Yuqiang Ren
Few-Shot Object Detection via Variational Feature Aggregation
Jan 31, 2023



Abstract:As few-shot object detectors are often trained with abundant base samples and fine-tuned on few-shot novel examples,the learned models are usually biased to base classes and sensitive to the variance of novel examples. To address this issue, we propose a meta-learning framework with two novel feature aggregation schemes. More precisely, we first present a Class-Agnostic Aggregation (CAA) method, where the query and support features can be aggregated regardless of their categories. The interactions between different classes encourage class-agnostic representations and reduce confusion between base and novel classes. Based on the CAA, we then propose a Variational Feature Aggregation (VFA) method, which encodes support examples into class-level support features for robust feature aggregation. We use a variational autoencoder to estimate class distributions and sample variational features from distributions that are more robust to the variance of support examples. Besides, we decouple classification and regression tasks so that VFA is performed on the classification branch without affecting object localization. Extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC and COCO demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms a strong baseline (up to 16\%) and previous state-of-the-art methods (4\% in average). Code will be available at: \url{https://github.com/csuhan/VFA}
Expanding Low-Density Latent Regions for Open-Set Object Detection
Mar 28, 2022



Abstract:Modern object detectors have achieved impressive progress under the close-set setup. However, open-set object detection (OSOD) remains challenging since objects of unknown categories are often misclassified to existing known classes. In this work, we propose to identify unknown objects by separating high/low-density regions in the latent space, based on the consensus that unknown objects are usually distributed in low-density latent regions. As traditional threshold-based methods only maintain limited low-density regions, which cannot cover all unknown objects, we present a novel Open-set Detector (OpenDet) with expanded low-density regions. To this aim, we equip OpenDet with two learners, Contrastive Feature Learner (CFL) and Unknown Probability Learner (UPL). CFL performs instance-level contrastive learning to encourage compact features of known classes, leaving more low-density regions for unknown classes; UPL optimizes unknown probability based on the uncertainty of predictions, which further divides more low-density regions around the cluster of known classes. Thus, unknown objects in low-density regions can be easily identified with the learned unknown probability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can significantly improve the OSOD performance, e.g., OpenDet reduces the Absolute Open-Set Errors by 25%-35% on six OSOD benchmarks. Code is available at: https://github.com/csuhan/opendet2.
Distributed Attention for Grounded Image Captioning
Aug 22, 2021
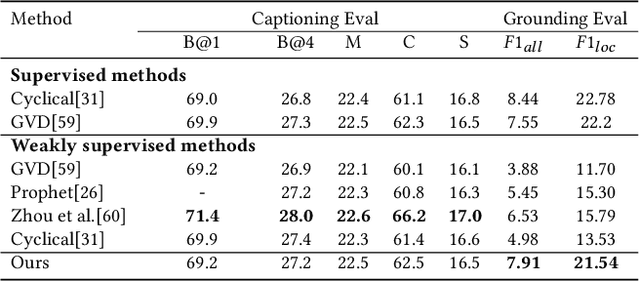

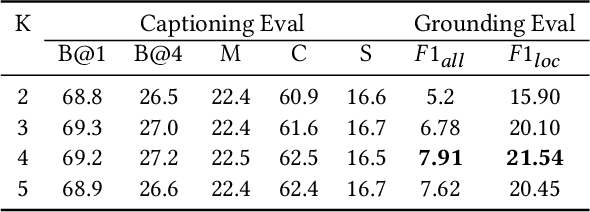
Abstract:We study the problem of weakly supervised grounded image captioning. That is, given an image, the goal is to automatically generate a sentence describing the context of the image with each noun word grounded to the corresponding region in the image. This task is challenging due to the lack of explicit fine-grained region word alignments as supervision. Previous weakly supervised methods mainly explore various kinds of regularization schemes to improve attention accuracy. However, their performances are still far from the fully supervised ones. One main issue that has been ignored is that the attention for generating visually groundable words may only focus on the most discriminate parts and can not cover the whole object. To this end, we propose a simple yet effective method to alleviate the issue, termed as partial grounding problem in our paper. Specifically, we design a distributed attention mechanism to enforce the network to aggregate information from multiple spatially different regions with consistent semantics while generating the words. Therefore, the union of the focused region proposals should form a visual region that encloses the object of interest completely. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the superiority of our proposed method compared with the state-of-the-arts.
Dynamic Refinement Network for Oriented and Densely Packed Object Detection
Jun 10, 2020



Abstract:Object detection has achieved remarkable progress in the past decade. However, the detection of oriented and densely packed objects remains challenging because of following inherent reasons: (1) receptive fields of neurons are all axis-aligned and of the same shape, whereas objects are usually of diverse shapes and align along various directions; (2) detection models are typically trained with generic knowledge and may not generalize well to handle specific objects at test time; (3) the limited dataset hinders the development on this task. To resolve the first two issues, we present a dynamic refinement network that consists of two novel components, i.e., a feature selection module (FSM) and a dynamic refinement head (DRH). Our FSM enables neurons to adjust receptive fields in accordance with the shapes and orientations of target objects, whereas the DRH empowers our model to refine the prediction dynamically in an object-aware manner. To address the limited availability of related benchmarks, we collect an extensive and fully annotated dataset, namely, SKU110K-R, which is relabeled with oriented bounding boxes based on SKU110K. We perform quantitative evaluations on several publicly available benchmarks including DOTA, HRSC2016, SKU110K, and our own SKU110K-R dataset. Experimental results show that our method achieves consistent and substantial gains compared with baseline approaches. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/Anymake/DRN_CVPR2020.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge