Zhe Xiao
See In Detail: Enhancing Sparse-view 3D Gaussian Splatting with Local Depth and Semantic Regularization
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown remarkable performance in novel view synthesis. However, its rendering quality deteriorates with sparse inphut views, leading to distorted content and reduced details. This limitation hinders its practical application. To address this issue, we propose a sparse-view 3DGS method. Given the inherently ill-posed nature of sparse-view rendering, incorporating prior information is crucial. We propose a semantic regularization technique, using features extracted from the pretrained DINO-ViT model, to ensure multi-view semantic consistency. Additionally, we propose local depth regularization, which constrains depth values to improve generalization on unseen views. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art novel view synthesis approaches, achieving up to 0.4dB improvement in terms of PSNR on the LLFF dataset, with reduced distortion and enhanced visual quality.
A Survey of Distance-Based Vessel Trajectory Clustering: Data Pre-processing, Methodologies, Applications, and Experimental Evaluation
Jul 13, 2024Abstract:Vessel trajectory clustering, a crucial component of the maritime intelligent transportation systems, provides valuable insights for applications such as anomaly detection and trajectory prediction. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the most prevalent distance-based vessel trajectory clustering methods, which encompass two main steps: trajectory similarity measurement and clustering. Initially, we conducted a thorough literature review using relevant keywords to gather and summarize pertinent research papers and datasets. Then, this paper discussed the principal methods of data pre-processing that prepare data for further analysis. The survey progresses to detail the leading algorithms for measuring vessel trajectory similarity and the main clustering techniques used in the field today. Furthermore, the various applications of trajectory clustering within the maritime context are explored. Finally, the paper evaluates the effectiveness of different algorithm combinations and pre-processing methods through experimental analysis, focusing on their impact on the performance of distance-based trajectory clustering algorithms. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of various trajectory clustering algorithms and notably highlight the significant improvements that trajectory compression techniques contribute to the efficiency and accuracy of trajectory clustering. This comprehensive approach ensures a deep understanding of current capabilities and future directions in vessel trajectory clustering.
Prediction of Vessel Arrival Time to Pilotage Area Using Multi-Data Fusion and Deep Learning
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the prediction of vessels' arrival time to the pilotage area using multi-data fusion and deep learning approaches. Firstly, the vessel arrival contour is extracted based on Multivariate Kernel Density Estimation (MKDE) and clustering. Secondly, multiple data sources, including Automatic Identification System (AIS), pilotage booking information, and meteorological data, are fused before latent feature extraction. Thirdly, a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) framework that incorporates a residual mechanism is constructed to learn the hidden arrival patterns of the vessels. Extensive tests on two real-world data sets from Singapore have been conducted and the following promising results have been obtained: 1) fusion of pilotage booking information and meteorological data improves the prediction accuracy, with pilotage booking information having a more significant impact; 2) using discrete embedding for the meteorological data performs better than using continuous embedding; 3) the TCN outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline methods in regression tasks, exhibiting Mean Absolute Error (MAE) ranging from 4.58 min to 4.86 min; and 4) approximately 89.41% to 90.61% of the absolute prediction residuals fall within a time frame of 10 min.
An Unsupervised Learning Method with Convolutional Auto-Encoder for Vessel Trajectory Similarity Computation
Jan 10, 2021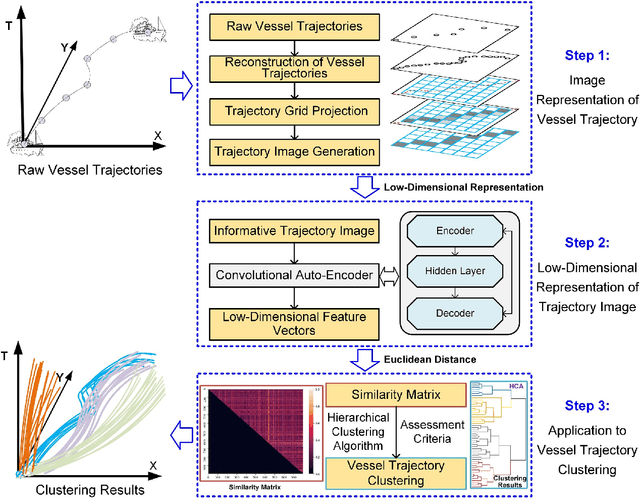
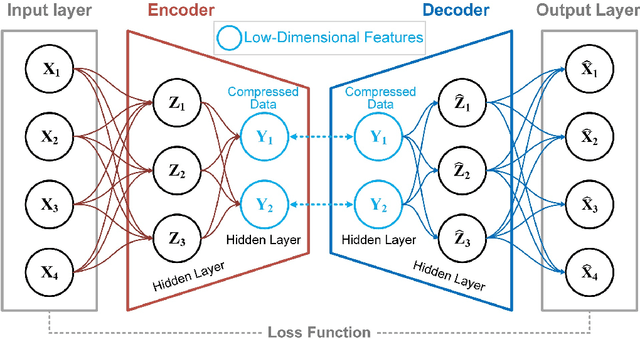
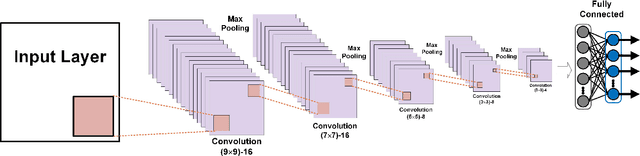
Abstract:To achieve reliable mining results for massive vessel trajectories, one of the most important challenges is how to efficiently compute the similarities between different vessel trajectories. The computation of vessel trajectory similarity has recently attracted increasing attention in the maritime data mining research community. However, traditional shape- and warping-based methods often suffer from several drawbacks such as high computational cost and sensitivity to unwanted artifacts and non-uniform sampling rates, etc. To eliminate these drawbacks, we propose an unsupervised learning method which automatically extracts low-dimensional features through a convolutional auto-encoder (CAE). In particular, we first generate the informative trajectory images by remapping the raw vessel trajectories into two-dimensional matrices while maintaining the spatio-temporal properties. Based on the massive vessel trajectories collected, the CAE can learn the low-dimensional representations of informative trajectory images in an unsupervised manner. The trajectory similarity is finally equivalent to efficiently computing the similarities between the learned low-dimensional features, which strongly correlate with the raw vessel trajectories. Comprehensive experiments on realistic data sets have demonstrated that the proposed method largely outperforms traditional trajectory similarity computation methods in terms of efficiency and effectiveness. The high-quality trajectory clustering performance could also be guaranteed according to the CAE-based trajectory similarity computation results.
Coverage Path Planning using Path Primitive Sampling and Primitive Coverage Graph for Visual Inspection
Aug 08, 2019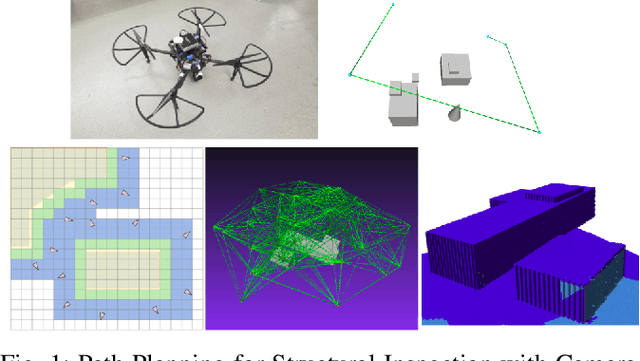
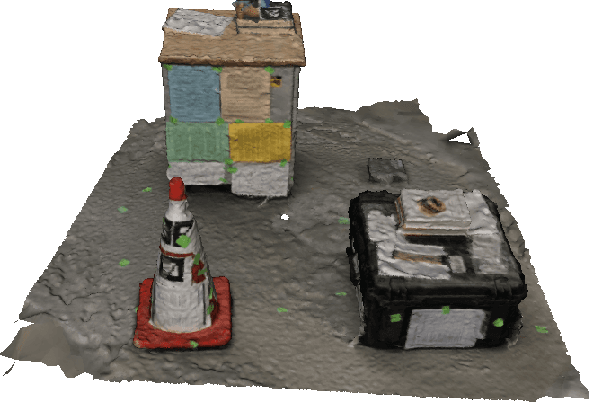
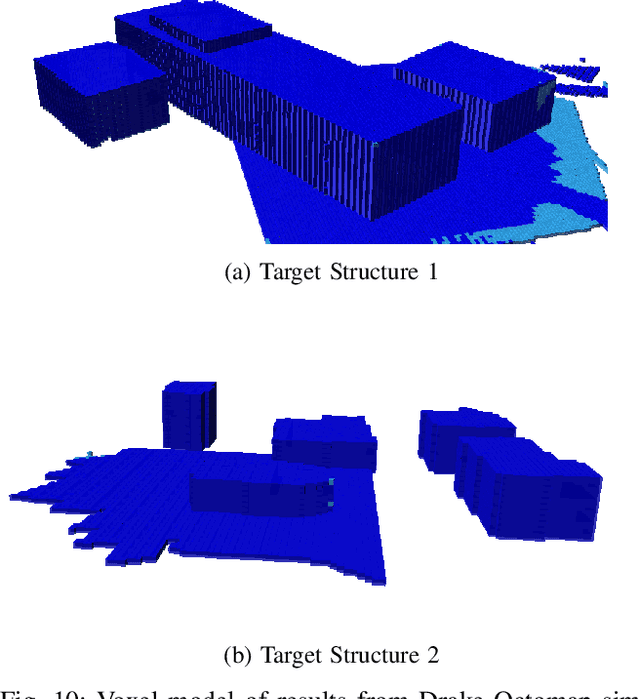
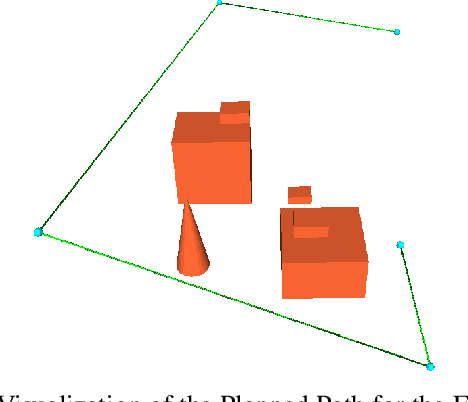

Abstract:Planning the path to gather the surface information of the target objects is crucial to improve the efficiency of and reduce the overall cost, for visual inspection applications with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Coverage Path Planning (CPP) problem is often formulated for these inspection applications because of the coverage requirement. Traditionally, researchers usually plan and optimize the viewpoints to capture the surface information first, and then optimize the path to visit the selected viewpoints. In this paper, we propose a novel planning method to directly sample and plan the inspection path for a camera-equipped UAV to acquire visual and geometric information of the target structures as a video stream setting in complex 3D environment. The proposed planning method first generates via-points and path primitives around the target object by using sampling methods based on voxel dilation and subtraction. A novel Primitive Coverage Graph (PCG) is then proposed to encode the topological information, flying distances, and visibility information, with the sampled via-points and path primitives. Finally graph search is performed to find the resultant path in the PCG to complete the inspection task with the coverage requirements. The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through simulation and field tests in this paper.
Variational Regularized Transmission Refinement for Image Dehazing
Feb 19, 2019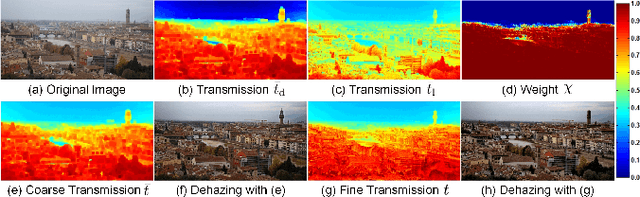

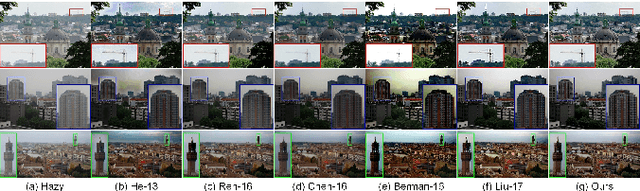
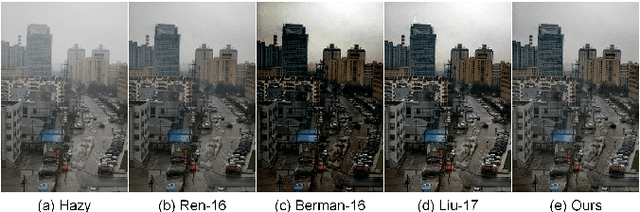
Abstract:High-quality dehazing performance is highly dependent upon the accurate estimation of transmission map. In this work, the coarse estimation version is first obtained by weightedly fusing two different transmission maps, which are generated from foreground and sky regions, respectively. A hybrid variational model with promoted regularization terms is then proposed to assisting in refining transmission map. The resulting complicated optimization problem is effectively solved via an alternating direction algorithm. The final haze-free image can be effectively obtained according to the refined transmission map and atmospheric scattering model. Our dehazing framework has the capacity of preserving important image details while suppressing undesirable artifacts, even for hazy images with large sky regions. Experiments on both synthetic and realistic images have illustrated that the proposed method is competitive with or even outperforms the state-of-the-art dehazing techniques under different imaging conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge