Segun Taofeek Aroyehun
A multitask learning framework for leveraging subjectivity of annotators to identify misogyny
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Identifying misogyny using artificial intelligence is a form of combating online toxicity against women. However, the subjective nature of interpreting misogyny poses a significant challenge to model the phenomenon. In this paper, we propose a multitask learning approach that leverages the subjectivity of this task to enhance the performance of the misogyny identification systems. We incorporated diverse perspectives from annotators in our model design, considering gender and age across six profile groups, and conducted extensive experiments and error analysis using two language models to validate our four alternative designs of the multitask learning technique to identify misogynistic content in English tweets. The results demonstrate that incorporating various viewpoints enhances the language models' ability to interpret different forms of misogyny. This research advances content moderation and highlights the importance of embracing diverse perspectives to build effective online moderation systems.
LEIA: Linguistic Embeddings for the Identification of Affect
Apr 21, 2023Abstract:The wealth of text data generated by social media has enabled new kinds of analysis of emotions with language models. These models are often trained on small and costly datasets of text annotations produced by readers who guess the emotions expressed by others in social media posts. This affects the quality of emotion identification methods due to training data size limitations and noise in the production of labels used in model development. We present LEIA, a model for emotion identification in text that has been trained on a dataset of more than 6 million posts with self-annotated emotion labels for happiness, affection, sadness, anger, and fear. LEIA is based on a word masking method that enhances the learning of emotion words during model pre-training. LEIA achieves macro-F1 values of approximately 73 on three in-domain test datasets, outperforming other supervised and unsupervised methods in a strong benchmark that shows that LEIA generalizes across posts, users, and time periods. We further perform an out-of-domain evaluation on five different datasets of social media and other sources, showing LEIA's robust performance across media, data collection methods, and annotation schemes. Our results show that LEIA generalizes its classification of anger, happiness, and sadness beyond the domain it was trained on. LEIA can be applied in future research to provide better identification of emotions in text from the perspective of the writer. The models produced for this article are publicly available at https://huggingface.co/LEIA
NLP-CIC @ PRELEARN: Mastering prerequisites relations, from handcrafted features to embeddings
Nov 07, 2020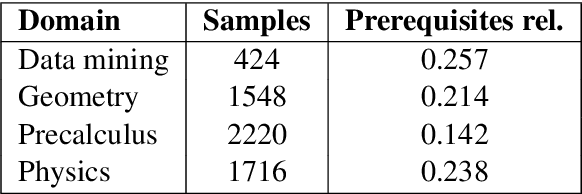
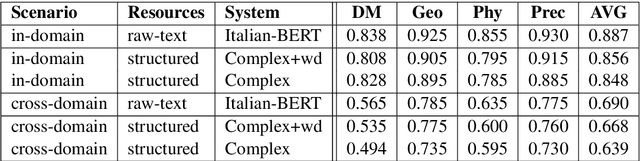
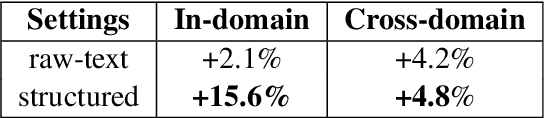
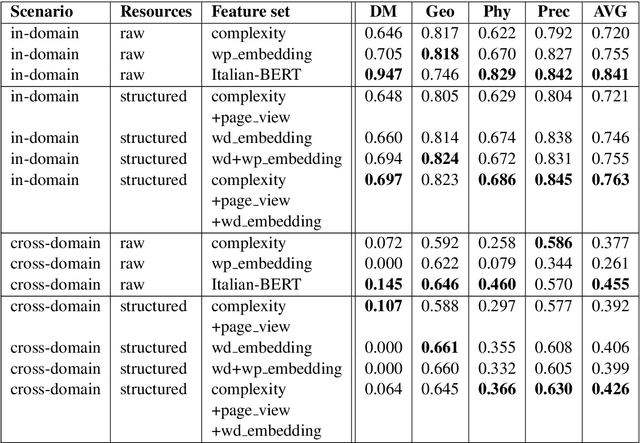
Abstract:We present our systems and findings for the prerequisite relation learning task (PRELEARN) at EVALITA 2020. The task aims to classify whether a pair of concepts hold a prerequisite relation or not. We model the problem using handcrafted features and embedding representations for in-domain and cross-domain scenarios. Our submissions ranked first place in both scenarios with average F1 score of 0.887 and 0.690 respectively across domains on the test sets. We made our code is freely available.
NLP-CIC at SemEval-2020 Task 9: Analysing sentiment in code-switching language using a simple deep-learning classifier
Sep 07, 2020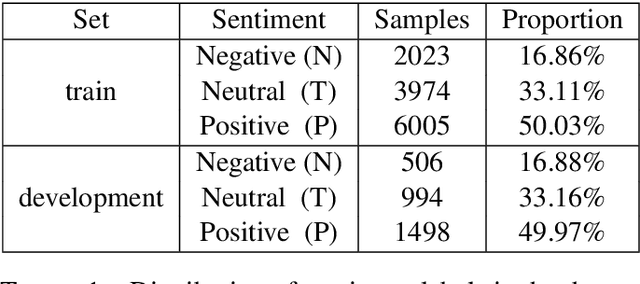
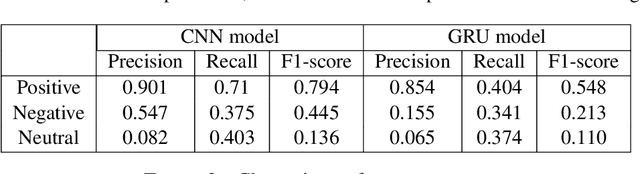
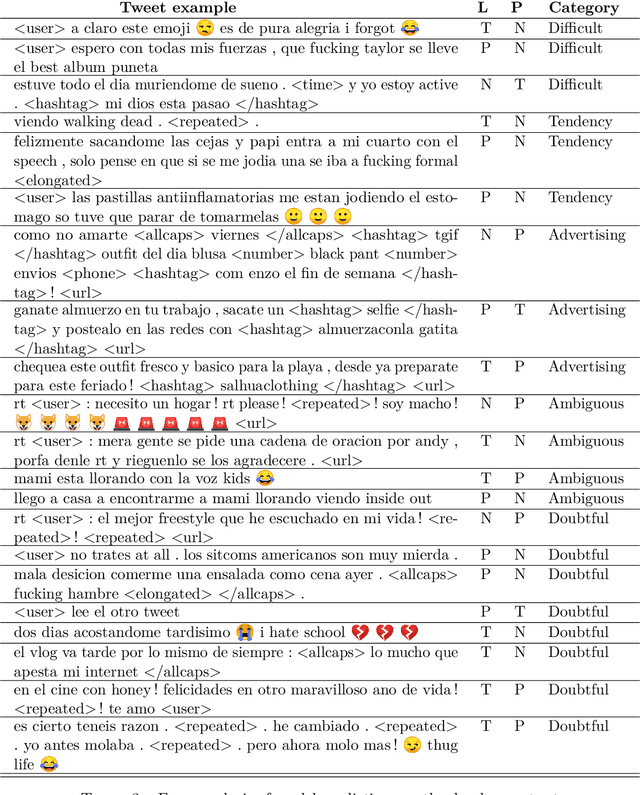
Abstract:Code-switching is a phenomenon in which two or more languages are used in the same message. Nowadays, it is quite common to find messages with languages mixed in social media. This phenomenon presents a challenge for sentiment analysis. In this paper, we use a standard convolutional neural network model to predict the sentiment of tweets in a blend of Spanish and English languages. Our simple approach achieved a F1-score of 0.71 on test set on the competition. We analyze our best model capabilities and perform error analysis to expose important difficulties for classifying sentiment in a code-switching setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge