Benchmarking Uncertainty Quantification Methods for Large Language Models with LM-Polygraph
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2024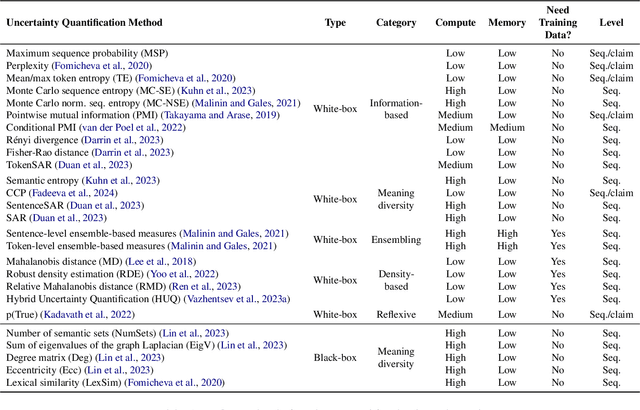
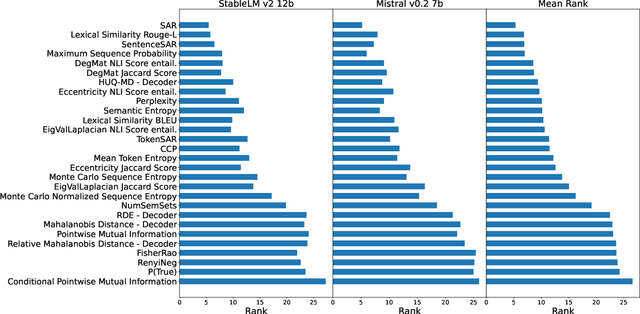
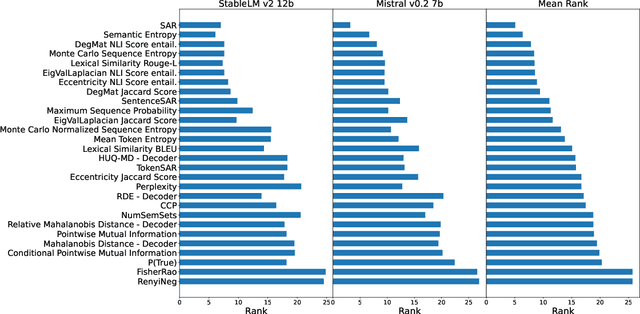
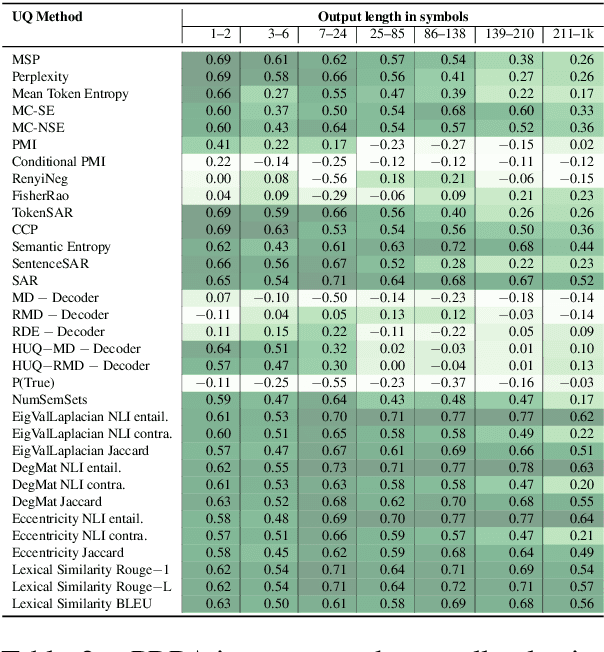
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is becoming increasingly recognized as a critical component of applications that rely on machine learning (ML). The rapid proliferation of large language models (LLMs) has stimulated researchers to seek efficient and effective approaches to UQ in text generation tasks, as in addition to their emerging capabilities, these models have introduced new challenges for building safe applications. As with other ML models, LLMs are prone to make incorrect predictions, ``hallucinate'' by fabricating claims, or simply generate low-quality output for a given input. UQ is a key element in dealing with these challenges. However research to date on UQ methods for LLMs has been fragmented, with disparate evaluation methods. In this work, we tackle this issue by introducing a novel benchmark that implements a collection of state-of-the-art UQ baselines, and provides an environment for controllable and consistent evaluation of novel techniques by researchers in various text generation tasks. Our benchmark also supports the assessment of confidence normalization methods in terms of their ability to provide interpretable scores. Using our benchmark, we conduct a large-scale empirical investigation of UQ and normalization techniques across nine tasks and shed light on the most promising approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge