Zhiwen Wu
Traffic Regulation-aware Path Planning with Regulation Databases and Vision-Language Models
Mar 12, 2025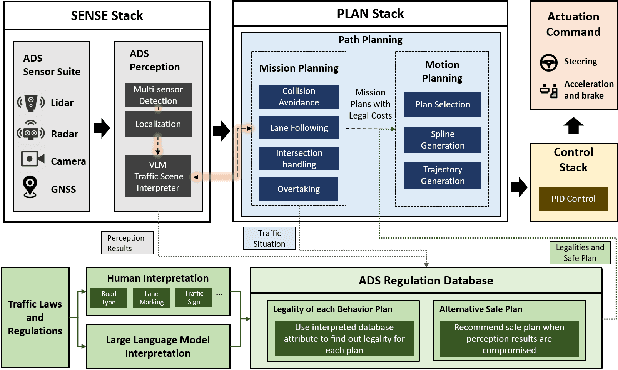
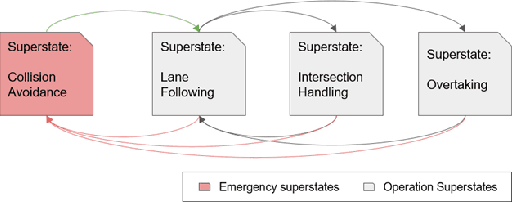
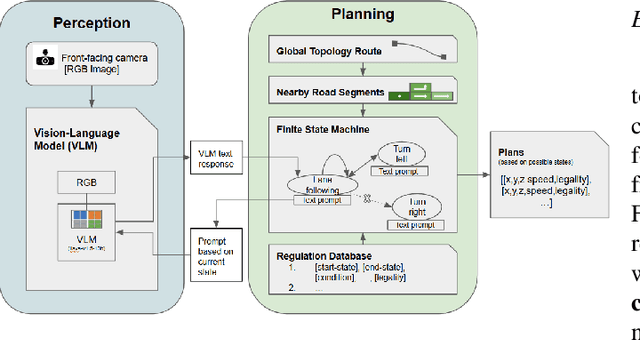
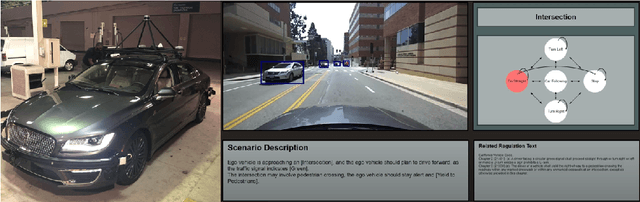
Abstract:This paper introduces and tests a framework integrating traffic regulation compliance into automated driving systems (ADS). The framework enables ADS to follow traffic laws and make informed decisions based on the driving environment. Using RGB camera inputs and a vision-language model (VLM), the system generates descriptive text to support a regulation-aware decision-making process, ensuring legal and safe driving practices. This information is combined with a machine-readable ADS regulation database to guide future driving plans within legal constraints. Key features include: 1) a regulation database supporting ADS decision-making, 2) an automated process using sensor input for regulation-aware path planning, and 3) validation in both simulated and real-world environments. Particularly, the real-world vehicle tests not only assess the framework's performance but also evaluate the potential and challenges of VLMs to solve complex driving problems by integrating detection, reasoning, and planning. This work enhances the legality, safety, and public trust in ADS, representing a significant step forward in the field.
CoDynTrust: Robust Asynchronous Collaborative Perception via Dynamic Feature Trust Modulus
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Collaborative perception, fusing information from multiple agents, can extend perception range so as to improve perception performance. However, temporal asynchrony in real-world environments, caused by communication delays, clock misalignment, or sampling configuration differences, can lead to information mismatches. If this is not well handled, then the collaborative performance is patchy, and what's worse safety accidents may occur. To tackle this challenge, we propose CoDynTrust, an uncertainty-encoded asynchronous fusion perception framework that is robust to the information mismatches caused by temporal asynchrony. CoDynTrust generates dynamic feature trust modulus (DFTM) for each region of interest by modeling aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty as well as selectively suppressing or retaining single-vehicle features, thereby mitigating information mismatches. We then design a multi-scale fusion module to handle multi-scale feature maps processed by DFTM. Compared to existing works that also consider asynchronous collaborative perception, CoDynTrust combats various low-quality information in temporally asynchronous scenarios and allows uncertainty to be propagated to downstream tasks such as planning and control. Experimental results demonstrate that CoDynTrust significantly reduces performance degradation caused by temporal asynchrony across multiple datasets, achieving state-of-the-art detection performance even with temporal asynchrony. The code is available at https://github.com/CrazyShout/CoDynTrust.
Driving with Regulation: Interpretable Decision-Making for Autonomous Vehicles with Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning via LLM
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:This work presents an interpretable decision-making framework for autonomous vehicles that integrates traffic regulations, norms, and safety guidelines comprehensively and enables seamless adaptation to different regions. While traditional rule-based methods struggle to incorporate the full scope of traffic rules, we develop a Traffic Regulation Retrieval (TRR) Agent based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to automatically retrieve relevant traffic rules and guidelines from extensive regulation documents and relevant records based on the ego vehicle's situation. Given the semantic complexity of the retrieved rules, we also design a reasoning module powered by a Large Language Model (LLM) to interpret these rules, differentiate between mandatory rules and safety guidelines, and assess actions on legal compliance and safety. Additionally, the reasoning is designed to be interpretable, enhancing both transparency and reliability. The framework demonstrates robust performance on both hypothesized and real-world cases across diverse scenarios, along with the ability to adapt to different regions with ease.
FeatherNets: Convolutional Neural Networks as Light as Feather for Face Anti-spoofing
Apr 22, 2019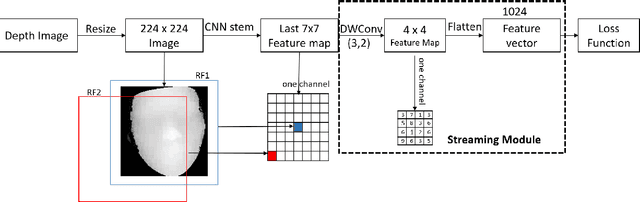
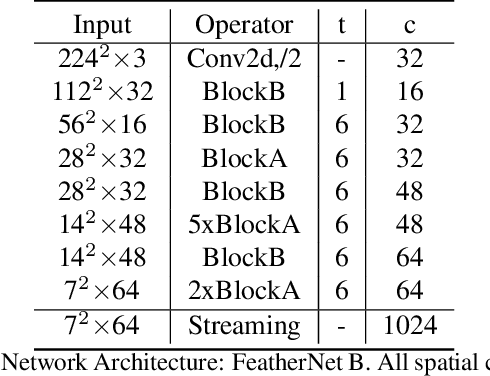
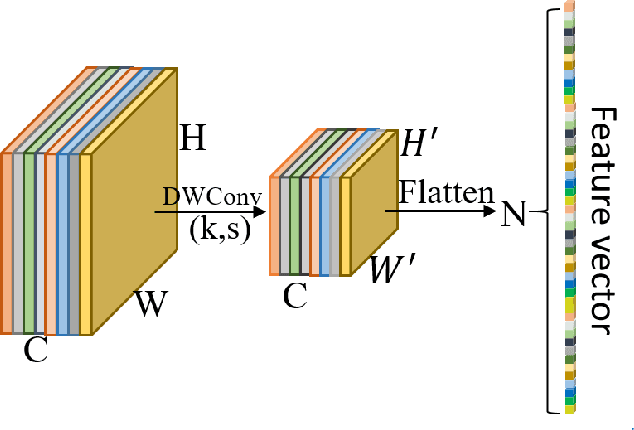
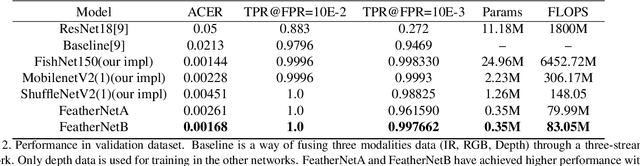
Abstract:Face Anti-spoofing gains increased attentions recently in both academic and industrial fields. With the emergence of various CNN based solutions, the multi-modal(RGB, depth and IR) methods based CNN showed better performance than single modal classifiers. However, there is a need for improving the performance and reducing the complexity. Therefore, an extreme light network architecture(FeatherNet A/B) is proposed with a streaming module which fixes the weakness of Global Average Pooling and uses less parameters. Our single FeatherNet trained by depth image only, provides a higher baseline with 0.00168 ACER, 0.35M parameters and 83M FLOPS. Furthermore, a novel fusion procedure with ``ensemble + cascade'' structure is presented to satisfy the performance preferred use cases. Meanwhile, the MMFD dataset is collected to provide more attacks and diversity to gain better generalization. We use the fusion method in the Face Anti-spoofing Attack Detection Challenge@CVPR2019 and got the result of 0.0013(ACER), 0.999(TPR@FPR=10e-2), 0.998(TPR@FPR=10e-3) and 0.9814(TPR@FPR=10e-4).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge