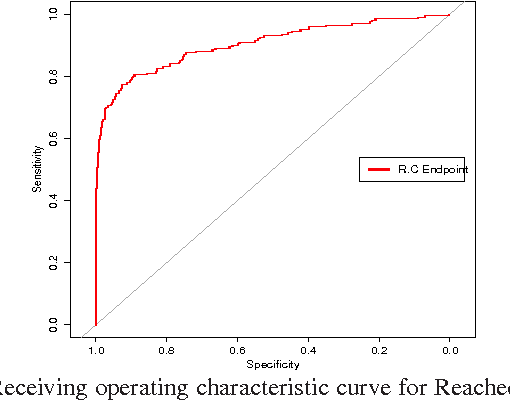
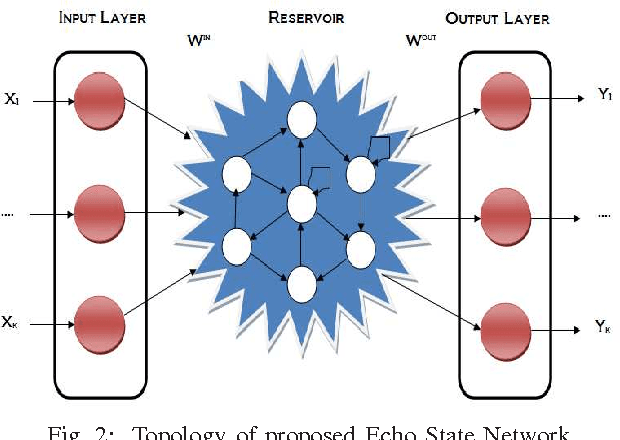
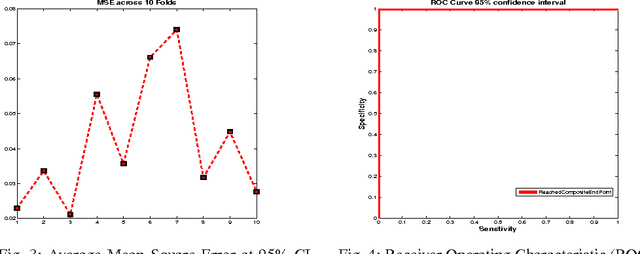
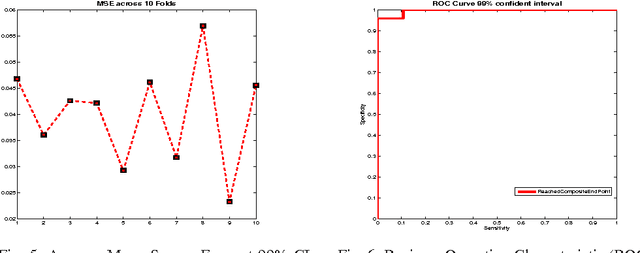
Abstract:Faecal Calprotectin (FC) is a surrogate marker for intestinal inflammation, termed Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), but not for cancer. In this retrospective study of 804 patients, an enhanced benchmark predictive model for analyzing FC is developed, based on a novel state-of-the-art Echo State Network (ESN), an advanced dynamic recurrent neural network which implements a biologically plausible architecture, and a supervised learning mechanism. The proposed machine learning driven predictive model is benchmarked against a conventional logistic regression model, demonstrating statistically significant performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge