Alay Dilipbhai Shah
Alopex: A Computational Framework for Enabling On-Device Function Calls with LLMs
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to their increased integration into mobile devices for personalized assistance, which enables LLMs to call external API functions to enhance their performance. However, challenges such as data scarcity, ineffective question formatting, and catastrophic forgetting hinder the development of on-device LLM agents. To tackle these issues, we propose Alopex, a framework that enables precise on-device function calls using the Fox LLM. Alopex introduces a logic-based method for generating high-quality training data and a novel ``description-question-output'' format for fine-tuning, reducing risks of function information leakage. Additionally, a data mixing strategy is used to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, combining function call data with textbook datasets to enhance performance in various tasks. Experimental results show that Alopex improves function call accuracy and significantly reduces catastrophic forgetting, providing a robust solution for integrating function call capabilities into LLMs without manual intervention.
PolyRouter: A Multi-LLM Querying System
Aug 26, 2024



Abstract:With the rapid growth of Large Language Models (LLMs) across various domains, numerous new LLMs have emerged, each possessing domain-specific expertise. This proliferation has highlighted the need for quick, high-quality, and cost-effective LLM query response methods. Yet, no single LLM exists to efficiently balance this trilemma. Some models are powerful but extremely costly, while others are fast and inexpensive but qualitatively inferior. To address this challenge, we present PolyRouter, a non-monolithic LLM querying system that seamlessly integrates various LLM experts into a single query interface and dynamically routes incoming queries to the most high-performant expert based on query's requirements. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that when compared to standalone expert models, PolyRouter improves query efficiency by up to 40%, and leads to significant cost reductions of up to 30%, while maintaining or enhancing model performance by up to 10%.
ScaleLLM: A Resource-Frugal LLM Serving Framework by Optimizing End-to-End Efficiency
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have surged in popularity and are extensively used in commercial applications, where the efficiency of model serving is crucial for the user experience. Most current research focuses on optimizing individual sub-procedures, e.g. local inference and communication, however, there is no comprehensive framework that provides a holistic system view for optimizing LLM serving in an end-to-end manner. In this work, we conduct a detailed analysis to identify major bottlenecks that impact end-to-end latency in LLM serving systems. Our analysis reveals that a comprehensive LLM serving endpoint must address a series of efficiency bottlenecks that extend beyond LLM inference. We then propose ScaleLLM, an optimized system for resource-efficient LLM serving. Our extensive experiments reveal that with 64 concurrent requests, ScaleLLM achieves a 4.3x speed up over vLLM and outperforms state-of-the-arts with 1.5x higher throughput.
FedCV: A Federated Learning Framework for Diverse Computer Vision Tasks
Nov 22, 2021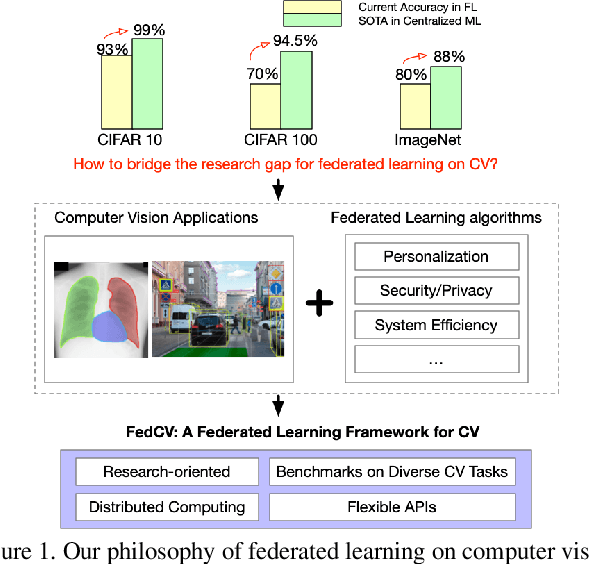
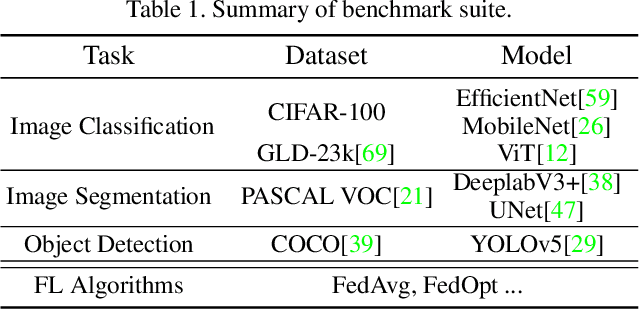
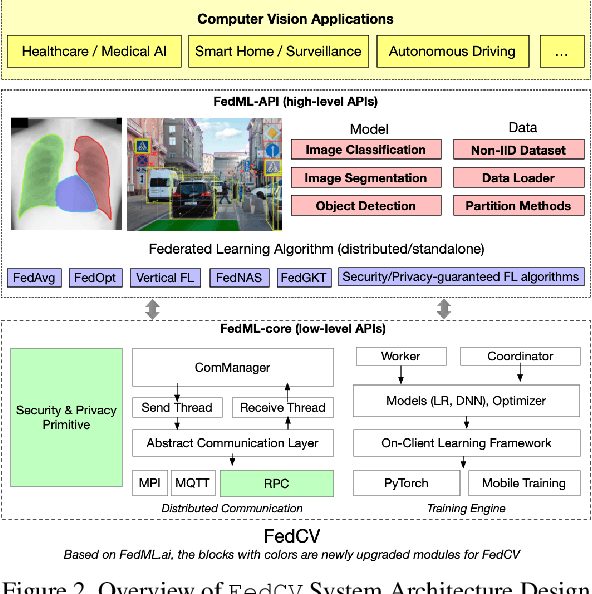
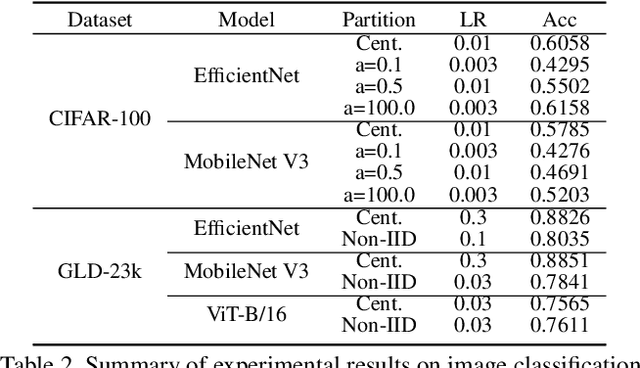
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a distributed learning paradigm that can learn a global or personalized model from decentralized datasets on edge devices. However, in the computer vision domain, model performance in FL is far behind centralized training due to the lack of exploration in diverse tasks with a unified FL framework. FL has rarely been demonstrated effectively in advanced computer vision tasks such as object detection and image segmentation. To bridge the gap and facilitate the development of FL for computer vision tasks, in this work, we propose a federated learning library and benchmarking framework, named FedCV, to evaluate FL on the three most representative computer vision tasks: image classification, image segmentation, and object detection. We provide non-I.I.D. benchmarking datasets, models, and various reference FL algorithms. Our benchmark study suggests that there are multiple challenges that deserve future exploration: centralized training tricks may not be directly applied to FL; the non-I.I.D. dataset actually downgrades the model accuracy to some degree in different tasks; improving the system efficiency of federated training is challenging given the huge number of parameters and the per-client memory cost. We believe that such a library and benchmark, along with comparable evaluation settings, is necessary to make meaningful progress in FL on computer vision tasks. FedCV is publicly available: https://github.com/FedML-AI/FedCV.
Predicting Future Sales of Retail Products using Machine Learning
Aug 18, 2020


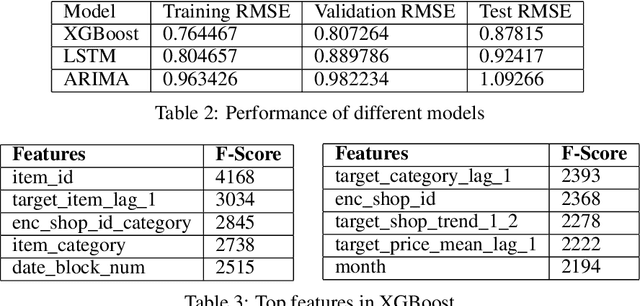
Abstract:Techniques for making future predictions based upon the present and past data, has always been an area with direct application to various real life problems. We are discussing a similar problem in this paper. The problem statement is provided by Kaggle, which also serves as an ongoing competition on the Kaggle platform. In this project, we worked with a challenging time-series dataset consisting of daily sales data, kindly provided by one of the largest Russian software firms - 1C Company. The objective is to predict the total sales for every product and store in the next month given the past data. In order to perform forecasting for next month, we have deployed eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) based network architecture to perform learning task. Root mean squared error (RMSE) between the actual and predicted target values is used to evaluate the performance, and make comparisons between the deployed algorithms. It has been found that XGBoost fared better than LSTM over this dataset which can be attributed to its relatively higher sparsity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge