Yufan Wu
A Multidimensional AI-powered Framework for Analyzing Tourist Perception in Historic Urban Quarters: A Case Study in Shanghai
Sep 04, 2025

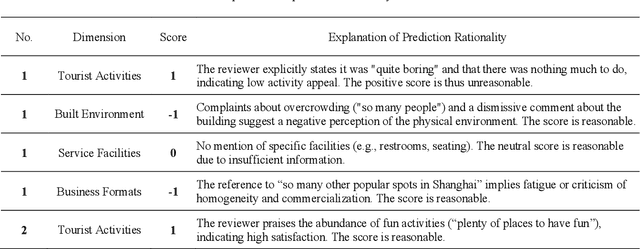

Abstract:Historic urban quarters play a vital role in preserving cultural heritage while serving as vibrant spaces for tourism and everyday life. Understanding how tourists perceive these environments is essential for sustainable, human-centered urban planning. This study proposes a multidimensional AI-powered framework for analyzing tourist perception in historic urban quarters using multimodal data from social media. Applied to twelve historic quarters in central Shanghai, the framework integrates focal point extraction, color theme analysis, and sentiment mining. Visual focus areas are identified from tourist-shared photos using a fine-tuned semantic segmentation model. To assess aesthetic preferences, dominant colors are extracted using a clustering method, and their spatial distribution across quarters is analyzed. Color themes are further compared between social media photos and real-world street views, revealing notable shifts. This divergence highlights potential gaps between visual expectations and the built environment, reflecting both stylistic preferences and perceptual bias. Tourist reviews are evaluated through a hybrid sentiment analysis approach combining a rule-based method and a multi-task BERT model. Satisfaction is assessed across four dimensions: tourist activities, built environment, service facilities, and business formats. The results reveal spatial variations in aesthetic appeal and emotional response. Rather than focusing on a single technical innovation, this framework offers an integrated, data-driven approach to decoding tourist perception and contributes to informed decision-making in tourism, heritage conservation, and the design of aesthetically engaging public spaces.
FastAvatar: Towards Unified Fast High-Fidelity 3D Avatar Reconstruction with Large Gaussian Reconstruction Transformers
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Despite significant progress in 3D avatar reconstruction, it still faces challenges such as high time complexity, sensitivity to data quality, and low data utilization. We propose FastAvatar, a feedforward 3D avatar framework capable of flexibly leveraging diverse daily recordings (e.g., a single image, multi-view observations, or monocular video) to reconstruct a high-quality 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) model within seconds, using only a single unified model. FastAvatar's core is a Large Gaussian Reconstruction Transformer featuring three key designs: First, a variant VGGT-style transformer architecture aggregating multi-frame cues while injecting initial 3D prompt to predict an aggregatable canonical 3DGS representation; Second, multi-granular guidance encoding (camera pose, FLAME expression, head pose) mitigating animation-induced misalignment for variable-length inputs; Third, incremental Gaussian aggregation via landmark tracking and sliced fusion losses. Integrating these features, FastAvatar enables incremental reconstruction, i.e., improving quality with more observations, unlike prior work wasting input data. This yields a quality-speed-tunable paradigm for highly usable avatar modeling. Extensive experiments show that FastAvatar has higher quality and highly competitive speed compared to existing methods.
HI-TOM: A Benchmark for Evaluating Higher-Order Theory of Mind Reasoning in Large Language Models
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) is the ability to reason about one's own and others' mental states. ToM plays a critical role in the development of intelligence, language understanding, and cognitive processes. While previous work has primarily focused on first and second-order ToM, we explore higher-order ToM, which involves recursive reasoning on others' beliefs. We introduce HI-TOM, a Higher Order Theory of Mind benchmark. Our experimental evaluation using various Large Language Models (LLMs) indicates a decline in performance on higher-order ToM tasks, demonstrating the limitations of current LLMs. We conduct a thorough analysis of different failure cases of LLMs, and share our thoughts on the implications of our findings on the future of NLP.
* Accepted at Findings of EMNLP 2023
Interpretability is a Kind of Safety: An Interpreter-based Ensemble for Adversary Defense
Apr 14, 2023Abstract:While having achieved great success in rich real-life applications, deep neural network (DNN) models have long been criticized for their vulnerability to adversarial attacks. Tremendous research efforts have been dedicated to mitigating the threats of adversarial attacks, but the essential trait of adversarial examples is not yet clear, and most existing methods are yet vulnerable to hybrid attacks and suffer from counterattacks. In light of this, in this paper, we first reveal a gradient-based correlation between sensitivity analysis-based DNN interpreters and the generation process of adversarial examples, which indicates the Achilles's heel of adversarial attacks and sheds light on linking together the two long-standing challenges of DNN: fragility and unexplainability. We then propose an interpreter-based ensemble framework called X-Ensemble for robust adversary defense. X-Ensemble adopts a novel detection-rectification process and features in building multiple sub-detectors and a rectifier upon various types of interpretation information toward target classifiers. Moreover, X-Ensemble employs the Random Forests (RF) model to combine sub-detectors into an ensemble detector for adversarial hybrid attacks defense. The non-differentiable property of RF further makes it a precious choice against the counterattack of adversaries. Extensive experiments under various types of state-of-the-art attacks and diverse attack scenarios demonstrate the advantages of X-Ensemble to competitive baseline methods.
* 10 pages, accepted to KDD'20
ConvTransformer: A Convolutional Transformer Network for Video Frame Synthesis
Nov 20, 2020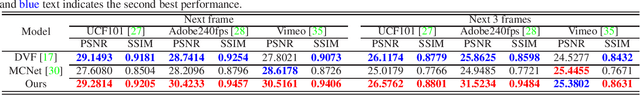
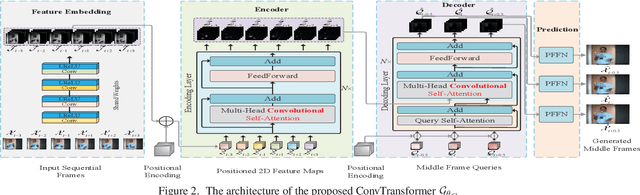
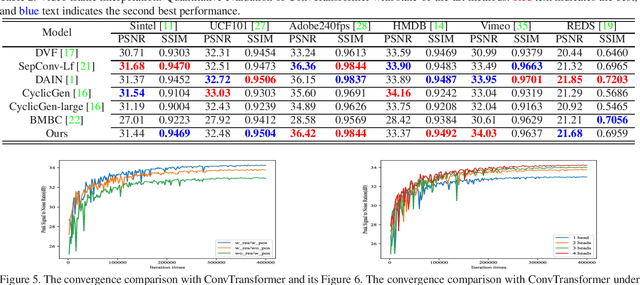
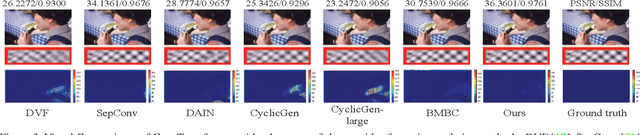
Abstract:Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are powerful models that have achieved excellent performance on difficult computer vision tasks. Although CNNS perform well whenever large labeled training samples are available, they work badly on video frame synthesis due to objects deforming and moving, scene lighting changes, and cameras moving in video sequence. In this paper, we present a novel and general end-to-end architecture, called convolutional Transformer or ConvTransformer, for video frame sequence learning and video frame synthesis. The core ingredient of ConvTransformer is the proposed attention layer, i.e., multi-head convolutional self-attention, that learns the sequential dependence of video sequence. Our method ConvTransformer uses an encoder, built upon multi-head convolutional self-attention layers, to map the input sequence to a feature map sequence, and then another deep networks, incorporating multi-head convolutional self-attention layers, decode the target synthesized frames from the feature maps sequence. Experiments on video future frame extrapolation task show ConvTransformer to be superior in quality while being more parallelizable to recent approaches built upon convoltuional LSTM (ConvLSTM). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that ConvTransformer architecture is proposed and applied to video frame synthesis.
Detecting and Recovering Adversarial Examples: An Input Sensitivity Guided Method
Feb 28, 2020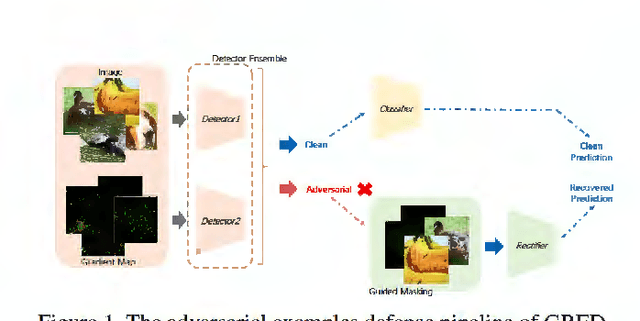
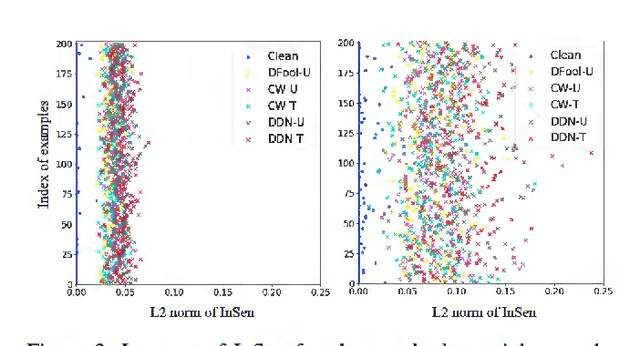

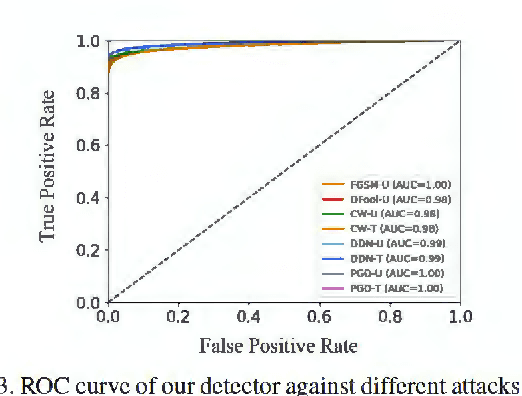
Abstract:Deep neural networks undergo rapid development and achieve notable success in various tasks, including many security concerned scenarios. However, a considerable amount of works have proved its vulnerability in adversaries. To address this problem, we propose a Guided Robust and Efficient Defensive Model GRED integrating detection and recovery processes together. From the lens of the properties of gradient distribution of adversarial examples, our model detects malicious inputs effectively, as well as recovering the ground-truth label with high accuracy. Compared with commonly used adversarial training methods, our model is more efficient and outperforms state-of-the-art adversarial trained models by a large margin up to 99% on MNIST, 89 % on CIFAR-10 and 87% on ImageNet subsets. When exclusively compared with previous adversarial detection methods, the detector of GRED is robust under all threat settings with a detection rate of over 95% against most of the attacks. It is also demonstrated by empirical assessment that our model could increase attacking cost significantly resulting in either unacceptable time consuming or human perceptible image distortions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge