Yuejia Xiang
Vision, Deduction and Alignment: An Empirical Study on Multi-modal Knowledge Graph Alignment
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Entity alignment (EA) for knowledge graphs (KGs) plays a critical role in knowledge engineering. Existing EA methods mostly focus on utilizing the graph structures and entity attributes (including literals), but ignore images that are common in modern multi-modal KGs. In this study we first constructed Multi-OpenEA -- eight large-scale, image-equipped EA benchmarks, and then evaluated some existing embedding-based methods for utilizing images. In view of the complementary nature of visual modal information and logical deduction, we further developed a new multi-modal EA method named LODEME using logical deduction and multi-modal KG embedding, with state-of-the-art performance achieved on Multi-OpenEA and other existing multi-modal EA benchmarks.
Graph-MVP: Multi-View Prototypical Contrastive Learning for Multiplex Graphs
Sep 08, 2021



Abstract:Contrastive Learning (CL) is one of the most popular self-supervised learning frameworks for graph representation learning, which trains a Graph Neural Network (GNN) by discriminating positive and negative node pairs. However, there are two challenges for CL on graphs. On the one hand, traditional CL methods will unavoidably introduce semantic errors since they will treat some semantically similar nodes as negative pairs. On the other hand, most of the existing CL methods ignore the multiplexity nature of the real-world graphs, where nodes are connected by various relations and each relation represents a view of the graph. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Graph Multi-View Prototypical (Graph-MVP) framework to extract node embeddings on multiplex graphs. Firstly, we introduce a Graph Prototypical Contrastive Learning (Graph-PCL) framework to capture both node-level and semantic-level information for each view of multiplex graphs. Graph-PCL captures the node-level information by a simple yet effective data transformation technique. It captures the semantic-level information by an Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm, which alternatively performs clustering over node embeddings and parameter updating for GNN. Next, we introduce Graph-MVP based on Graph-PCL to jointly model different views of the multiplex graphs. Our key insight behind Graph-MVP is that different view-specific embeddings of the same node should have similar underlying semantic, based on which we propose two versions of Graph-MVP: Graph-MVP_hard and Graph-MVP_soft to align embeddings across views. Finally, we evaluate the proposed Graph-PCL and Graph-MVP on a variety of real-world datasets and downstream tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed Graph-PCL and Graph-MVP frameworks.
OntoEA: Ontology-guided Entity Alignment via Joint Knowledge Graph Embedding
May 24, 2021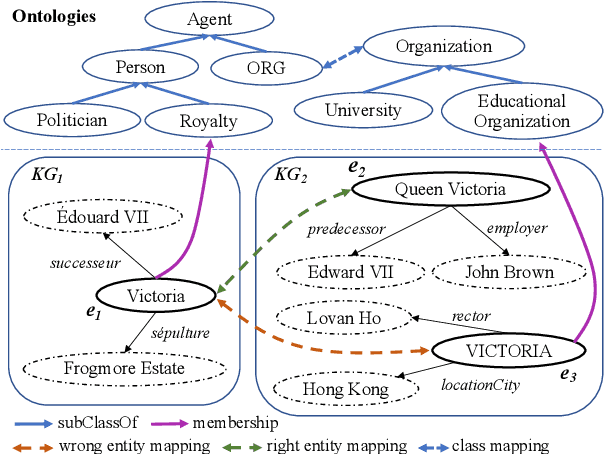
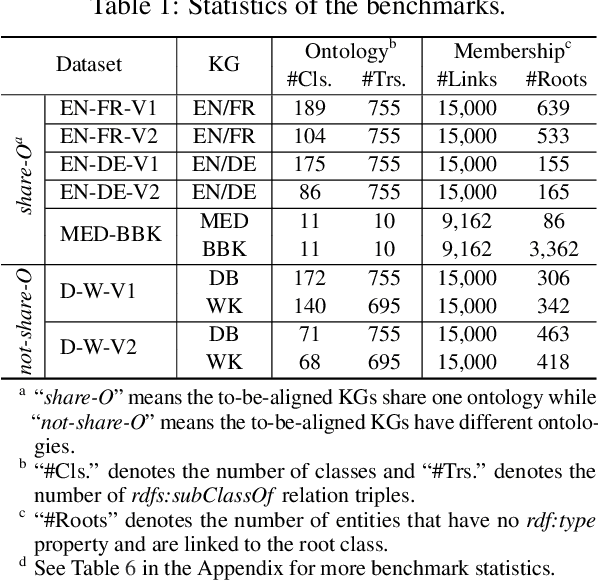
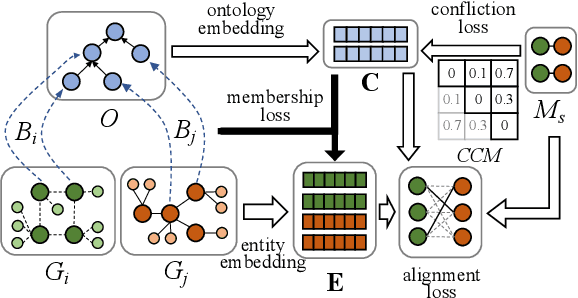
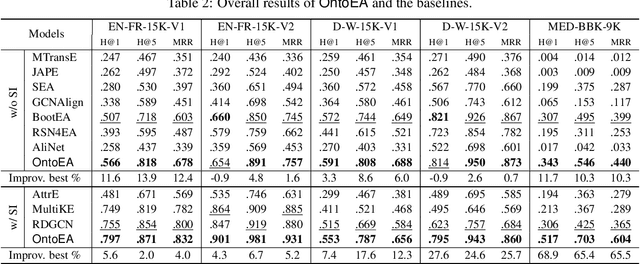
Abstract:Semantic embedding has been widely investigated for aligning knowledge graph (KG) entities. Current methods have explored and utilized the graph structure, the entity names and attributes, but ignore the ontology (or ontological schema) which contains critical meta information such as classes and their membership relationships with entities. In this paper, we propose an ontology-guided entity alignment method named OntoEA, where both KGs and their ontologies are jointly embedded, and the class hierarchy and the class disjointness are utilized to avoid false mappings. Extensive experiments on seven public and industrial benchmarks have demonstrated the state-of-the-art performance of OntoEA and the effectiveness of the ontologies.
Unsupervised Knowledge Graph Alignment by Probabilistic Reasoning and Semantic Embedding
May 19, 2021



Abstract:Knowledge Graph (KG) alignment is to discover the mappings (i.e., equivalent entities, relations, and others) between two KGs. The existing methods can be divided into the embedding-based models, and the conventional reasoning and lexical matching based systems. The former compute the similarity of entities via their cross-KG embeddings, but they usually rely on an ideal supervised learning setting for good performance and lack appropriate reasoning to avoid logically wrong mappings; while the latter address the reasoning issue but are poor at utilizing the KG graph structures and the entity contexts. In this study, we aim at combining the above two solutions and thus propose an iterative framework named PRASE which is based on probabilistic reasoning and semantic embedding. It learns the KG embeddings via entity mappings from a probabilistic reasoning system named PARIS, and feeds the resultant entity mappings and embeddings back into PARIS for augmentation. The PRASE framework is compatible with different embedding-based models, and our experiments on multiple datasets have demonstrated its state-of-the-art performance.
An Industry Evaluation of Embedding-based Entity Alignment
Nov 07, 2020



Abstract:Embedding-based entity alignment has been widely investigated in recent years, but most proposed methods still rely on an ideal supervised learning setting with a large number of unbiased seed mappings for training and validation, which significantly limits their usage. In this study, we evaluate those state-of-the-art methods in an industrial context, where the impact of seed mappings with different sizes and different biases is explored. Besides the popular benchmarks from DBpedia and Wikidata, we contribute and evaluate a new industrial benchmark that is extracted from two heterogeneous knowledge graphs (KGs) under deployment for medical applications. The experimental results enable the analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of these alignment methods and the further discussion of suitable strategies for their industrial deployment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge