Yuyang Tu
ToolEENet: Tool Affordance 6D Pose Estimation
Apr 05, 2024Abstract:The exploration of robotic dexterous hands utilizing tools has recently attracted considerable attention. A significant challenge in this field is the precise awareness of a tool's pose when grasped, as occlusion by the hand often degrades the quality of the estimation. Additionally, the tool's overall pose often fails to accurately represent the contact interaction, thereby limiting the effectiveness of vision-guided, contact-dependent activities. To overcome this limitation, we present the innovative TOOLEE dataset, which, to the best of our knowledge, is the first to feature affordance segmentation of a tool's end-effector (EE) along with its defined 6D pose based on its usage. Furthermore, we propose the ToolEENet framework for accurate 6D pose estimation of the tool's EE. This framework begins by segmenting the tool's EE from raw RGBD data, then uses a diffusion model-based pose estimator for 6D pose estimation at a category-specific level. Addressing the issue of symmetry in pose estimation, we introduce a symmetry-aware pose representation that enhances the consistency of pose estimation. Our approach excels in this field, demonstrating high levels of precision and generalization. Furthermore, it shows great promise for application in contact-based manipulation scenarios. All data and codes are available on the project website: https://yuyangtu.github.io/projectToolEENet.html
PoseFusion: Robust Object-in-Hand Pose Estimation with SelectLSTM
Apr 10, 2023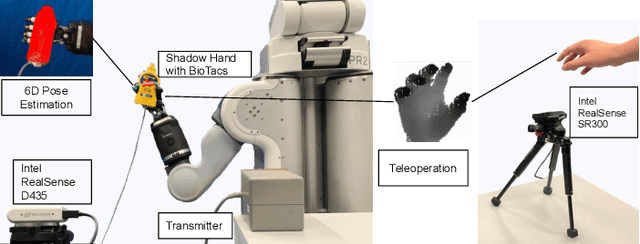
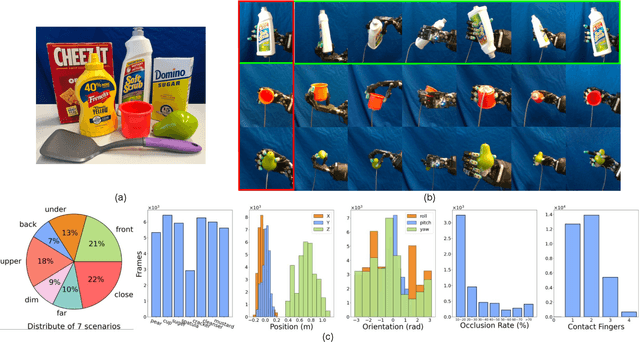
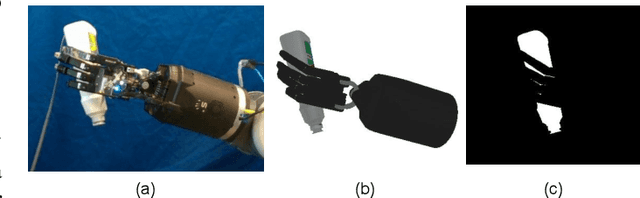
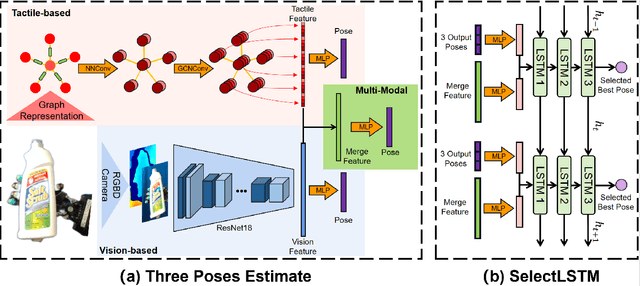
Abstract:Accurate estimation of the relative pose between an object and a robot hand is critical for many manipulation tasks. However, most of the existing object-in-hand pose datasets use two-finger grippers and also assume that the object remains fixed in the hand without any relative movements, which is not representative of real-world scenarios. To address this issue, a 6D object-in-hand pose dataset is proposed using a teleoperation method with an anthropomorphic Shadow Dexterous hand. Our dataset comprises RGB-D images, proprioception and tactile data, covering diverse grasping poses, finger contact states, and object occlusions. To overcome the significant hand occlusion and limited tactile sensor contact in real-world scenarios, we propose PoseFusion, a hybrid multi-modal fusion approach that integrates the information from visual and tactile perception channels. PoseFusion generates three candidate object poses from three estimators (tactile only, visual only, and visuo-tactile fusion), which are then filtered by a SelectLSTM network to select the optimal pose, avoiding inferior fusion poses resulting from modality collapse. Extensive experiments demonstrate the robustness and advantages of our framework. All data and codes are available on the project website: https://elevenjiang1.github.io/ObjectInHand-Dataset/
Learning Friction Model for Magnet-actuated Tethered Capsule Robot
Oct 01, 2021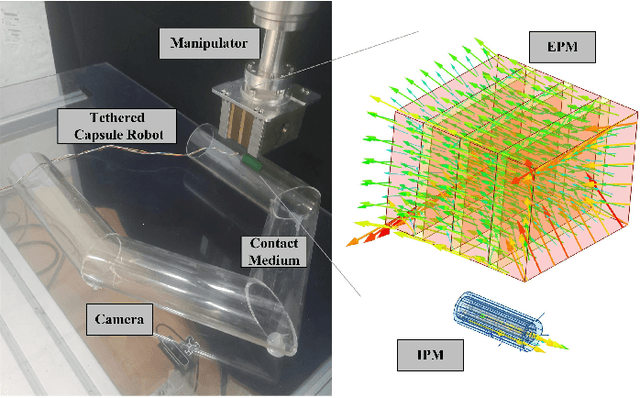
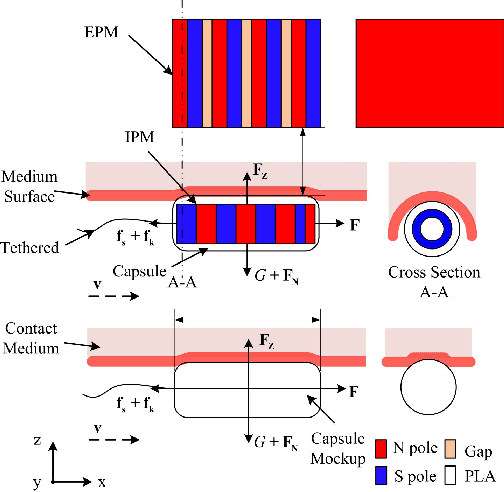
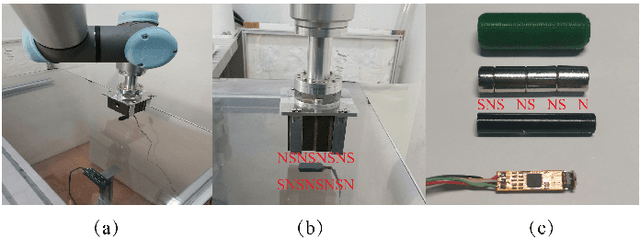
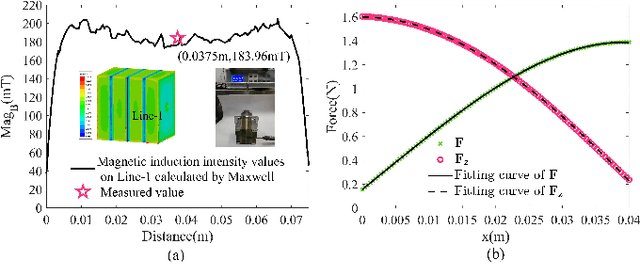
Abstract:The potential diagnostic applications of magnet-actuated capsules have been greatly increased in recent years. For most of these potential applications, accurate position control of the capsule have been highly demanding. However, the friction between the robot and the environment as well as the drag force from the tether play a significant role during the motion control of the capsule. Moreover, these forces especially the friction force are typically hard to model beforehand. In this paper, we first designed a magnet-actuated tethered capsule robot, where the driving magnet is mounted on the end of a robotic arm. Then, we proposed a learning-based approach to model the friction force between the capsule and the environment, with the goal of increasing the control accuracy of the whole system. Finally, several real robot experiments are demonstrated to showcase the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge