Ziad Kobti
Comparing Reconstruction Attacks on Pretrained Versus Full Fine-tuned Large Language Model Embeddings on Homo Sapiens Splice Sites Genomic Data
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:This study investigates embedding reconstruction attacks in large language models (LLMs) applied to genomic sequences, with a specific focus on how fine-tuning affects vulnerability to these attacks. Building upon Pan et al.'s seminal work demonstrating that embeddings from pretrained language models can leak sensitive information, we conduct a comprehensive analysis using the HS3D genomic dataset to determine whether task-specific optimization strengthens or weakens privacy protections. Our research extends Pan et al.'s work in three significant dimensions. First, we apply their reconstruction attack pipeline to pretrained and fine-tuned model embeddings, addressing a critical gap in their methodology that did not specify embedding types. Second, we implement specialized tokenization mechanisms tailored specifically for DNA sequences, enhancing the model's ability to process genomic data, as these models are pretrained on natural language and not DNA. Third, we perform a detailed comparative analysis examining position-specific, nucleotide-type, and privacy changes between pretrained and fine-tuned embeddings. We assess embeddings vulnerabilities across different types and dimensions, providing deeper insights into how task adaptation shifts privacy risks throughout genomic sequences. Our findings show a clear distinction in reconstruction vulnerability between pretrained and fine-tuned embeddings. Notably, fine-tuning strengthens resistance to reconstruction attacks in multiple architectures -- XLNet (+19.8\%), GPT-2 (+9.8\%), and BERT (+7.8\%) -- pointing to task-specific optimization as a potential privacy enhancement mechanism. These results highlight the need for advanced protective mechanisms for language models processing sensitive genomic data, while highlighting fine-tuning as a potential privacy-enhancing technique worth further exploration.
A Multi-Task Learning Framework for COVID-19 Monitoring and Prediction of PPE Demand in Community Health Centres
Aug 20, 2021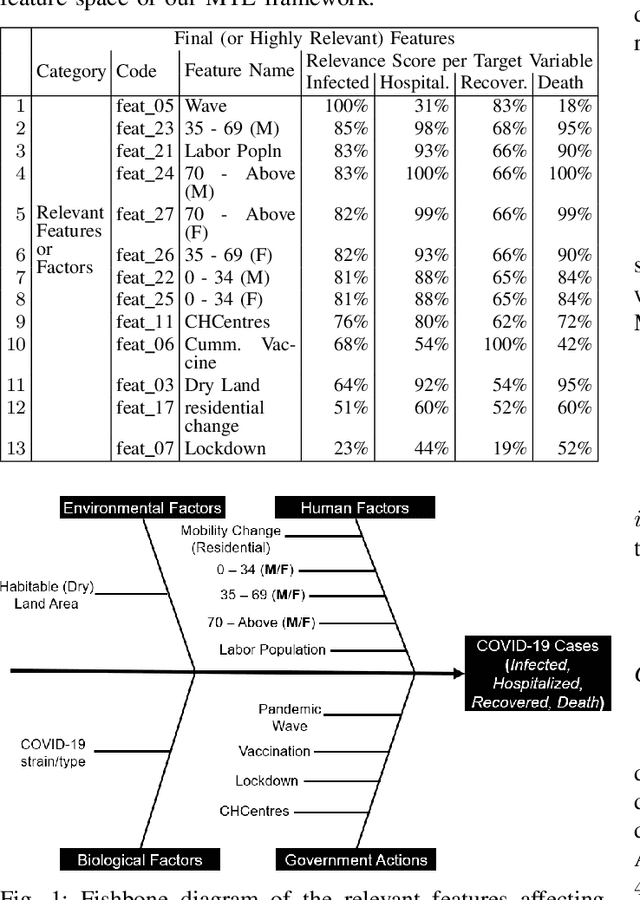
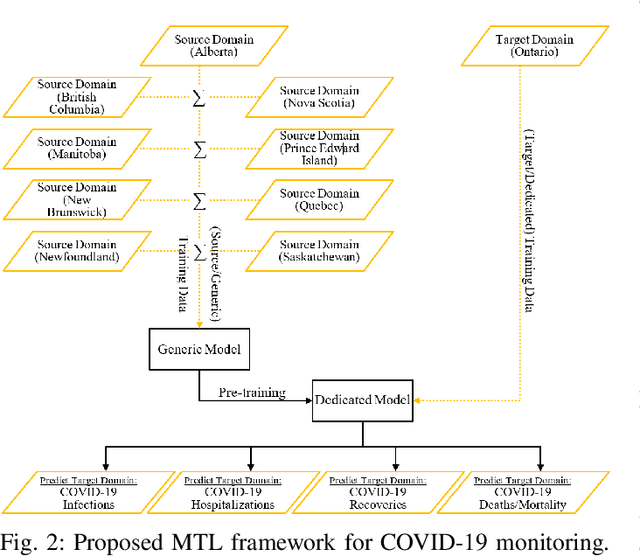
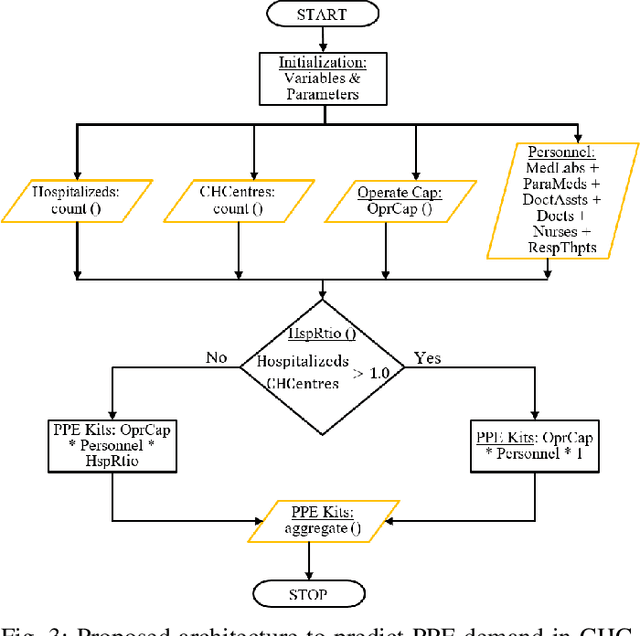
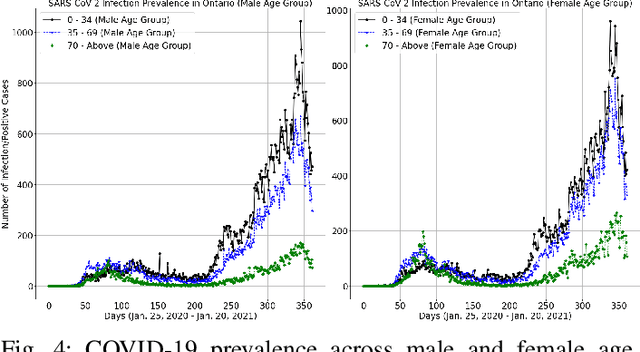
Abstract:Currently, the world seeks to find appropriate mitigation techniques to control and prevent the spread of the new SARS-CoV-2. In our paper herein, we present a peculiar Multi-Task Learning framework that jointly predicts the effect of SARS-CoV-2 as well as Personal-Protective-Equipment consumption in Community Health Centres for a given populace. Predicting the effect of the virus (SARS-CoV-2), via studies and analyses, enables us to understand the nature of SARS-CoV- 2 with reference to factors that promote its growth and spread. Therefore, these foster widespread awareness; and the populace can become more proactive and cautious so as to mitigate the spread of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID- 19). Furthermore, understanding and predicting the demand for Personal Protective Equipment promotes the efficiency and safety of healthcare workers in Community Health Centres. Owing to the novel nature and strains of SARS-CoV-2, relatively few literature and research exist in this regard. These existing literature have attempted to solve the problem statement(s) using either Agent-based Models, Machine Learning Models, or Mathematical Models. In view of this, our work herein adds to existing literature via modeling our problem statements as Multi- Task Learning problems. Results from our research indicate that government actions and human factors are the most significant determinants that influence the spread of SARS-CoV-2.
A new recurrent neural network based predictive model for Faecal Calprotectin analysis: A retrospective study
Dec 17, 2016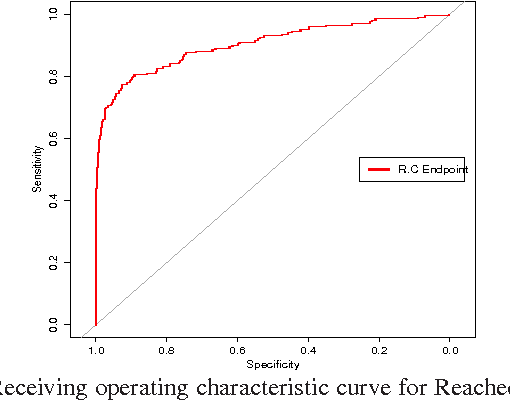
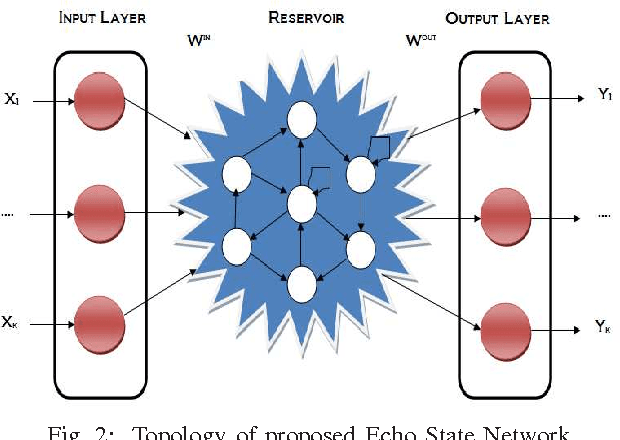
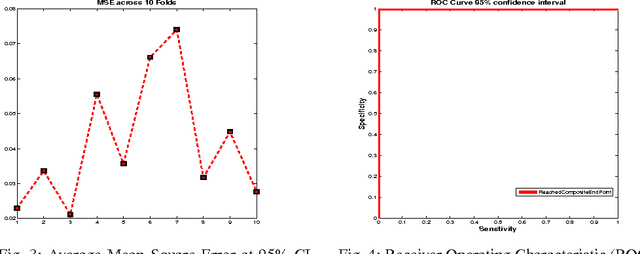
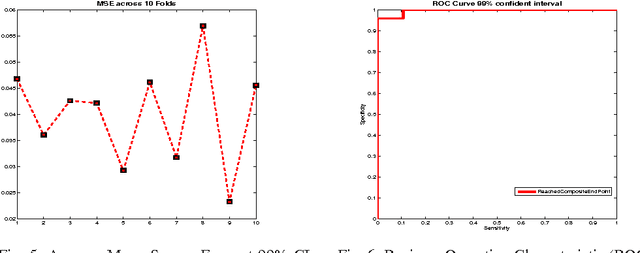
Abstract:Faecal Calprotectin (FC) is a surrogate marker for intestinal inflammation, termed Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), but not for cancer. In this retrospective study of 804 patients, an enhanced benchmark predictive model for analyzing FC is developed, based on a novel state-of-the-art Echo State Network (ESN), an advanced dynamic recurrent neural network which implements a biologically plausible architecture, and a supervised learning mechanism. The proposed machine learning driven predictive model is benchmarked against a conventional logistic regression model, demonstrating statistically significant performance improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge