precipitation Downscaling
Papers and Code
Extreme Event Aware ($η$-) Learning
Oct 22, 2025Quantifying and predicting rare and extreme events persists as a crucial yet challenging task in understanding complex dynamical systems. Many practical challenges arise from the infrequency and severity of these events, including the considerable variance of simple sampling methods and the substantial computational cost of high-fidelity numerical simulations. Numerous data-driven methods have recently been developed to tackle these challenges. However, a typical assumption for the success of these methods is the occurrence of multiple extreme events, either within the training dataset or during the sampling process. This leads to accurate models in regions of quiescent events but with high epistemic uncertainty in regions associated with extremes. To overcome this limitation, we introduce Extreme Event Aware (e2a or eta) or $\eta$-learning which does not assume the existence of extreme events in the available data. $\eta$-learning reduces the uncertainty even in `uncharted' extreme event regions, by enforcing the extreme event statistics of an observable indicative of extremeness during training, which can be available through qualitative arguments or estimated with unlabeled data. This type of statistical regularization results in models that fit the observed data, while enforcing consistency with the prescribed observable statistics, enabling the generation of unprecedented extreme events even when the training data lack extremes therein. Theoretical results based on optimal transport offer a rigorous justification and highlight the optimality of the introduced method. Additionally, extensive numerical experiments illustrate the favorable properties of the $\eta$-learning framework on several prototype problems and real-world precipitation downscaling problems.
Wasserstein GAN-Based Precipitation Downscaling with Optimal Transport for Enhancing Perceptual Realism
Jul 23, 2025High-resolution (HR) precipitation prediction is essential for reducing damage from stationary and localized heavy rainfall; however, HR precipitation forecasts using process-driven numerical weather prediction models remains challenging. This study proposes using Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network (WGAN) to perform precipitation downscaling with an optimal transport cost. In contrast to a conventional neural network trained with mean squared error, the WGAN generated visually realistic precipitation fields with fine-scale structures even though the WGAN exhibited slightly lower performance on conventional evaluation metrics. The learned critic of WGAN correlated well with human perceptual realism. Case-based analysis revealed that large discrepancies in critic scores can help identify both unrealistic WGAN outputs and potential artifacts in the reference data. These findings suggest that the WGAN framework not only improves perceptual realism in precipitation downscaling but also offers a new perspective for evaluating and quality-controlling precipitation datasets.
Efficient Kilometer-Scale Precipitation Downscaling with Conditional Wavelet Diffusion
Jul 02, 2025


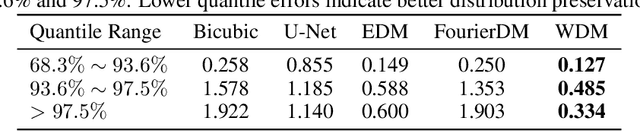
Effective hydrological modeling and extreme weather analysis demand precipitation data at a kilometer-scale resolution, which is significantly finer than the 10 km scale offered by standard global products like IMERG. To address this, we propose the Wavelet Diffusion Model (WDM), a generative framework that achieves 10x spatial super-resolution (downscaling to 1 km) and delivers a 9x inference speedup over pixel-based diffusion models. WDM is a conditional diffusion model that learns the learns the complex structure of precipitation from MRMS radar data directly in the wavelet domain. By focusing on high-frequency wavelet coefficients, it generates exceptionally realistic and detailed 1-km precipitation fields. This wavelet-based approach produces visually superior results with fewer artifacts than pixel-space models, and delivers a significant gains in sampling efficiency. Our results demonstrate that WDM provides a robust solution to the dual challenges of accuracy and speed in geoscience super-resolution, paving the way for more reliable hydrological forecasts.
Rainy: Unlocking Satellite Calibration for Deep Learning in Precipitation
Apr 15, 2025Precipitation plays a critical role in the Earth's hydrological cycle, directly affecting ecosystems, agriculture, and water resource management. Accurate precipitation estimation and prediction are crucial for understanding climate dynamics, disaster preparedness, and environmental monitoring. In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has gained increasing attention in quantitative remote sensing (QRS), enabling more advanced data analysis and improving precipitation estimation accuracy. Although traditional methods have been widely used for precipitation estimation, they face limitations due to the difficulty of data acquisition and the challenge of capturing complex feature relationships. Furthermore, the lack of standardized multi-source satellite datasets, and in most cases, the exclusive reliance on station data, significantly hinders the effective application of advanced AI models. To address these challenges, we propose the Rainy dataset, a multi-source spatio-temporal dataset that integrates pure satellite data with station data, and propose Taper Loss, designed to fill the gap in tasks where only in-situ data is available without area-wide support. The Rainy dataset supports five main tasks: (1) satellite calibration, (2) precipitation event prediction, (3) precipitation level prediction, (4) spatiotemporal prediction, and (5) precipitation downscaling. For each task, we selected benchmark models and evaluation metrics to provide valuable references for researchers. Using precipitation as an example, the Rainy dataset and Taper Loss demonstrate the seamless collaboration between QRS and computer vision, offering data support for AI for Science in the field of QRS and providing valuable insights for interdisciplinary collaboration and integration.
RainScaleGAN: a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Rainfall Downscaling
Mar 17, 2025To this day, accurately simulating local-scale precipitation and reliably reproducing its distribution remains a challenging task. The limited horizontal resolution of Global Climate Models is among the primary factors undermining their skill in this context. The physical mechanisms driving the onset and development of precipitation, especially in extreme events, operate at spatio-temporal scales smaller than those numerically resolved, thus struggling to be captured accurately. In order to circumvent this limitation, several downscaling approaches have been developed over the last decades to address the discrepancy between the spatial resolution of models output and the resolution required by local-scale applications. In this paper, we introduce RainScaleGAN, a conditional deep convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) for precipitation downscaling. GANs have been effectively used in image super-resolution, an approach highly relevant for downscaling tasks. RainScaleGAN's capabilities are tested in a perfect-model setup, where the spatial resolution of a precipitation dataset is artificially degraded from 0.25$^{\circ}\times$0.25$^{\circ}$ to 2$^{\circ}\times$2$^\circ$, and RainScaleGAN is used to restore it. The developed model outperforms one of the leading precipitation downscaling method found in the literature. RainScaleGAN not only generates a synthetic dataset featuring plausible high-resolution spatial patterns and intensities, but also produces a precipitation distribution with statistics closely mirroring those of the ground-truth dataset. Given that RainScaleGAN's approach is agnostic with respect to the underlying physics, the method has the potential to be applied to other physical variables such as surface winds or temperature.
Downscaling Precipitation with Bias-informed Conditional Diffusion Model
Dec 19, 2024

Climate change is intensifying rainfall extremes, making high-resolution precipitation projections crucial for society to better prepare for impacts such as flooding. However, current Global Climate Models (GCMs) operate at spatial resolutions too coarse for localized analyses. To address this limitation, deep learning-based statistical downscaling methods offer promising solutions, providing high-resolution precipitation projections with a moderate computational cost. In this work, we introduce a bias-informed conditional diffusion model for statistical downscaling of precipitation. Specifically, our model leverages a conditional diffusion approach to learn distribution priors from large-scale, high-resolution precipitation datasets. The long-tail distribution of precipitation poses a unique challenge for training diffusion models; to address this, we apply gamma correction during preprocessing. Additionally, to correct biases in the downscaled results, we employ a guided-sampling strategy to enhance bias correction. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves highly accurate results in an 8 times downscaling setting, outperforming previous deterministic methods. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/RoseLV/research_super-resolution
Continuous latent representations for modeling precipitation with deep learning
Dec 19, 2024The sparse and spatio-temporally discontinuous nature of precipitation data presents significant challenges for simulation and statistical processing for bias correction and downscaling. These include incorrect representation of intermittency and extreme values (critical for hydrology applications), Gibbs phenomenon upon regridding, and lack of fine scales details. To address these challenges, a common approach is to transform the precipitation variable nonlinearly into one that is more malleable. In this work, we explore how deep learning can be used to generate a smooth, spatio-temporally continuous variable as a proxy for simulation of precipitation data. We develop a normally distributed field called pseudo-precipitation (PP) as an alternative for simulating precipitation. The practical applicability of this variable is investigated by applying it for downscaling precipitation from \(1\degree\) (\(\sim\) 100 km) to \(0.25\degree\) (\(\sim\) 25 km).
PrecipDiff: Leveraging image diffusion models to enhance satellite-based precipitation observations
Jan 13, 2025



A recent report from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) highlights that water-related disasters have caused the highest human losses among natural disasters over the past 50 years, with over 91\% of deaths occurring in low-income countries. This disparity is largely due to the lack of adequate ground monitoring stations, such as weather surveillance radars (WSR), which are expensive to install. For example, while the US and Europe combined possess over 600 WSRs, Africa, despite having almost one and half times their landmass, has fewer than 40. To address this issue, satellite-based observations offer a global, near-real-time monitoring solution. However, they face several challenges like accuracy, bias, and low spatial resolution. This study leverages the power of diffusion models and residual learning to address these limitations in a unified framework. We introduce the first diffusion model for correcting the inconsistency between different precipitation products. Our method demonstrates the effectiveness in downscaling satellite precipitation estimates from 10 km to 1 km resolution. Extensive experiments conducted in the Seattle region demonstrate significant improvements in accuracy, bias reduction, and spatial detail. Importantly, our approach achieves these results using only precipitation data, showcasing the potential of a purely computer vision-based approach for enhancing satellite precipitation products and paving the way for further advancements in this domain.
Global spatio-temporal downscaling of ERA5 precipitation through generative AI
Nov 22, 2024The spatial and temporal distribution of precipitation has a significant impact on human lives by determining freshwater resources and agricultural yield, but also rainfall-driven hazards like flooding or landslides. While the ERA5 reanalysis dataset provides consistent long-term global precipitation information that allows investigations of these impacts, it lacks the resolution to capture the high spatio-temporal variability of precipitation. ERA5 misses intense local rainfall events that are crucial drivers of devastating flooding - a critical limitation since extreme weather events become increasingly frequent. Here, we introduce spateGAN-ERA5, the first deep learning based spatio-temporal downscaling of precipitation data on a global scale. SpateGAN-ERA5 uses a conditional generative adversarial neural network (cGAN) that enhances the resolution of ERA5 precipitation data from 24 km and 1 hour to 2 km and 10 minutes, delivering high-resolution rainfall fields with realistic spatio-temporal patterns and accurate rain rate distribution including extremes. Its computational efficiency enables the generation of a large ensemble of solutions, addressing uncertainties inherent to the challenges of downscaling. Trained solely on data from Germany and validated in the US and Australia considering diverse climate zones, spateGAN-ERA5 demonstrates strong generalization indicating a robust global applicability. SpateGAN-ERA5 fulfils a critical need for high-resolution precipitation data in hydrological and meteorological research, offering new capabilities for flood risk assessment, AI-enhanced weather forecasting, and impact modelling to address climate-driven challenges worldwide.
Refined climatologies of future precipitation over High Mountain Asia using probabilistic ensemble learning
Jan 26, 2025High Mountain Asia holds the largest concentration of frozen water outside the polar regions, serving as a crucial water source for more than 1.9 billion people. In the face of climate change, precipitation represents the largest source of uncertainty for hydrological modelling in this area. Future precipitation predictions remain challenging due to complex orography, lack of in situ hydrological observations, and limitations in climate model resolution and parametrisation for this region. To address the uncertainty posed by these challenges, climate models are often aggregated into multi-model ensembles. While multi-model ensembles are known to improve the predictive accuracy and analysis of future climate projections, consensus regarding how models are aggregated is lacking. In this study, we propose a probabilistic machine learning framework to systematically combine 13 regional climate models from the Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX) over High Mountain Asia. Our approach accounts for seasonal and spatial biases within the models, enabling the prediction of more faithful precipitation distributions. The framework is validated against gridded historical precipitation data and is used to generate projections for the near-future (2036-2065) and far-future (2066-2095) under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge