Zhicheng Chen
MSDformer: Multi-scale Discrete Transformer For Time Series Generation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Discrete Token Modeling (DTM), which employs vector quantization techniques, has demonstrated remarkable success in modeling non-natural language modalities, particularly in time series generation. While our prior work SDformer established the first DTM-based framework to achieve state-of-the-art performance in this domain, two critical limitations persist in existing DTM approaches: 1) their inability to capture multi-scale temporal patterns inherent to complex time series data, and 2) the absence of theoretical foundations to guide model optimization. To address these challenges, we proposes a novel multi-scale DTM-based time series generation method, called Multi-Scale Discrete Transformer (MSDformer). MSDformer employs a multi-scale time series tokenizer to learn discrete token representations at multiple scales, which jointly characterize the complex nature of time series data. Subsequently, MSDformer applies a multi-scale autoregressive token modeling technique to capture the multi-scale patterns of time series within the discrete latent space. Theoretically, we validate the effectiveness of the DTM method and the rationality of MSDformer through the rate-distortion theorem. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MSDformer significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Both theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that incorporating multi-scale information and modeling multi-scale patterns can substantially enhance the quality of generated time series in DTM-based approaches. The code will be released upon acceptance.
LLMs in Software Security: A Survey of Vulnerability Detection Techniques and Insights
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are emerging as transformative tools for software vulnerability detection, addressing critical challenges in the security domain. Traditional methods, such as static and dynamic analysis, often falter due to inefficiencies, high false positive rates, and the growing complexity of modern software systems. By leveraging their ability to analyze code structures, identify patterns, and generate repair sugges- tions, LLMs, exemplified by models like GPT, BERT, and CodeBERT, present a novel and scalable approach to mitigating vulnerabilities. This paper provides a detailed survey of LLMs in vulnerability detection. It examines key aspects, including model architectures, application methods, target languages, fine-tuning strategies, datasets, and evaluation metrics. We also analyze the scope of current research problems, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of existing approaches. Further, we address challenges such as cross-language vulnerability detection, multimodal data integration, and repository-level analysis. Based on these findings, we propose solutions for issues like dataset scalability, model interpretability, and applications in low-resource scenarios. Our contributions are threefold: (1) a systematic review of how LLMs are applied in vulnerability detection; (2) an analysis of shared patterns and differences across studies, with a unified framework for understanding the field; and (3) a summary of key challenges and future research directions. This work provides valuable insights for advancing LLM-based vulnerability detection. We also maintain and regularly update latest selected paper on https://github.com/OwenSanzas/LLM-For-Vulnerability-Detection
Large Language Models in Software Security: A Survey of Vulnerability Detection Techniques and Insights
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are emerging as transformative tools for software vulnerability detection, addressing critical challenges in the security domain. Traditional methods, such as static and dynamic analysis, often falter due to inefficiencies, high false positive rates, and the growing complexity of modern software systems. By leveraging their ability to analyze code structures, identify patterns, and generate repair sugges- tions, LLMs, exemplified by models like GPT, BERT, and CodeBERT, present a novel and scalable approach to mitigating vulnerabilities. This paper provides a detailed survey of LLMs in vulnerability detection. It examines key aspects, including model architectures, application methods, target languages, fine-tuning strategies, datasets, and evaluation metrics. We also analyze the scope of current research problems, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of existing approaches. Further, we address challenges such as cross-language vulnerability detection, multimodal data integration, and repository-level analysis. Based on these findings, we propose solutions for issues like dataset scalability, model interpretability, and applications in low-resource scenarios. Our contributions are threefold: (1) a systematic review of how LLMs are applied in vulnerability detection; (2) an analysis of shared patterns and differences across studies, with a unified framework for understanding the field; and (3) a summary of key challenges and future research directions. This work provides valuable insights for advancing LLM-based vulnerability detection. We also maintain and regularly update latest selected paper on https://github.com/OwenSanzas/LLM-For-Vulnerability-Detection
Self-Introspective Decoding: Alleviating Hallucinations for Large Vision-Language Models
Aug 04, 2024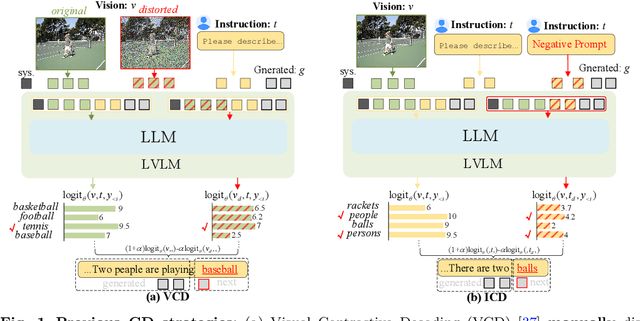
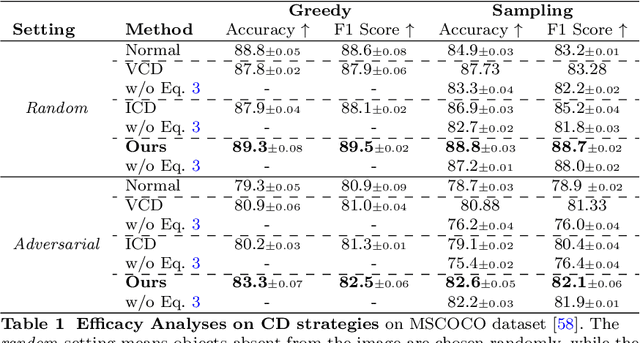
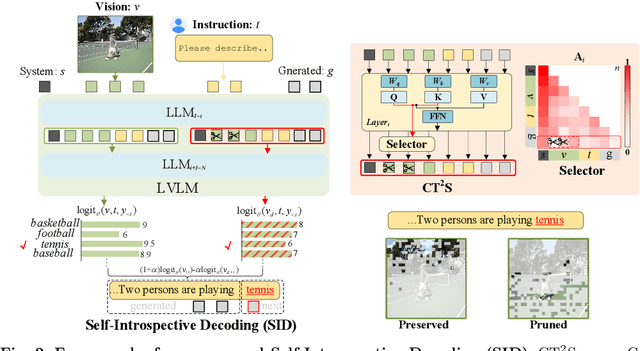
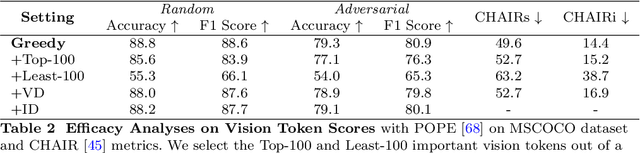
Abstract:While Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have rapidly advanced in recent years, the prevalent issue known as the `hallucination' problem has emerged as a significant bottleneck, hindering their real-world deployments. Existing methods mitigate this issue mainly from two perspectives: One approach leverages extra knowledge like robust instruction tuning LVLMs with curated datasets or employing auxiliary analysis networks, which inevitable incur additional costs. Another approach, known as contrastive decoding, induces hallucinations by manually disturbing the vision or instruction raw inputs and mitigates them by contrasting the outputs of the disturbed and original LVLMs. However, these approaches rely on empirical holistic input disturbances and double the inference cost. To avoid these issues, we propose a simple yet effective method named Self-Introspective Decoding (SID). Our empirical investigation reveals that pretrained LVLMs can introspectively assess the importance of vision tokens based on preceding vision and text (both instruction and generated) tokens. We develop the Context and Text-aware Token Selection (CT2S) strategy, which preserves only unimportant vision tokens after early layers of LVLMs to adaptively amplify text-informed hallucination during the auto-regressive decoding. This approach ensures that multimodal knowledge absorbed in the early layers induces multimodal contextual rather than aimless hallucinations. Subsequently, the original token logits subtract the amplified vision-and-text association hallucinations, guiding LVLMs decoding faithfully. Extensive experiments illustrate SID generates less-hallucination and higher-quality texts across various metrics, without extra knowledge and much additional computation burdens.
MGCP: A Multi-Grained Correlation based Prediction Network for Multivariate Time Series
May 30, 2024
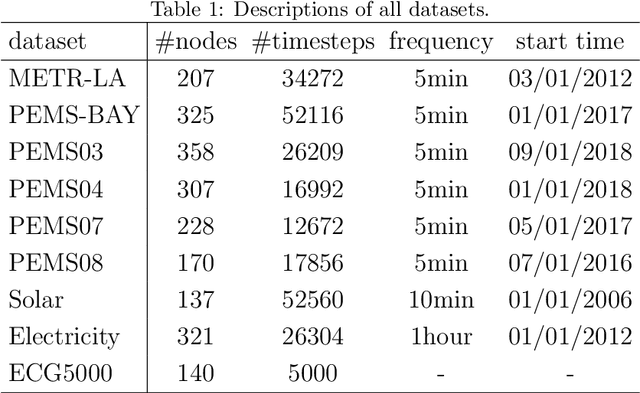
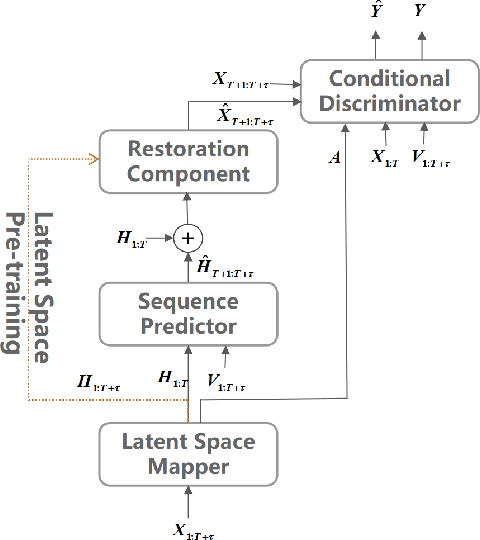
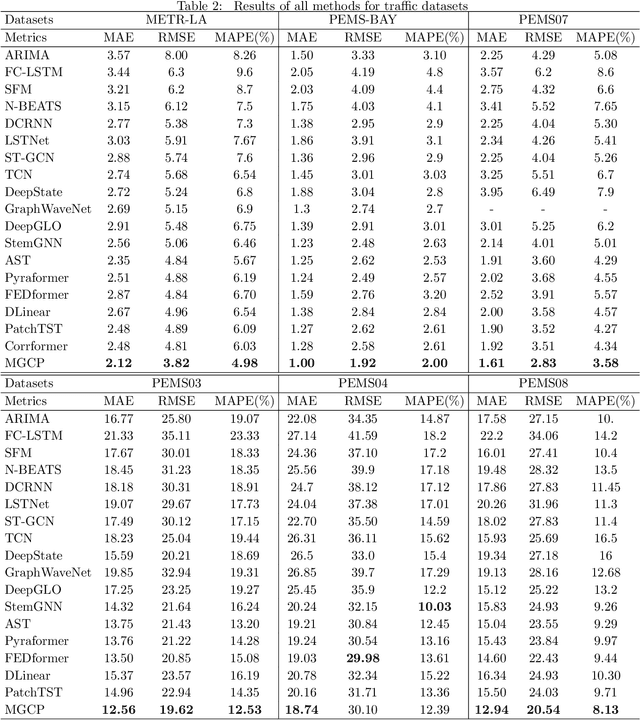
Abstract:Multivariate time series prediction is widely used in daily life, which poses significant challenges due to the complex correlations that exist at multi-grained levels. Unfortunately, the majority of current time series prediction models fail to simultaneously learn the correlations of multivariate time series at multi-grained levels, resulting in suboptimal performance. To address this, we propose a Multi-Grained Correlations-based Prediction (MGCP) Network, which simultaneously considers the correlations at three granularity levels to enhance prediction performance. Specifically, MGCP utilizes Adaptive Fourier Neural Operators and Graph Convolutional Networks to learn the global spatiotemporal correlations and inter-series correlations, enabling the extraction of potential features from multivariate time series at fine-grained and medium-grained levels. Additionally, MGCP employs adversarial training with an attention mechanism-based predictor and conditional discriminator to optimize prediction results at coarse-grained level, ensuring high fidelity between the generated forecast results and the actual data distribution. Finally, we compare MGCP with several state-of-the-art time series prediction algorithms on real-world benchmark datasets, and our results demonstrate the generality and effectiveness of the proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge