Yingjie Yin
Facial Affect Analysis: Learning from Synthetic Data & Multi-Task Learning Challenges
Jul 20, 2022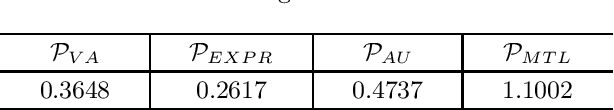
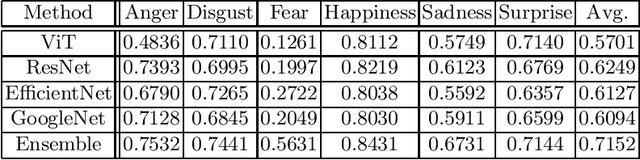
Abstract:Facial affect analysis remains a challenging task with its setting transitioned from lab-controlled to in-the-wild situations. In this paper, we present novel frameworks to handle the two challenges in the 4th Affective Behavior Analysis In-The-Wild (ABAW) competition: i) Multi-Task-Learning (MTL) Challenge and ii) Learning from Synthetic Data (LSD) Challenge. For MTL challenge, we adopt the SMM-EmotionNet with a better ensemble strategy of feature vectors. For LSD challenge, we propose respective methods to combat the problems of single labels, imbalanced distribution, fine-tuning limitations, and choice of model architectures. Experimental results on the official validation sets from the competition demonstrated that our proposed approaches outperformed baselines by a large margin. The code is available at https://github.com/sylyoung/ABAW4-HUST-ANT.
Directional Deep Embedding and Appearance Learning for Fast Video Object Segmentation
Feb 17, 2020



Abstract:Most recent semi-supervised video object segmentation (VOS) methods rely on fine-tuning deep convolutional neural networks online using the given mask of the first frame or predicted masks of subsequent frames. However, the online fine-tuning process is usually time-consuming, limiting the practical use of such methods. We propose a directional deep embedding and appearance learning (DDEAL) method, which is free of the online fine-tuning process, for fast VOS. First, a global directional matching module, which can be efficiently implemented by parallel convolutional operations, is proposed to learn a semantic pixel-wise embedding as an internal guidance. Second, an effective directional appearance model based statistics is proposed to represent the target and background on a spherical embedding space for VOS. Equipped with the global directional matching module and the directional appearance model learning module, DDEAL learns static cues from the labeled first frame and dynamically updates cues of the subsequent frames for object segmentation. Our method exhibits state-of-the-art VOS performance without using online fine-tuning. Specifically, it achieves a J & F mean score of 74.8% on DAVIS 2017 dataset and an overall score G of 71.3% on the large-scale YouTube-VOS dataset, while retaining a speed of 25 fps with a single NVIDIA TITAN Xp GPU. Furthermore, our faster version runs 31 fps with only a little accuracy loss. Our code and trained networks are available at https://github.com/YingjieYin/Directional-Deep-Embedding-and-Appearance-Learning-for-Fast-Video-Object-Segmentation.
Multiple receptive fields and small-object-focusing weakly-supervised segmentation network for fast object detection
May 22, 2019



Abstract:Object detection plays an important role in various visual applications. However, the precision and speed of detector are usually contradictory. One main reason for fast detectors' precision reduction is that small objects are hard to be detected. To address this problem, we propose a multiple receptive field and small-object-focusing weakly-supervised segmentation network (MRFSWSnet) to achieve fast object detection. In MRFSWSnet, multiple receptive fields block (MRF) is used to pay attention to the object and its adjacent background's different spatial location with different weights to enhance the feature's discriminability. In addition, in order to improve the accuracy of small object detection, a small-object-focusing weakly-supervised segmentation module which only focuses on small object instead of all objects is integrated into the detection network for auxiliary training to improve the precision of small object detection. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our method on both PASCAL VOC and MS COCO detection datasets. In particular, with a lower resolution version of 300x300, MRFSWSnet achieves 80.9% mAP on VOC2007 test with an inference speed of 15 milliseconds per frame, which is the state-of-the-art detector among real-time detectors.
Adversarial Feature Sampling Learning for Efficient Visual Tracking
Sep 15, 2018



Abstract:The tracking-by-detection framework usually consist of two stages: drawing samples around the target object in the first stage and classifying each sample as the target object or background in the second stage. Current popular trackers based on tracking-by-detection framework typically draw samples in the raw image as the inputs of deep convolution networks in the first stage, which usually results in high computational burden and low running speed. In this paper, we propose a new visual tracking method using sampling deep convolutional features to address this problem. Only one cropped image around the target object is input into the designed deep convolution network and the samples is sampled on the feature maps of the network by spatial bilinear resampling. In addition, a generative adversarial network is integrated into our network framework to augment positive samples and improve the tracking performance. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a comparable performance to state-of-the-art trackers and accelerates tracking-by-detection trackers based on raw-image samples effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge