Abdelrahman Boda Sadallah
Benchmarking Uncertainty Quantification Methods for Large Language Models with LM-Polygraph
Jun 21, 2024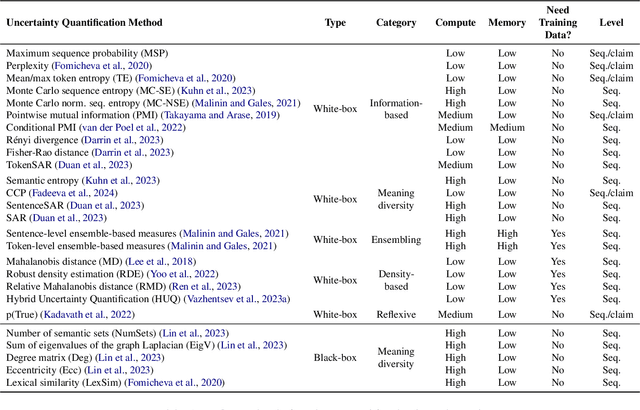
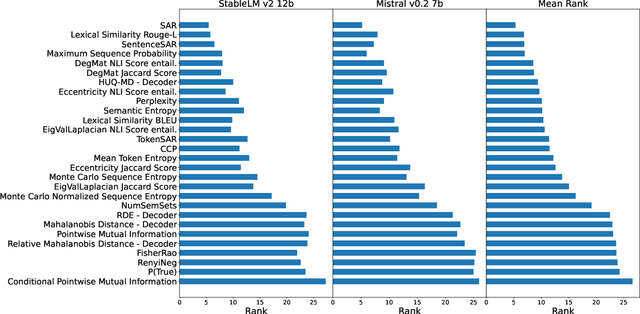
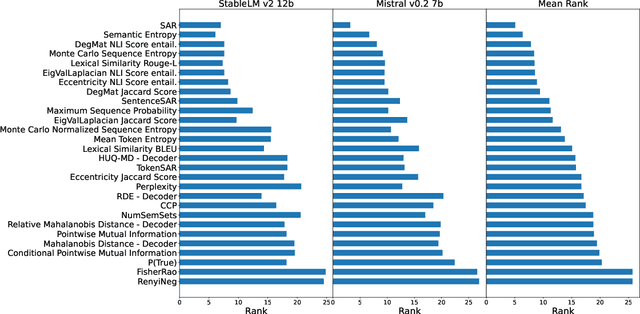
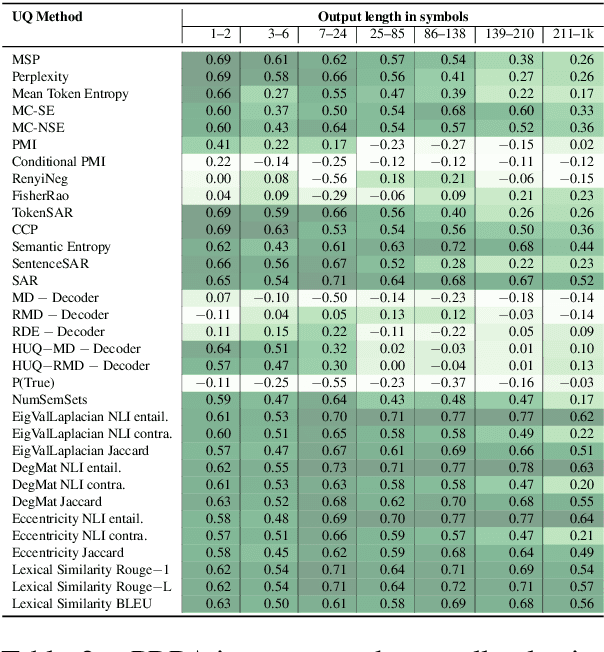
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is becoming increasingly recognized as a critical component of applications that rely on machine learning (ML). The rapid proliferation of large language models (LLMs) has stimulated researchers to seek efficient and effective approaches to UQ in text generation tasks, as in addition to their emerging capabilities, these models have introduced new challenges for building safe applications. As with other ML models, LLMs are prone to make incorrect predictions, ``hallucinate'' by fabricating claims, or simply generate low-quality output for a given input. UQ is a key element in dealing with these challenges. However research to date on UQ methods for LLMs has been fragmented, with disparate evaluation methods. In this work, we tackle this issue by introducing a novel benchmark that implements a collection of state-of-the-art UQ baselines, and provides an environment for controllable and consistent evaluation of novel techniques by researchers in various text generation tasks. Our benchmark also supports the assessment of confidence normalization methods in terms of their ability to provide interpretable scores. Using our benchmark, we conduct a large-scale empirical investigation of UQ and normalization techniques across nine tasks and shed light on the most promising approaches.
ArabicMMLU: Assessing Massive Multitask Language Understanding in Arabic
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:The focus of language model evaluation has transitioned towards reasoning and knowledge-intensive tasks, driven by advancements in pretraining large models. While state-of-the-art models are partially trained on large Arabic texts, evaluating their performance in Arabic remains challenging due to the limited availability of relevant datasets. To bridge this gap, we present ArabicMMLU, the first multi-task language understanding benchmark for Arabic language, sourced from school exams across diverse educational levels in different countries spanning North Africa, the Levant, and the Gulf regions. Our data comprises 40 tasks and 14,575 multiple-choice questions in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), and is carefully constructed by collaborating with native speakers in the region. Our comprehensive evaluations of 35 models reveal substantial room for improvement, particularly among the best open-source models. Notably, BLOOMZ, mT0, LLama2, and Falcon struggle to achieve a score of 50%, while even the top-performing Arabic-centric model only achieves a score of 62.3%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge