Yilin Jia
HI-TOM: A Benchmark for Evaluating Higher-Order Theory of Mind Reasoning in Large Language Models
Oct 25, 2023



Abstract:Theory of Mind (ToM) is the ability to reason about one's own and others' mental states. ToM plays a critical role in the development of intelligence, language understanding, and cognitive processes. While previous work has primarily focused on first and second-order ToM, we explore higher-order ToM, which involves recursive reasoning on others' beliefs. We introduce HI-TOM, a Higher Order Theory of Mind benchmark. Our experimental evaluation using various Large Language Models (LLMs) indicates a decline in performance on higher-order ToM tasks, demonstrating the limitations of current LLMs. We conduct a thorough analysis of different failure cases of LLMs, and share our thoughts on the implications of our findings on the future of NLP.
* Accepted at Findings of EMNLP 2023
Enhancing Long-form Text Generation Efficacy with Task-adaptive Tokenization
Oct 23, 2023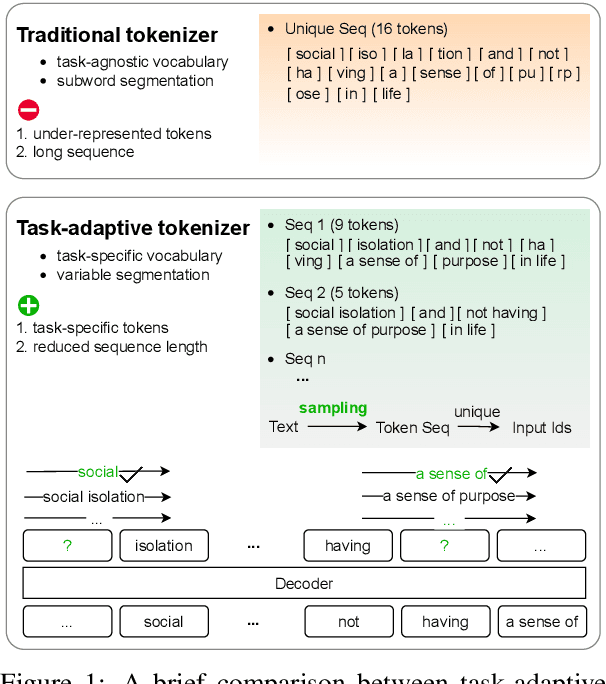
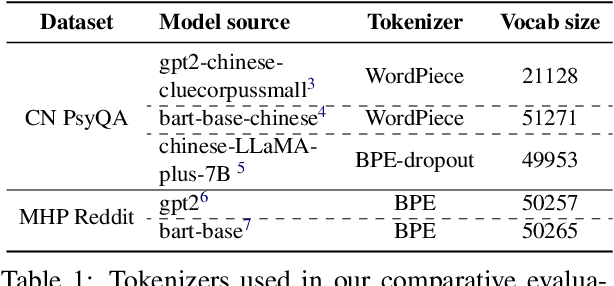
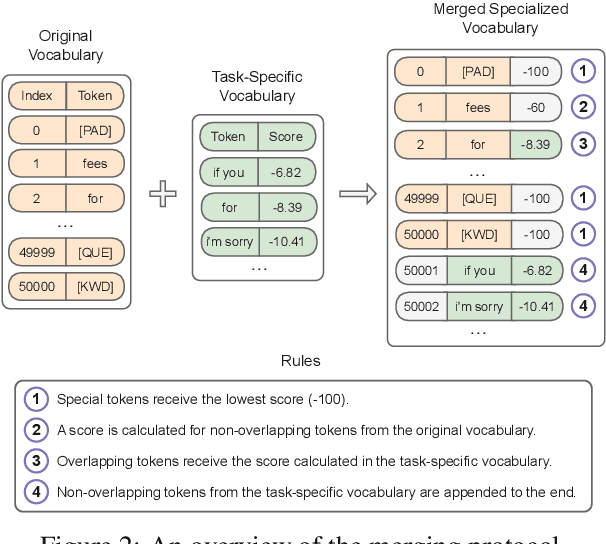
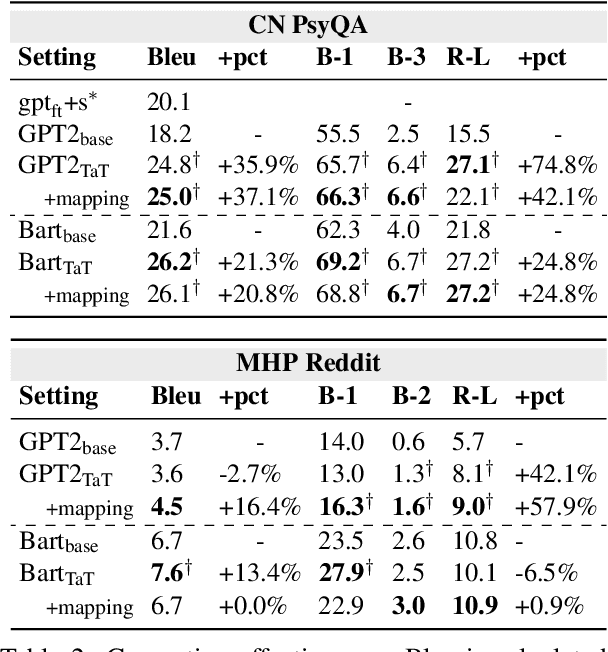
Abstract:We propose task-adaptive tokenization as a way to adapt the generation pipeline to the specifics of a downstream task and enhance long-form generation in mental health. Inspired by insights from cognitive science, our task-adaptive tokenizer samples variable segmentations from multiple outcomes, with sampling probabilities optimized based on task-specific data. We introduce a strategy for building a specialized vocabulary and introduce a vocabulary merging protocol that allows for the integration of task-specific tokens into the pre-trained model's tokenization step. Through extensive experiments on psychological question-answering tasks in both Chinese and English, we find that our task-adaptive tokenization approach brings a significant improvement in generation performance while using up to 60% fewer tokens. Preliminary experiments point to promising results when using our tokenization approach with very large language models.
* Accepted at the main conference of The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; 8 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge