Zinan Zeng
Unveiling the Hidden: Movie Genre and User Bias in Spoiler Detection
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Spoilers in movie reviews are important on platforms like IMDb and Rotten Tomatoes, offering benefits and drawbacks. They can guide some viewers' choices but also affect those who prefer no plot details in advance, making effective spoiler detection essential. Existing spoiler detection methods mainly analyze review text, often overlooking the impact of movie genres and user bias, limiting their effectiveness. To address this, we analyze movie review data, finding genre-specific variations in spoiler rates and identifying that certain users are more likely to post spoilers. Based on these findings, we introduce a new spoiler detection framework called GUSD (The code is available at https://github.com/AI-explorer-123/GUSD) (Genre-aware and User-specific Spoiler Detection), which incorporates genre-specific data and user behavior bias. User bias is calculated through dynamic graph modeling of review history. Additionally, the R2GFormer module combines RetGAT (Retentive Graph Attention Network) for graph information and GenreFormer for genre-specific aggregation. The GMoE (Genre-Aware Mixture of Experts) model further assigns reviews to specialized experts based on genre. Extensive testing on benchmark datasets shows that GUSD achieves state-of-the-art results. This approach advances spoiler detection by addressing genre and user-specific patterns, enhancing user experience on movie review platforms.
PTCL: Pseudo-Label Temporal Curriculum Learning for Label-Limited Dynamic Graph
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Dynamic node classification is critical for modeling evolving systems like financial transactions and academic collaborations. In such systems, dynamically capturing node information changes is critical for dynamic node classification, which usually requires all labels at every timestamp. However, it is difficult to collect all dynamic labels in real-world scenarios due to high annotation costs and label uncertainty (e.g., ambiguous or delayed labels in fraud detection). In contrast, final timestamp labels are easier to obtain as they rely on complete temporal patterns and are usually maintained as a unique label for each user in many open platforms, without tracking the history data. To bridge this gap, we propose PTCL(Pseudo-label Temporal Curriculum Learning), a pioneering method addressing label-limited dynamic node classification where only final labels are available. PTCL introduces: (1) a temporal decoupling architecture separating the backbone (learning time-aware representations) and decoder (strictly aligned with final labels), which generate pseudo-labels, and (2) a Temporal Curriculum Learning strategy that prioritizes pseudo-labels closer to the final timestamp by assigning them higher weights using an exponentially decaying function. We contribute a new academic dataset (CoOAG), capturing long-range research interest in dynamic graph. Experiments across real-world scenarios demonstrate PTCL's consistent superiority over other methods adapted to this task. Beyond methodology, we propose a unified framework FLiD (Framework for Label-Limited Dynamic Node Classification), consisting of a complete preparation workflow, training pipeline, and evaluation standards, and supporting various models and datasets. The code can be found at https://github.com/3205914485/FLiD.
MMoE: Robust Spoiler Detection with Multi-modal Information and Domain-aware Mixture-of-Experts
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:Online movie review websites are valuable for information and discussion about movies. However, the massive spoiler reviews detract from the movie-watching experience, making spoiler detection an important task. Previous methods simply focus on reviews' text content, ignoring the heterogeneity of information in the platform. For instance, the metadata and the corresponding user's information of a review could be helpful. Besides, the spoiler language of movie reviews tends to be genre-specific, thus posing a domain generalization challenge for existing methods. To this end, we propose MMoE, a multi-modal network that utilizes information from multiple modalities to facilitate robust spoiler detection and adopts Mixture-of-Experts to enhance domain generalization. MMoE first extracts graph, text, and meta feature from the user-movie network, the review's textual content, and the review's metadata respectively. To handle genre-specific spoilers, we then adopt Mixture-of-Experts architecture to process information in three modalities to promote robustness. Finally, we use an expert fusion layer to integrate the features from different perspectives and make predictions based on the fused embedding. Experiments demonstrate that MMoE achieves state-of-the-art performance on two widely-used spoiler detection datasets, surpassing previous SOTA methods by 2.56% and 8.41% in terms of accuracy and F1-score. Further experiments also demonstrate MMoE's superiority in robustness and generalization.
ROML: A Robust Feature Correspondence Approach for Matching Objects in A Set of Images
Mar 31, 2015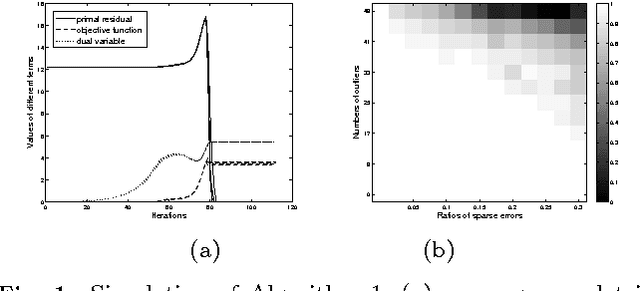
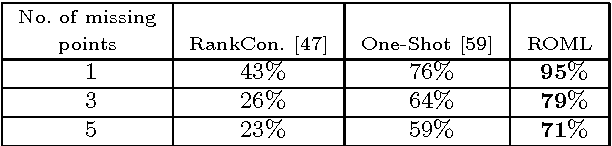

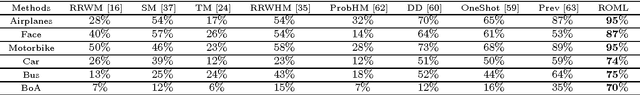
Abstract:Feature-based object matching is a fundamental problem for many applications in computer vision, such as object recognition, 3D reconstruction, tracking, and motion segmentation. In this work, we consider simultaneously matching object instances in a set of images, where both inlier and outlier features are extracted. The task is to identify the inlier features and establish their consistent correspondences across the image set. This is a challenging combinatorial problem, and the problem complexity grows exponentially with the image number. To this end, we propose a novel framework, termed ROML, to address this problem. ROML optimizes simultaneously a partial permutation matrix (PPM) for each image, and feature correspondences are established by the obtained PPMs. Two of our key contributions are summarized as follows. (1) We formulate the problem as rank and sparsity minimization for PPM optimization, and treat simultaneous optimization of multiple PPMs as a regularized consensus problem in the context of distributed optimization. (2) We use the ADMM method to solve the thus formulated ROML problem, in which a subproblem associated with a single PPM optimization appears to be a difficult integer quadratic program (IQP). We prove that under wildly applicable conditions, this IQP is equivalent to a linear sum assignment problem (LSAP), which can be efficiently solved to an exact solution. Extensive experiments on rigid/non-rigid object matching, matching instances of a common object category, and common object localization show the efficacy of our proposed method.
PCANet: A Simple Deep Learning Baseline for Image Classification?
Aug 28, 2014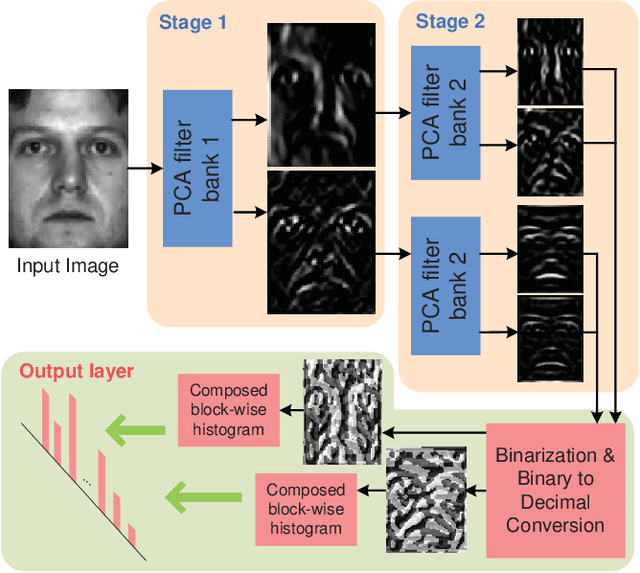
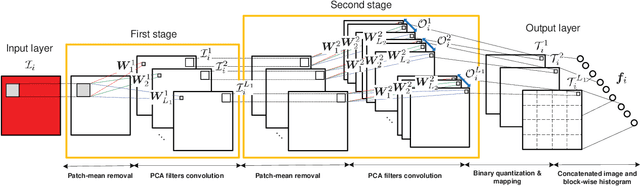
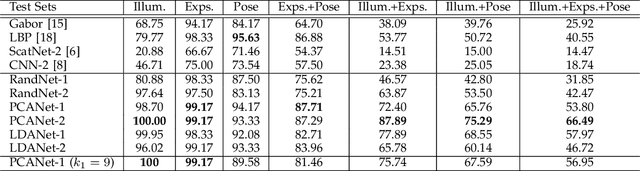
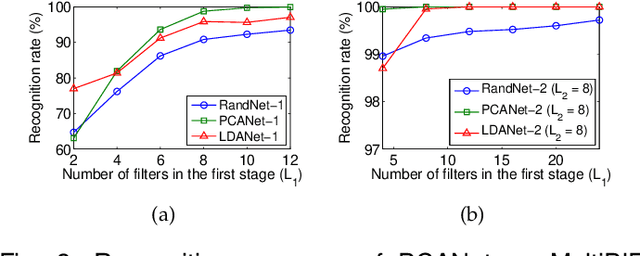
Abstract:In this work, we propose a very simple deep learning network for image classification which comprises only the very basic data processing components: cascaded principal component analysis (PCA), binary hashing, and block-wise histograms. In the proposed architecture, PCA is employed to learn multistage filter banks. It is followed by simple binary hashing and block histograms for indexing and pooling. This architecture is thus named as a PCA network (PCANet) and can be designed and learned extremely easily and efficiently. For comparison and better understanding, we also introduce and study two simple variations to the PCANet, namely the RandNet and LDANet. They share the same topology of PCANet but their cascaded filters are either selected randomly or learned from LDA. We have tested these basic networks extensively on many benchmark visual datasets for different tasks, such as LFW for face verification, MultiPIE, Extended Yale B, AR, FERET datasets for face recognition, as well as MNIST for hand-written digits recognition. Surprisingly, for all tasks, such a seemingly naive PCANet model is on par with the state of the art features, either prefixed, highly hand-crafted or carefully learned (by DNNs). Even more surprisingly, it sets new records for many classification tasks in Extended Yale B, AR, FERET datasets, and MNIST variations. Additional experiments on other public datasets also demonstrate the potential of the PCANet serving as a simple but highly competitive baseline for texture classification and object recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge