Zhichao Ye
StarGen: A Spatiotemporal Autoregression Framework with Video Diffusion Model for Scalable and Controllable Scene Generation
Jan 10, 2025
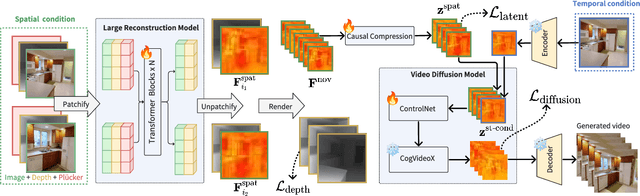

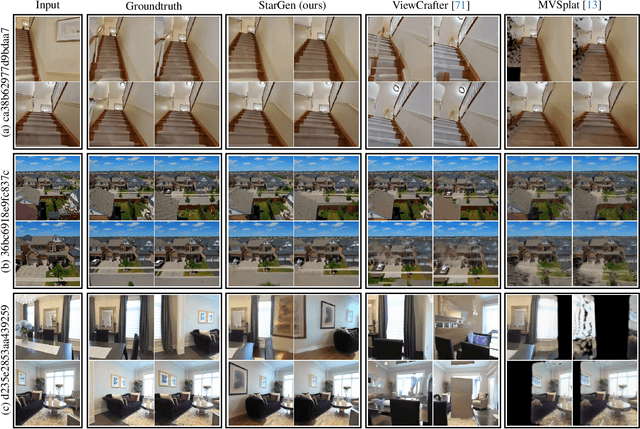
Abstract:Recent advances in large reconstruction and generative models have significantly improved scene reconstruction and novel view generation. However, due to compute limitations, each inference with these large models is confined to a small area, making long-range consistent scene generation challenging. To address this, we propose StarGen, a novel framework that employs a pre-trained video diffusion model in an autoregressive manner for long-range scene generation. The generation of each video clip is conditioned on the 3D warping of spatially adjacent images and the temporally overlapping image from previously generated clips, improving spatiotemporal consistency in long-range scene generation with precise pose control. The spatiotemporal condition is compatible with various input conditions, facilitating diverse tasks, including sparse view interpolation, perpetual view generation, and layout-conditioned city generation. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate StarGen's superior scalability, fidelity, and pose accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods.
EC-SfM: Efficient Covisibility-based Structure-from-Motion for Both Sequential and Unordered Images
Feb 21, 2023
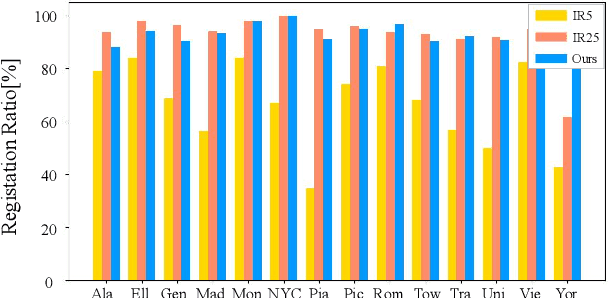
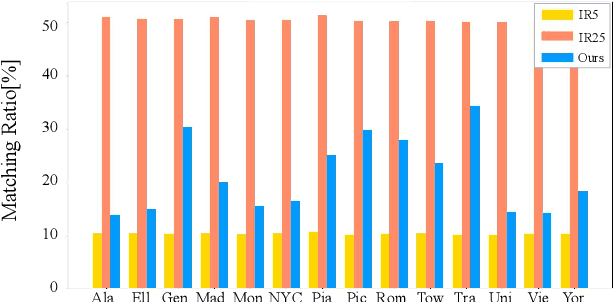

Abstract:Structure-from-Motion is a technology used to obtain scene structure through image collection, which is a fundamental problem in computer vision. For unordered Internet images, SfM is very slow due to the lack of prior knowledge about image overlap. For sequential images, knowing the large overlap between adjacent frames, SfM can adopt a variety of acceleration strategies, which are only applicable to sequential data. To further improve the reconstruction efficiency and break the gap of strategies between these two kinds of data, this paper presents an efficient covisibility-based incremental SfM. Different from previous methods, we exploit covisibility and registration dependency to describe the image connection which is suitable to any kind of data. Based on this general image connection, we propose a unified framework to efficiently reconstruct sequential images, unordered images, and the mixture of these two. Experiments on the unordered images and mixed data verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, which is three times faster than the state of the art on feature matching, and an order of magnitude faster on reconstruction without sacrificing the accuracy. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/openxrlab/xrsfm
Generative Category-Level Shape and Pose Estimation with Semantic Primitives
Oct 03, 2022



Abstract:Empowering autonomous agents with 3D understanding for daily objects is a grand challenge in robotics applications. When exploring in an unknown environment, existing methods for object pose estimation are still not satisfactory due to the diversity of object shapes. In this paper, we propose a novel framework for category-level object shape and pose estimation from a single RGB-D image. To handle the intra-category variation, we adopt a semantic primitive representation that encodes diverse shapes into a unified latent space, which is the key to establish reliable correspondences between observed point clouds and estimated shapes. Then, by using a SIM(3)-invariant shape descriptor, we gracefully decouple the shape and pose of an object, thus supporting latent shape optimization of target objects in arbitrary poses. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method achieves SOTA pose estimation performance and better generalization in the real-world dataset. Code and video are available at https://zju3dv.github.io/gCasp
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge