Yongqun He
N3C Natural Language Processing
A Fourfold Pathogen Reference Ontology Suite
Dec 31, 2024
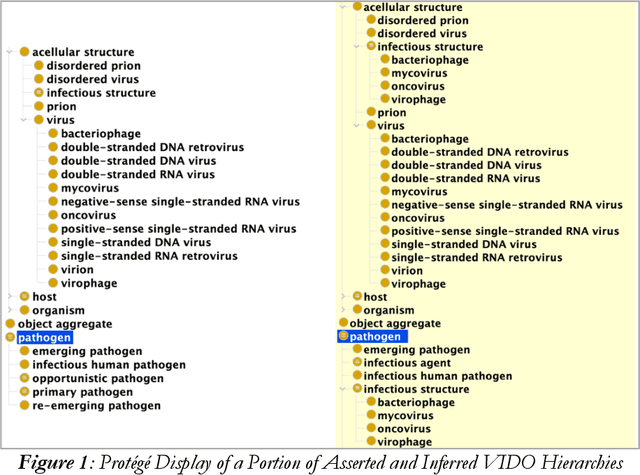


Abstract:Infectious diseases remain a critical global health challenge, and the integration of standardized ontologies plays a vital role in managing related data. The Infectious Disease Ontology (IDO) and its extensions, such as the Coronavirus Infectious Disease Ontology (CIDO), are essential for organizing and disseminating information related to infectious diseases. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for updating IDO and its virus-specific extensions. There is an additional need to update IDO extensions specific to bacteria, fungus, and parasite infectious diseases. We adopt the "hub and spoke" methodology to generate pathogen-specific extensions of IDO: Virus Infectious Disease Ontology (VIDO), Bacteria Infectious Disease Ontology (BIDO), Mycosis Infectious Disease Ontology (MIDO), and Parasite Infectious Disease Ontology (PIDO). The creation of pathogen-specific reference ontologies advances modularization and reusability of infectious disease data within the IDO ecosystem. Future work will focus on further refining these ontologies, creating new extensions, and developing application ontologies based on them, in line with ongoing efforts to standardize biological and biomedical terminologies for improved data sharing and analysis.
Grounding Realizable Entities
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:Ontological representations of qualities, dispositions, and roles have been refined over the past decade, clarifying subtle distinctions in life science research. After articulating a widely-used characterization of these entities within the context of Basic Formal Ontology (BFO), we identify gaps in this treatment and motivate the need for supplementing the BFO characterization. By way of supplement, we propose definitions for grounding relations holding between qualities and dispositions, and dispositions and roles, illustrating our proposal by representing subtle aspects of host-pathogen interactions.
Credentials in the Occupation Ontology
Apr 30, 2024



Abstract:The term credential encompasses educational certificates, degrees, certifications, and government-issued licenses. An occupational credential is a verification of an individuals qualification or competence issued by a third party with relevant authority. Job seekers often leverage such credentials as evidence that desired qualifications are satisfied by their holders. Many U.S. education and workforce development organizations have recognized the importance of credentials for employment and the challenges of understanding the value of credentials. In this study, we identified and ontologically defined credential and credential-related terms at the textual and semantic levels based on the Occupation Ontology (OccO), a BFO-based ontology. Different credential types and their authorization logic are modeled. We additionally defined a high-level hierarchy of credential related terms and relations among many terms, which were initiated in concert with the Alabama Talent Triad (ATT) program, which aims to connect learners, earners, employers and education/training providers through credentials and skills. To our knowledge, our research provides for the first time systematic ontological modeling of the important domain of credentials and related contents, supporting enhanced credential data and knowledge integration in the future.
Evaluation of GPT and BERT-based models on identifying protein-protein interactions in biomedical text
Mar 30, 2023Abstract:Detecting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) is crucial for understanding genetic mechanisms, disease pathogenesis, and drug design. However, with the fast-paced growth of biomedical literature, there is a growing need for automated and accurate extraction of PPIs to facilitate scientific knowledge discovery. Pre-trained language models, such as generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) and bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT), have shown promising results in natural language processing (NLP) tasks. We evaluated the PPI identification performance of various GPT and BERT models using a manually curated benchmark corpus of 164 PPIs in 77 sentences from learning language in logic (LLL). BERT-based models achieved the best overall performance, with PubMedBERT achieving the highest precision (85.17%) and F1-score (86.47%) and BioM-ALBERT achieving the highest recall (93.83%). Despite not being explicitly trained for biomedical texts, GPT-4 achieved comparable performance to the best BERT models with 83.34% precision, 76.57% recall, and 79.18% F1-score. These findings suggest that GPT models can effectively detect PPIs from text data and have the potential for use in biomedical literature mining tasks.
An Open Natural Language Processing Development Framework for EHR-based Clinical Research: A case demonstration using the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C)
Oct 20, 2021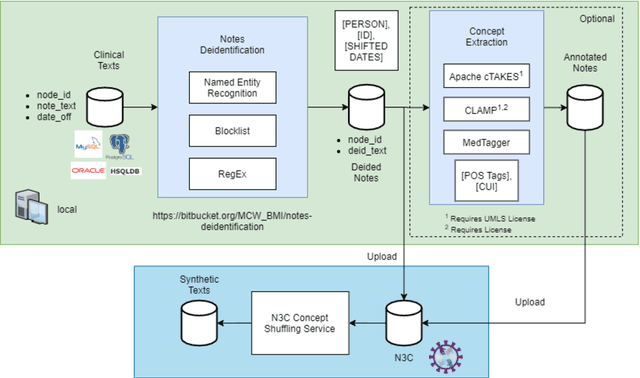
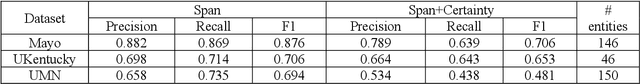
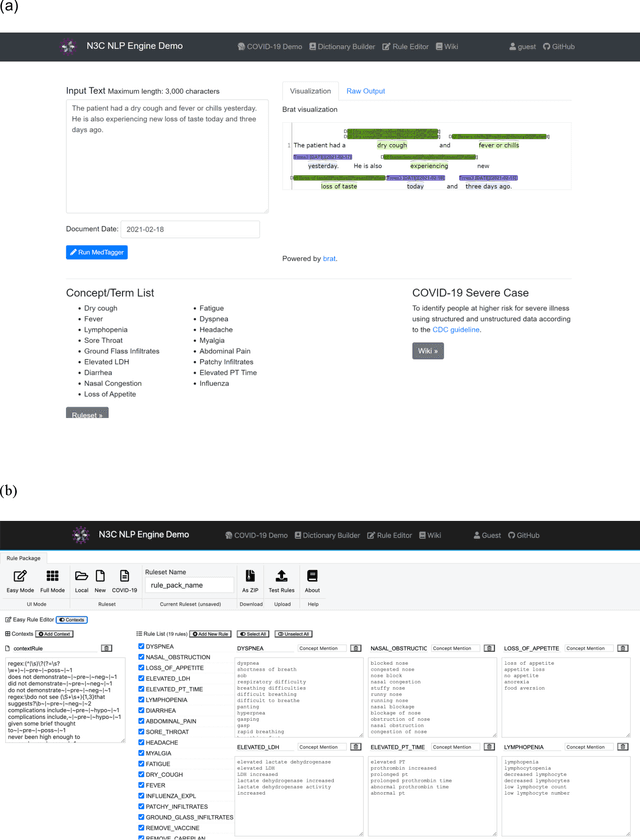
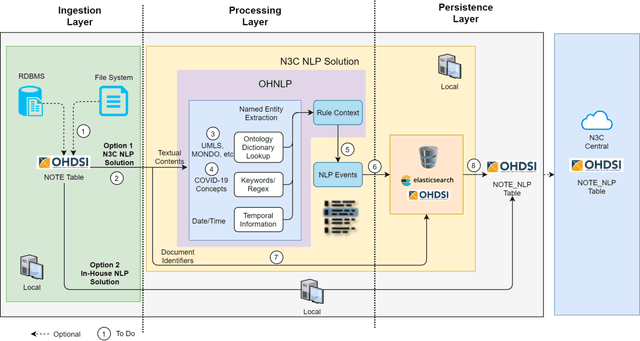
Abstract:While we pay attention to the latest advances in clinical natural language processing (NLP), we can notice some resistance in the clinical and translational research community to adopt NLP models due to limited transparency, Interpretability and usability. Built upon our previous work, in this study, we proposed an open natural language processing development framework and evaluated it through the implementation of NLP algorithms for the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C). Based on the interests in information extraction from COVID-19 related clinical notes, our work includes 1) an open data annotation process using COVID-19 signs and symptoms as the use case, 2) a community-driven ruleset composing platform, and 3) a synthetic text data generation workflow to generate texts for information extraction tasks without involving human subjects. The generated corpora derived out of the texts from multiple intuitions and gold standard annotation are tested on a single institution's rule set has the performances in F1 score of 0.876, 0.706 and 0.694, respectively. The study as a consortium effort of the N3C NLP subgroup demonstrates the feasibility of creating a federated NLP algorithm development and benchmarking platform to enhance multi-institution clinical NLP study.
OntoPlot: A Novel Visualisation for Non-hierarchical Associations in Large Ontologies
Aug 02, 2019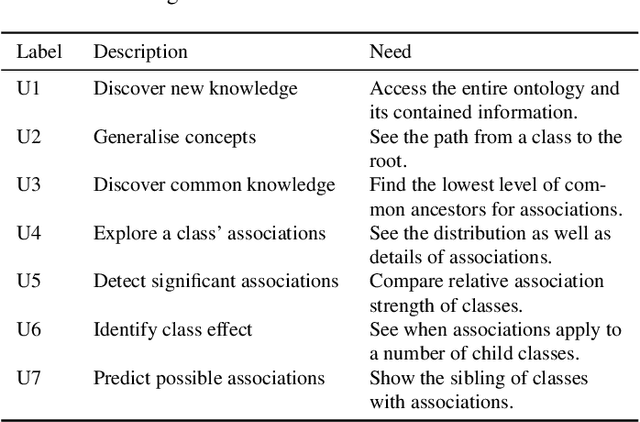
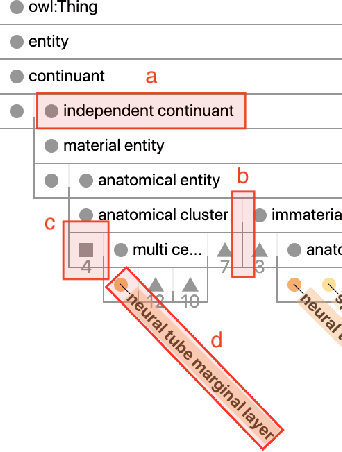
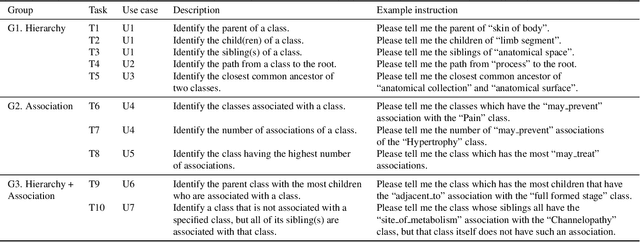
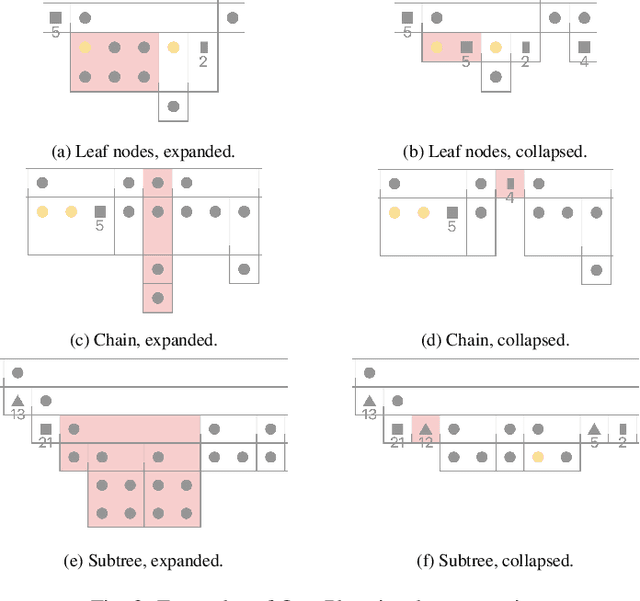
Abstract:Ontologies are formal representations of concepts and complex relationships among them. They have been widely used to capture comprehensive domain knowledge in areas such as biology and medicine, where large and complex ontologies can contain hundreds of thousands of concepts. Especially due to the large size of ontologies, visualisation is useful for authoring, exploring and understanding their underlying data. Existing ontology visualisation tools generally focus on the hierarchical structure, giving much less emphasis to non-hierarchical associations. In this paper we present OntoPlot, a novel visualisation specifically designed to facilitate the exploration of all concept associations whilst still showing an ontology's large hierarchical structure. This hybrid visualisation combines icicle plots, visual compression techniques and interactivity, improving space-efficiency and reducing visual structural complexity. We conducted a user study with domain experts to evaluate the usability of OntoPlot, comparing it with the de facto ontology editor Prot{\'e}g{\'e}. The results confirm that OntoPlot attains our design goals for association-related tasks and is strongly favoured by domain experts.
HINO: a BFO-aligned ontology representing human molecular interactions and pathways
Nov 14, 2013



Abstract:Many database resources, such as Reactome, collect manually annotated reactions, interactions, and pathways from peer-reviewed publications. The interactors (e.g., a protein), interactions, and pathways in these data resources are often represented as instances in using BioPAX, a standard pathway data exchange format. However, these interactions are better represented as classes (or universals) since they always occur given appropriate conditions. This study aims to represent various human interaction pathways and networks as classes via a formal ontology aligned with the Basic Formal Ontology (BFO). Towards this goal, the Human Interaction Network Ontology (HINO) was generated by extending the BFO-aligned Interaction Network Ontology (INO). All human pathways and associated processes and interactors listed in Reactome and represented in BioPAX were first converted to ontology classes by aligning them under INO. Related terms and associated relations and hierarchies from external ontologies (e.g., CHEBI and GO) were also retrieved and imported into HINO. HINO ontology terms were resolved in the linked ontology data server Ontobee. The RDF triples stored in the RDF triple store are queryable through a SPARQL program. Such an ontology system supports advanced pathway data integration and applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge