Zeyu Fang
MINT: Minimal Information Neuro-Symbolic Tree for Objective-Driven Knowledge-Gap Reasoning and Active Elicitation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Joint planning through language-based interactions is a key area of human-AI teaming. Planning problems in the open world often involve various aspects of incomplete information and unknowns, e.g., objects involved, human goals/intents -- thus leading to knowledge gaps in joint planning. We consider the problem of discovering optimal interaction strategies for AI agents to actively elicit human inputs in object-driven planning. To this end, we propose Minimal Information Neuro-Symbolic Tree (MINT) to reason about the impact of knowledge gaps and leverage self-play with MINT to optimize the AI agent's elicitation strategies and queries. More precisely, MINT builds a symbolic tree by making propositions of possible human-AI interactions and by consulting a neural planning policy to estimate the uncertainty in planning outcomes caused by remaining knowledge gaps. Finally, we leverage LLM to search and summarize MINT's reasoning process and curate a set of queries to optimally elicit human inputs for best planning performance. By considering a family of extended Markov decision processes with knowledge gaps, we analyze the return guarantee for a given MINT with active human elicitation. Our evaluation on three benchmarks involving unseen/unknown objects of increasing realism shows that MINT-based planning attains near-expert returns by issuing a limited number of questions per task while achieving significantly improved rewards and success rates.
Structuring Value Representations via Geometric Coherence in Markov Decision Processes
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Geometric properties can be leveraged to stabilize and speed reinforcement learning. Existing examples include encoding symmetry structure, geometry-aware data augmentation, and enforcing structural restrictions. In this paper, we take a novel view of RL through the lens of order theory and recast value function estimates into learning a desired poset (partially ordered set). We propose \emph{GCR-RL} (Geometric Coherence Regularized Reinforcement Learning) that computes a sequence of super-poset refinements -- by refining posets in previous steps and learning additional order relationships from temporal difference signals -- thus ensuring geometric coherence across the sequence of posets underpinning the learned value functions. Two novel algorithms by Q-learning and by actor--critic are developed to efficiently realize these super-poset refinements. Their theoretical properties and convergence rates are analyzed. We empirically evaluate GCR-RL in a range of tasks and demonstrate significant improvements in sample efficiency and stable performance over strong baselines.
Manifold-Constrained Energy-Based Transition Models for Offline Reinforcement Learning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Model-based offline reinforcement learning is brittle under distribution shift: policy improvement drives rollouts into state--action regions weakly supported by the dataset, where compounding model error yields severe value overestimation. We propose Manifold-Constrained Energy-based Transition Models (MC-ETM), which train conditional energy-based transition models using a manifold projection--diffusion negative sampler. MC-ETM learns a latent manifold of next states and generates near-manifold hard negatives by perturbing latent codes and running Langevin dynamics in latent space with the learned conditional energy, sharpening the energy landscape around the dataset support and improving sensitivity to subtle out-of-distribution deviations. For policy optimization, the learned energy provides a single reliability signal: rollouts are truncated when the minimum energy over sampled next states exceeds a threshold, and Bellman backups are stabilized via pessimistic penalties based on Q-value-level dispersion across energy-guided samples. We formalize MC-ETM through a hybrid pessimistic MDP formulation and derive a conservative performance bound separating in-support evaluation error from truncation risk. Empirically, MC-ETM improves multi-step dynamics fidelity and yields higher normalized returns on standard offline control benchmarks, particularly under irregular dynamics and sparse data coverage.
Towards a Unified Framework of Clustering-based Anomaly Detection
Jun 01, 2024
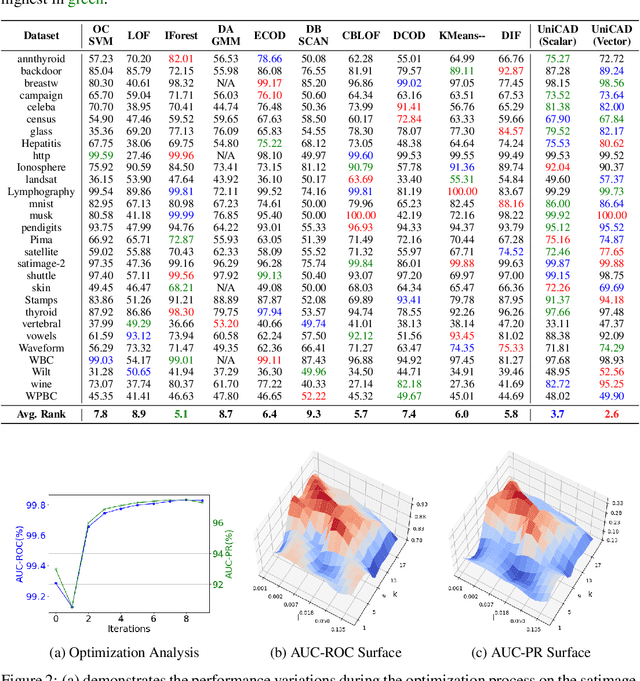
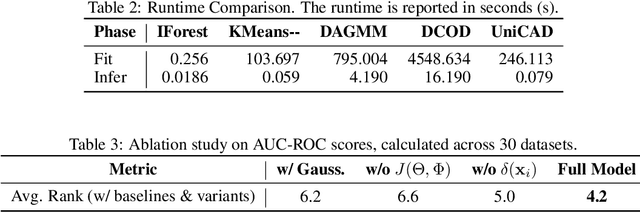
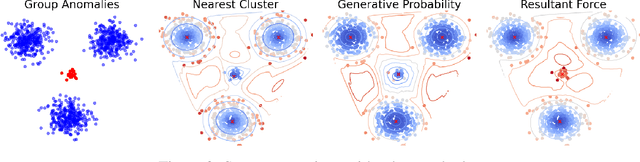
Abstract:Unsupervised Anomaly Detection (UAD) plays a crucial role in identifying abnormal patterns within data without labeled examples, holding significant practical implications across various domains. Although the individual contributions of representation learning and clustering to anomaly detection are well-established, their interdependencies remain under-explored due to the absence of a unified theoretical framework. Consequently, their collective potential to enhance anomaly detection performance remains largely untapped. To bridge this gap, in this paper, we propose a novel probabilistic mixture model for anomaly detection to establish a theoretical connection among representation learning, clustering, and anomaly detection. By maximizing a novel anomaly-aware data likelihood, representation learning and clustering can effectively reduce the adverse impact of anomalous data and collaboratively benefit anomaly detection. Meanwhile, a theoretically substantiated anomaly score is naturally derived from this framework. Lastly, drawing inspiration from gravitational analysis in physics, we have devised an improved anomaly score that more effectively harnesses the combined power of representation learning and clustering. Extensive experiments, involving 17 baseline methods across 30 diverse datasets, validate the effectiveness and generalization capability of the proposed method, surpassing state-of-the-art methods.
Learning from Random Demonstrations: Offline Reinforcement Learning with Importance-Sampled Diffusion Models
May 30, 2024Abstract:Generative models such as diffusion have been employed as world models in offline reinforcement learning to generate synthetic data for more effective learning. Existing work either generates diffusion models one-time prior to training or requires additional interaction data to update it. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for offline reinforcement learning with closed-loop policy evaluation and world-model adaptation. It iteratively leverages a guided diffusion world model to directly evaluate the offline target policy with actions drawn from it, and then performs an importance-sampled world model update to adaptively align the world model with the updated policy. We analyzed the performance of the proposed method and provided an upper bound on the return gap between our method and the real environment under an optimal policy. The result sheds light on various factors affecting learning performance. Evaluations in the D4RL environment show significant improvement over state-of-the-art baselines, especially when only random or medium-expertise demonstrations are available -- thus requiring improved alignment between the world model and offline policy evaluation.
Rethinking Propagation for Unsupervised Graph Domain Adaptation
Feb 08, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised Graph Domain Adaptation (UGDA) aims to transfer knowledge from a labelled source graph to an unlabelled target graph in order to address the distribution shifts between graph domains. Previous works have primarily focused on aligning data from the source and target graph in the representation space learned by graph neural networks (GNNs). However, the inherent generalization capability of GNNs has been largely overlooked. Motivated by our empirical analysis, we reevaluate the role of GNNs in graph domain adaptation and uncover the pivotal role of the propagation process in GNNs for adapting to different graph domains. We provide a comprehensive theoretical analysis of UGDA and derive a generalization bound for multi-layer GNNs. By formulating GNN Lipschitz for k-layer GNNs, we show that the target risk bound can be tighter by removing propagation layers in source graph and stacking multiple propagation layers in target graph. Based on the empirical and theoretical analysis mentioned above, we propose a simple yet effective approach called A2GNN for graph domain adaptation. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed A2GNN framework.
Coordinate-Aligned Multi-Camera Collaboration for Active Multi-Object Tracking
Feb 22, 2022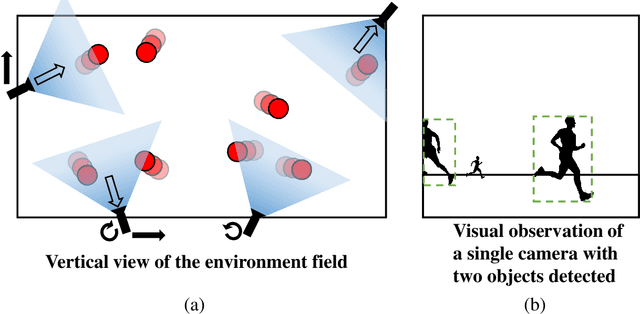
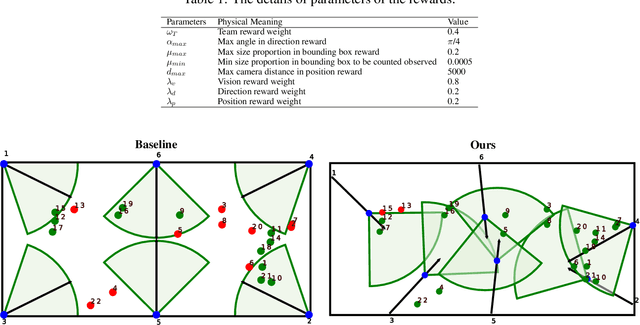
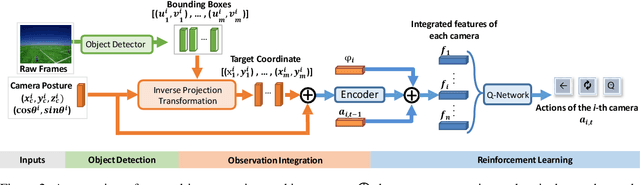

Abstract:Active Multi-Object Tracking (AMOT) is a task where cameras are controlled by a centralized system to adjust their poses automatically and collaboratively so as to maximize the coverage of targets in their shared visual field. In AMOT, each camera only receives partial information from its observation, which may mislead cameras to take locally optimal action. Besides, the global goal, i.e., maximum coverage of objects, is hard to be directly optimized. To address the above issues, we propose a coordinate-aligned multi-camera collaboration system for AMOT. In our approach, we regard each camera as an agent and address AMOT with a multi-agent reinforcement learning solution. To represent the observation of each agent, we first identify the targets in the camera view with an image detector, and then align the coordinates of the targets in 3D environment. We define the reward of each agent based on both global coverage as well as four individual reward terms. The action policy of the agents is derived with a value-based Q-network. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to study the AMOT task. To train and evaluate the efficacy of our system, we build a virtual yet credible 3D environment, named "Soccer Court", to mimic the real-world AMOT scenario. The experimental results show that our system achieves a coverage of 71.88%, outperforming the baseline method by 8.9%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge