Yongcheng Liu
Differentiable Convolution Search for Point Cloud Processing
Aug 29, 2021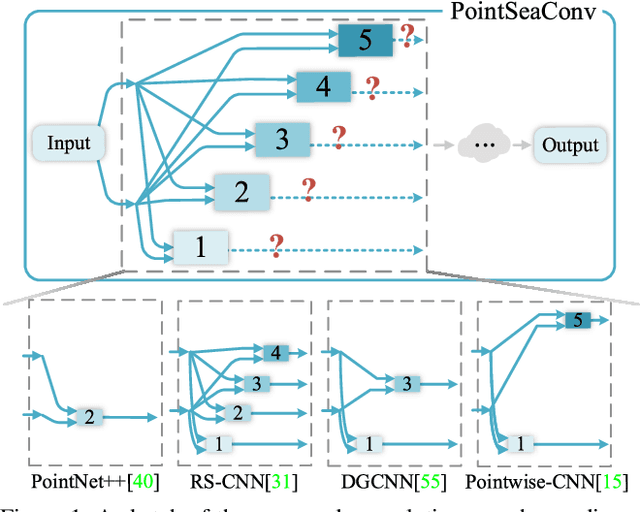

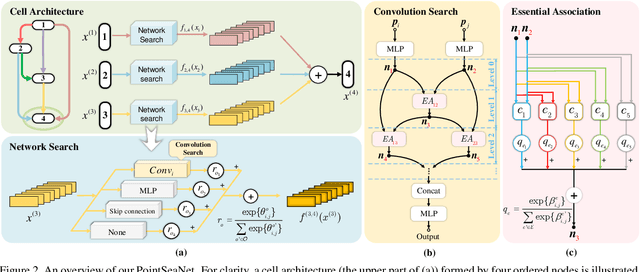
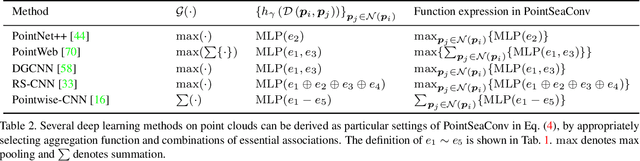
Abstract:Exploiting convolutional neural networks for point cloud processing is quite challenging, due to the inherent irregular distribution and discrete shape representation of point clouds. To address these problems, many handcrafted convolution variants have sprung up in recent years. Though with elaborate design, these variants could be far from optimal in sufficiently capturing diverse shapes formed by discrete points. In this paper, we propose PointSeaConv, i.e., a novel differential convolution search paradigm on point clouds. It can work in a purely data-driven manner and thus is capable of auto-creating a group of suitable convolutions for geometric shape modeling. We also propose a joint optimization framework for simultaneous search of internal convolution and external architecture, and introduce epsilon-greedy algorithm to alleviate the effect of discretization error. As a result, PointSeaNet, a deep network that is sufficient to capture geometric shapes at both convolution level and architecture level, can be searched out for point cloud processing. Extensive experiments strongly evidence that our proposed PointSeaNet surpasses current handcrafted deep models on challenging benchmarks across multiple tasks with remarkable margins.
DensePoint: Learning Densely Contextual Representation for Efficient Point Cloud Processing
Sep 09, 2019



Abstract:Point cloud processing is very challenging, as the diverse shapes formed by irregular points are often indistinguishable. A thorough grasp of the elusive shape requires sufficiently contextual semantic information, yet few works devote to this. Here we propose DensePoint, a general architecture to learn densely contextual representation for point cloud processing. Technically, it extends regular grid CNN to irregular point configuration by generalizing a convolution operator, which holds the permutation invariance of points, and achieves efficient inductive learning of local patterns. Architecturally, it finds inspiration from dense connection mode, to repeatedly aggregate multi-level and multi-scale semantics in a deep hierarchy. As a result, densely contextual information along with rich semantics, can be acquired by DensePoint in an organic manner, making it highly effective. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks across four tasks, as well as thorough model analysis, verify DensePoint achieves the state of the arts.
Relation-Shape Convolutional Neural Network for Point Cloud Analysis
May 26, 2019



Abstract:Point cloud analysis is very challenging, as the shape implied in irregular points is difficult to capture. In this paper, we propose RS-CNN, namely, Relation-Shape Convolutional Neural Network, which extends regular grid CNN to irregular configuration for point cloud analysis. The key to RS-CNN is learning from relation, i.e., the geometric topology constraint among points. Specifically, the convolutional weight for local point set is forced to learn a high-level relation expression from predefined geometric priors, between a sampled point from this point set and the others. In this way, an inductive local representation with explicit reasoning about the spatial layout of points can be obtained, which leads to much shape awareness and robustness. With this convolution as a basic operator, RS-CNN, a hierarchical architecture can be developed to achieve contextual shape-aware learning for point cloud analysis. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks across three tasks verify RS-CNN achieves the state of the arts.
Multi-Label Image Classification via Knowledge Distillation from Weakly-Supervised Detection
Sep 16, 2018



Abstract:Multi-label image classification is a fundamental but challenging task towards general visual understanding. Existing methods found the region-level cues (e.g., features from RoIs) can facilitate multi-label classification. Nevertheless, such methods usually require laborious object-level annotations (i.e., object labels and bounding boxes) for effective learning of the object-level visual features. In this paper, we propose a novel and efficient deep framework to boost multi-label classification by distilling knowledge from weakly-supervised detection task without bounding box annotations. Specifically, given the image-level annotations, (1) we first develop a weakly-supervised detection (WSD) model, and then (2) construct an end-to-end multi-label image classification framework augmented by a knowledge distillation module that guides the classification model by the WSD model according to the class-level predictions for the whole image and the object-level visual features for object RoIs. The WSD model is the teacher model and the classification model is the student model. After this cross-task knowledge distillation, the performance of the classification model is significantly improved and the efficiency is maintained since the WSD model can be safely discarded in the test phase. Extensive experiments on two large-scale datasets (MS-COCO and NUS-WIDE) show that our framework achieves superior performances over the state-of-the-art methods on both performance and efficiency.
Semantic Labeling in Very High Resolution Images via a Self-Cascaded Convolutional Neural Network
Jul 30, 2018



Abstract:Semantic labeling for very high resolution (VHR) images in urban areas, is of significant importance in a wide range of remote sensing applications. However, many confusing manmade objects and intricate fine-structured objects make it very difficult to obtain both coherent and accurate labeling results. For this challenging task, we propose a novel deep model with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), i.e., an end-to-end self-cascaded network (ScasNet). Specifically, for confusing manmade objects, ScasNet improves the labeling coherence with sequential global-to-local contexts aggregation. Technically, multi-scale contexts are captured on the output of a CNN encoder, and then they are successively aggregated in a self-cascaded manner. Meanwhile, for fine-structured objects, ScasNet boosts the labeling accuracy with a coarse-to-fine refinement strategy. It progressively refines the target objects using the low-level features learned by CNN's shallow layers. In addition, to correct the latent fitting residual caused by multi-feature fusion inside ScasNet, a dedicated residual correction scheme is proposed. It greatly improves the effectiveness of ScasNet. Extensive experimental results on three public datasets, including two challenging benchmarks, show that ScasNet achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge