Zongsheng Wang
RAIDEN-R1: Improving Role-awareness of LLMs via GRPO with Verifiable Reward
May 15, 2025Abstract:Role-playing conversational agents (RPCAs) face persistent challenges in maintaining role consistency. To address this, we propose RAIDEN-R1, a novel reinforcement learning framework that integrates Verifiable Role-Awareness Reward (VRAR). The method introduces both singular and multi-term mining strategies to generate quantifiable rewards by assessing role-specific keys. Additionally, we construct a high-quality, role-aware Chain-of-Thought dataset through multi-LLM collaboration, and implement experiments to enhance reasoning coherence. Experiments on the RAIDEN benchmark demonstrate RAIDEN-R1's superiority: our 14B-GRPO model achieves 88.04% and 88.65% accuracy on Script-Based Knowledge and Conversation Memory metrics, respectively, outperforming baseline models while maintaining robustness. Case analyses further reveal the model's enhanced ability to resolve conflicting contextual cues and sustain first-person narrative consistency. This work bridges the non-quantifiability gap in RPCA training and provides insights into role-aware reasoning patterns, advancing the development of RPCAs.
MVQ:Towards Efficient DNN Compression and Acceleration with Masked Vector Quantization
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Vector quantization(VQ) is a hardware-friendly DNN compression method that can reduce the storage cost and weight-loading datawidth of hardware accelerators. However, conventional VQ techniques lead to significant accuracy loss because the important weights are not well preserved. To tackle this problem, a novel approach called MVQ is proposed, which aims at better approximating important weights with a limited number of codewords. At the algorithm level, our approach removes the less important weights through N:M pruning and then minimizes the vector clustering error between the remaining weights and codewords by the masked k-means algorithm. Only distances between the unpruned weights and the codewords are computed, which are then used to update the codewords. At the architecture level, our accelerator implements vector quantization on an EWS (Enhanced weight stationary) CNN accelerator and proposes a sparse systolic array design to maximize the benefits brought by masked vector quantization.\\ Our algorithm is validated on various models for image classification, object detection, and segmentation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that MVQ not only outperforms conventional vector quantization methods at comparable compression ratios but also reduces FLOPs. Under ASIC evaluation, our MVQ accelerator boosts energy efficiency by 2.3$\times$ and reduces the size of the systolic array by 55\% when compared with the base EWS accelerator. Compared to the previous sparse accelerators, MVQ achieves 1.73$\times$ higher energy efficiency.
An Ultra Fast Low Power Convolutional Neural Network Image Sensor with Pixel-level Computing
Jan 09, 2021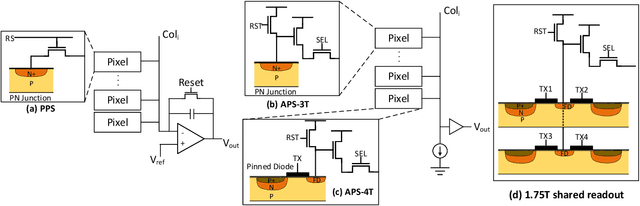
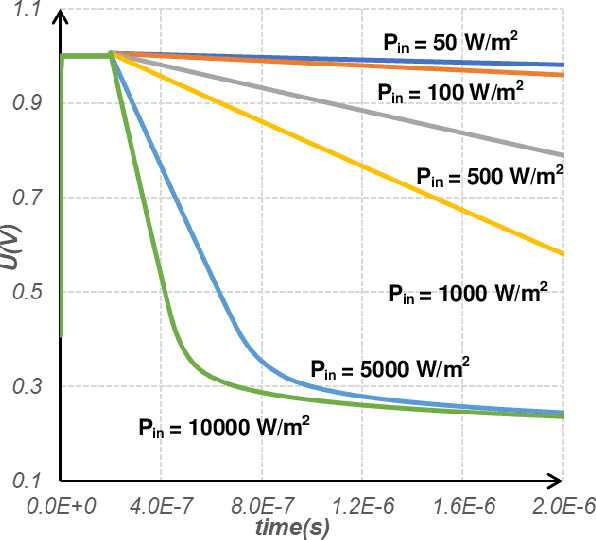
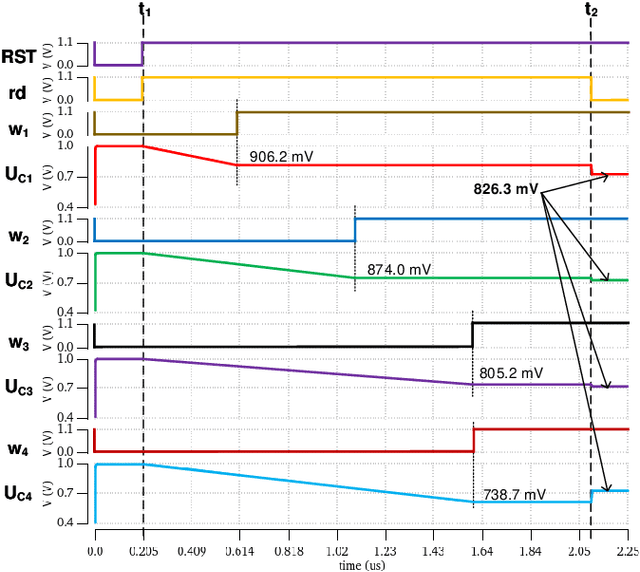
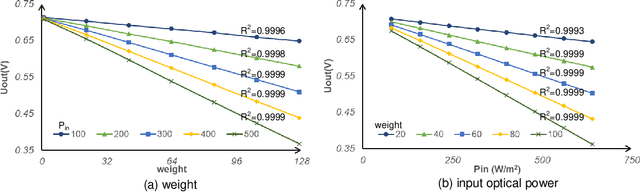
Abstract:The separation of the data capture and analysis in modern vision systems has led to a massive amount of data transfer between the end devices and cloud computers, resulting in long latency, slow response, and high power consumption. Efficient hardware architectures are under focused development to enable Artificial Intelligence (AI) at the resource-limited end sensing devices. This paper proposes a Processing-In-Pixel (PIP) CMOS sensor architecture, which allows convolution operation before the column readout circuit to significantly improve the image reading speed with much lower power consumption. The simulation results show that the proposed architecture enables convolution operation (kernel size=3*3, stride=2, input channel=3, output channel=64) in a 1080P image sensor array with only 22.62 mW power consumption. In other words, the computational efficiency is 4.75 TOPS/w, which is about 3.6 times as higher as the state-of-the-art.
Towards Non-task-specific Distillation of BERT via Sentence Representation Approximation
Apr 07, 2020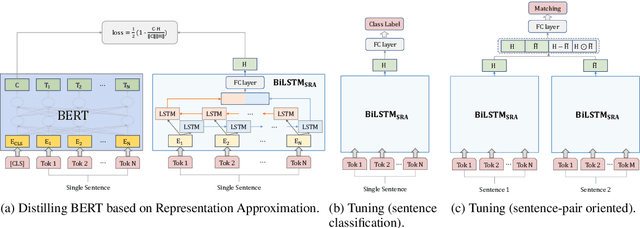
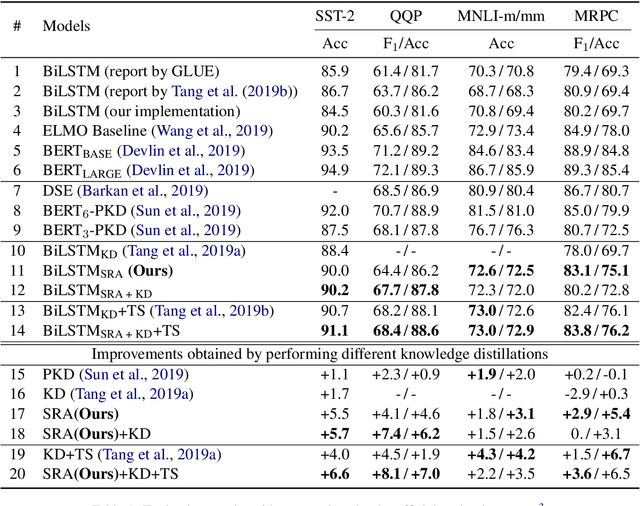
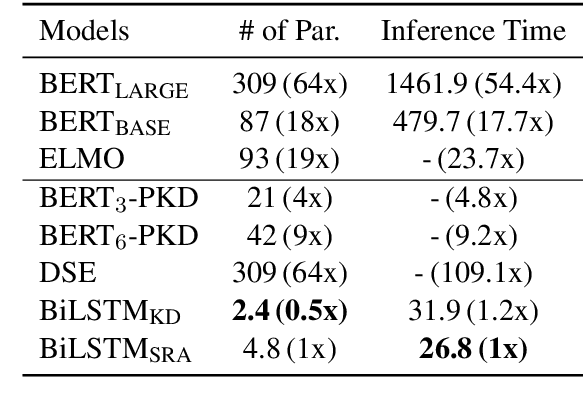
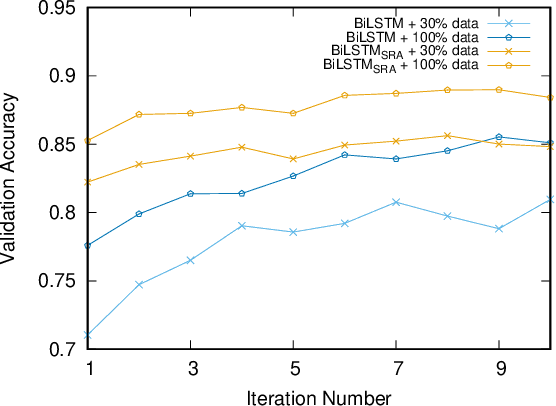
Abstract:Recently, BERT has become an essential ingredient of various NLP deep models due to its effectiveness and universal-usability. However, the online deployment of BERT is often blocked by its large-scale parameters and high computational cost. There are plenty of studies showing that the knowledge distillation is efficient in transferring the knowledge from BERT into the model with a smaller size of parameters. Nevertheless, current BERT distillation approaches mainly focus on task-specified distillation, such methodologies lead to the loss of the general semantic knowledge of BERT for universal-usability. In this paper, we propose a sentence representation approximating oriented distillation framework that can distill the pre-trained BERT into a simple LSTM based model without specifying tasks. Consistent with BERT, our distilled model is able to perform transfer learning via fine-tuning to adapt to any sentence-level downstream task. Besides, our model can further cooperate with task-specific distillation procedures. The experimental results on multiple NLP tasks from the GLUE benchmark show that our approach outperforms other task-specific distillation methods or even much larger models, i.e., ELMO, with efficiency well-improved.
Guiding Variational Response Generator to Exploit Persona
Nov 06, 2019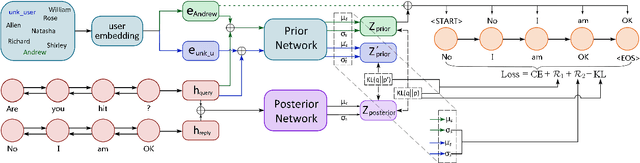
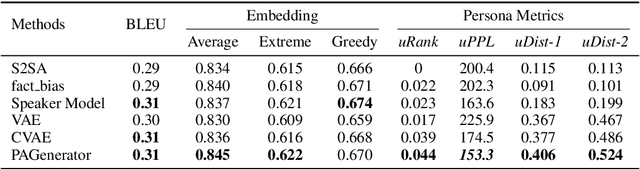

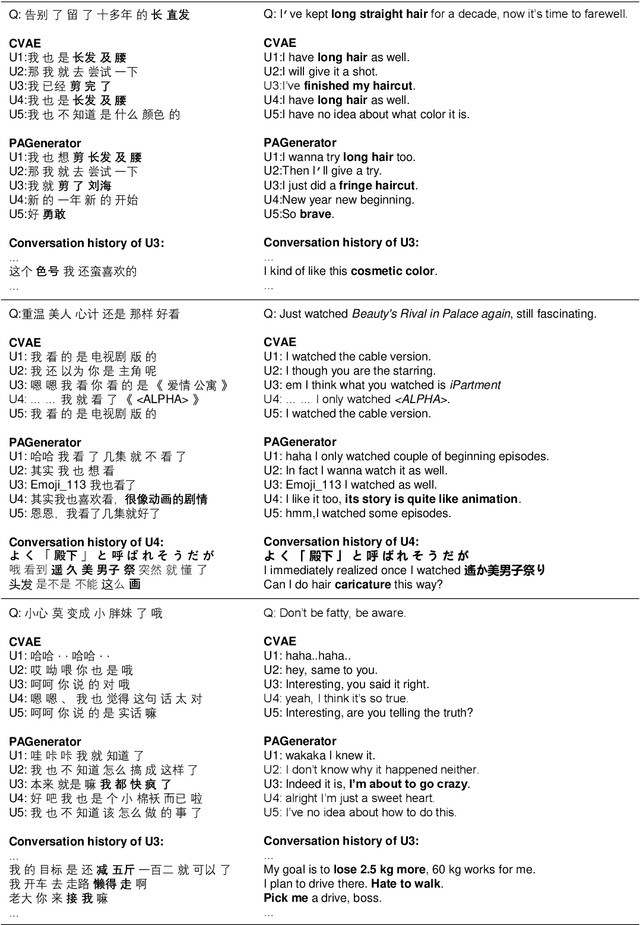
Abstract:Leveraging persona information of users in Neural Response Generators (NRG) to perform personalized conversations has been considered as an attractive and important topic in the research of conversational agents over the past few years. Despite of the promising progresses achieved by recent studies in this field, persona information tends to be incorporated into neural networks in the form of user embeddings, with the expectation that the persona can be involved via the End-to-End learning. This paper proposes to adopt the personality-related characteristics of human conversations into variational response generators, by designing a specific conditional variational autoencoder based deep model with two new regularization terms employed to the loss function, so as to guide the optimization towards the direction of generating both persona-aware and relevant responses. Besides, to reasonably evaluate the performances of various persona modeling approaches, this paper further presents three direct persona-oriented metrics from different perspectives. The experimental results have shown that our proposed methodology can notably improve the performance of persona-aware response generation, and the metrics are reasonable to evaluate the results.
MemeFaceGenerator: Adversarial Synthesis of Chinese Meme-face from Natural Sentences
Aug 14, 2019



Abstract:Chinese meme-face is a special kind of internet subculture widely spread in Chinese Social Community Networks. It usually consists of a template image modified by some amusing details and a text caption. In this paper, we present MemeFaceGenerator, a Generative Adversarial Network with the attention module and template information as supplementary signals, to automatically generate meme-faces from text inputs. We also develop a web service as system demonstration of meme-face synthesis. MemeFaceGenerator has been shown to be capable of generating high-quality meme-faces from random text inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge