Ying-Jun Angela Zhang
FISMO: Fisher-Structured Momentum-Orthogonalized Optimizer
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Training large-scale neural networks requires solving nonconvex optimization where the choice of optimizer fundamentally determines both convergence behavior and computational efficiency. While adaptive methods like Adam have long dominated practice, the recently proposed Muon optimizer achieves superior performance through orthogonalized momentum updates that enforce isotropic geometry with uniform singular values. However, this strict isotropy discards potentially valuable curvature information encoded in gradient spectra, motivating optimization methods that balance geometric structure with adaptivity. We introduce FISMO (Fisher-Structured Momentum-Orthogonalized) optimizer, which generalizes isotropic updates to incorporate anisotropic curvature information through Fisher information geometry. By reformulating the optimizer update as a trust-region problem constrained by a Kronecker-factored Fisher metric, FISMO achieves structured preconditioning that adapts to local loss landscape geometry while maintaining computational tractability. We establish convergence guarantees for FISMO in stochastic nonconvex settings, proving an $\mathcal{O}(1/\sqrt{T})$ rate for the expected squared gradient norm with explicit characterization of variance reduction through mini-batching. Empirical evaluation on image classification and language modeling benchmarks demonstrates that FISMO achieves superior training efficiency and final performance compared to established baselines.
Near-Field Multi-User Communications via Polar-Domain Beamfocusing: Analytical Framework and Performance Analysis
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:As wireless systems evolve toward higher frequencies and extremely large antenna arrays, near-field (NF) propagation becomes increasingly dominant. Unlike far-field (FF) communication, which relies on a planar-wavefront model and is limited to angular-domain beamsteering, NF propagation exhibits spherical wavefronts that enable beamfocusing in both angle and distance, i.e., the polar domain, offering new opportunities for spatial multiple access. This paper develops an analytical stochastic geometry (SG) framework for a multi-user system assisted by polar-domain beamfocusing, which jointly captures NF propagation characteristics and the spatial randomness of user locations. The intrinsic coupling between angle and distance in the NF antenna pattern renders inter-user interference analysis intractable. To address this challenge, we propose a tractable near-field multi-level antenna pattern (NF-MLAP) approximation, which enables computationally efficient expressions and tight upper bounds for key performance metrics, including coverage probability, spectrum efficiency, and area spectrum efficiency. Analytical and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed framework accurately captures performance trends and reveals fundamental trade-offs between hardware configuration (including the number of antennas and radio frequency chains) and system performance (in terms of spatial resource reuse and interference mitigation).
Near-Field Position and Orientation Tracking With Hybrid ELAA Architecture
Dec 19, 2025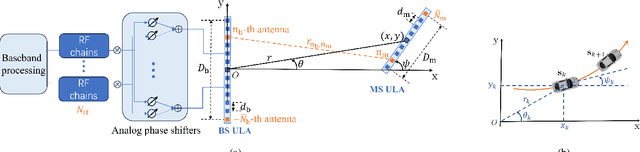
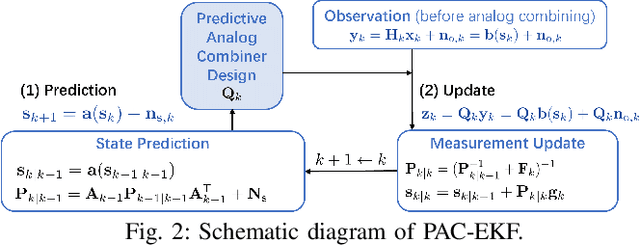
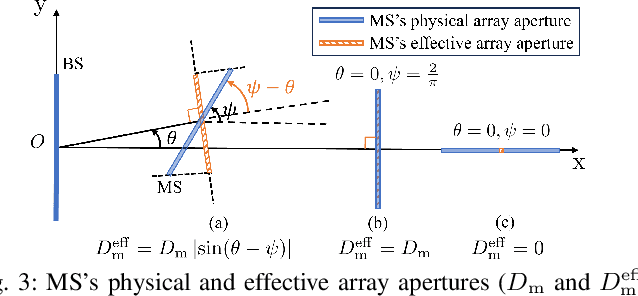
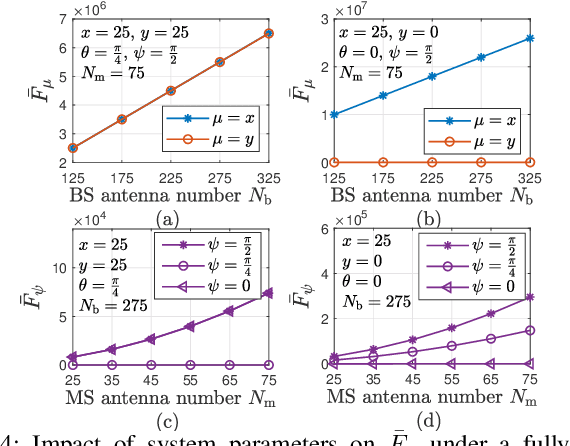
Abstract:This paper investigates near-field (NF) position and orientation tracking of a multi-antenna mobile station (MS) using an extremely large antenna array (ELAA)-equipped base station (BS) with a limited number of radio frequency (RF) chains. Under this hybrid array architecture, the received uplink pilot signal at the BS is first combined by analog phase shifters, producing a low-dimensional observation before digital processing. Such analog compression provides only partial access to the ELAA measurement, making it essential to design an analog combiner that can preserve pose-relevant signal components despite channel uncertainty and unit-modulus hardware constraints. To address this, we propose a predictive analog combining-assisted extended Kalman filter (PAC-EKF) framework, where the analog combiner can leverage the temporal correlation in the MS pose variation to capture the most informative signal components predictively. We then analyze fundamental performance limits via Bayesian Cramér-Rao bound and Fisher information matrix, explicitly quantifying how the analog combiner, array size, signal-to-noise ratio, and MS pose influence the pose information contained in the uplink observation. Building on these insights, we develop two methods for designing a low-complexity analog combiner. Numerical results show that the proposed predictive analog combining approach significantly improves tracking accuracy, even with fewer RF chains and lower transmit power.
Near-Field Beam Training Through Beam Diverging
Sep 19, 2025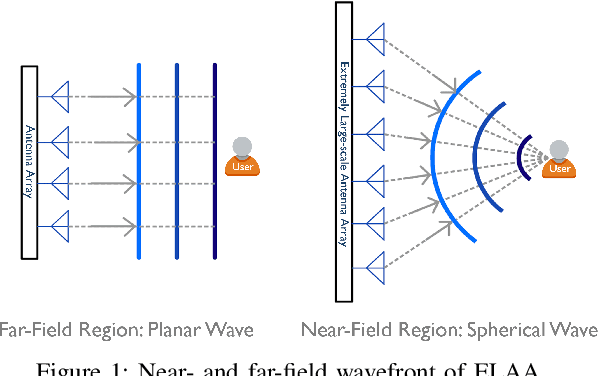
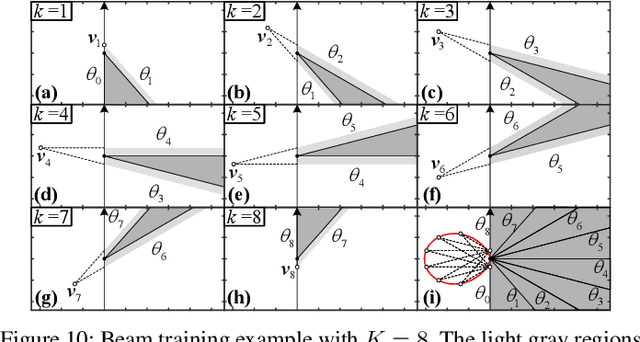
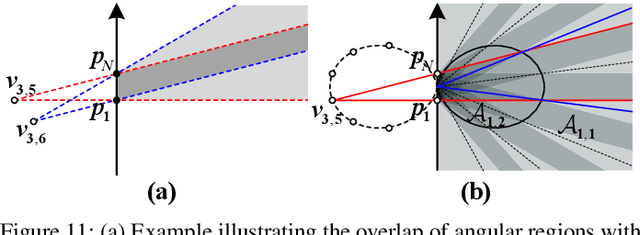
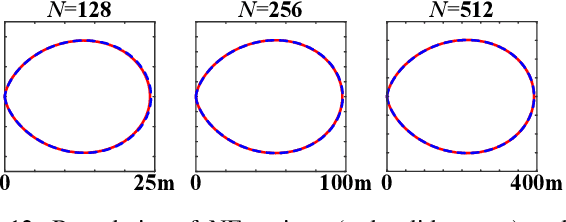
Abstract:This paper investigates beam training techniques for near-field (NF) extremely large-scale antenna arrays (ELAAs). Existing NF beam training methods predominantly rely on beam focusing, where the base station (BS) transmits highly spatially selective beams to locate the user equipment (UE). However, these beam-focusing-based schemes suffer from both high beam sweeping overhead and limited accuracy in the NF, primarily due to the narrow beams' high susceptibility to misalignment. To address this, we propose a novel NF beam training paradigm using diverging beams. Specifically, we introduce the beam diverging effect and exploit it for low-overhead, high-accuracy beam training. First, we design a diverging codeword to induce the beam diverging effect with a single radio frequency (RF) chain. Next, we develop a diverging polar-domain codebook (DPC) along with a hierarchical method that enables angular-domain localization of the UE with only 2 log_2(N) pilots, where N denotes the number of antennas. Finally, we enhance beam training performance through two additional techniques: a DPC angular range reduction strategy to improve the effectiveness of beam diverging, and a pilot set expansion method to increase overall beam training accuracy. Numerical results show that our algorithm achieves near-optimal accuracy with a small pilot overhead, outperforming existing methods.
3D Near-Field Beam Training for Uniform Planar Arrays through Beam Diverging
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In future 6G communication systems, large-scale antenna arrays promise enhanced signal strength and spatial resolution, but they also increase the complexity of beam training. Moreover, as antenna counts grow and carrier wavelengths shrink, the channel model transits from far-field (FF) planar waves to near-field (NF) spherical waves, further complicating the beam training process. This paper focuses on millimeter-wave (mmWave) systems equipped with large-scale uniform planar arrays (UPAs), which produce 3D beam patterns and introduce additional challenges for NF beam training. Existing methods primarily rely on either FF steering or NF focusing codewords, both of which are highly sensitive to mismatches in user equipment (UE) location, leading to high sensitivity to even slight mismatch and excessive training overhead. In contrast, we introduce a novel beam training approach leveraging the beam-diverging effect, which enables adjustable wide-beam coverage using only a single radio frequency (RF) chain. Specifically, we first analyze the spatial characteristics of this effect in UPA systems and leverage them to construct hierarchical codebooks for coarse UE localization. Then, we develop a 3D sampling mechanism to build an NF refinement codebook for precise beam training. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm achieves superior beam training performance while maintaining low training overhead.
Graph Attention-based Decentralized Actor-Critic for Dual-Objective Control of Multi-UAV Swarms
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:This research focuses on optimizing multi-UAV systems with dual objectives: maximizing service coverage as the primary goal while extending battery lifetime as the secondary objective. We propose a Graph Attention-based Decentralized Actor-Critic (GADC) to optimize the dual objectives. The proposed approach leverages a graph attention network to process UAVs' limited local observation and reduce the dimension of the environment states. Subsequently, an actor-double-critic network is developed to manage dual policies for joint objective optimization. The proposed GADC uses a Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence factor to balance the tradeoff between coverage performance and battery lifetime in the multi-UAV system. We assess the scalability and efficiency of GADC through comprehensive benchmarking against state-of-the-art methods, considering both theory and experimental aspects. Extensive testing in both ideal settings and NVIDIA Sionna's realistic ray tracing environment demonstrates GADC's superior performance.
Score-Based Turbo Message Passing for Plug-and-Play Compressive Image Recovery
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:Message passing algorithms have been tailored for compressive imaging applications by plugging in different types of off-the-shelf image denoisers. These off-the-shelf denoisers mostly rely on some generic or hand-crafted priors for denoising. Due to their insufficient accuracy in capturing the true image prior, these methods often fail to produce satisfactory results, especially in largely underdetermined scenarios. On the other hand, score-based generative modeling offers a promising way to accurately characterize the sophisticated image distribution. In this paper, by exploiting the close relation between score-based modeling and empirical Bayes-optimal denoising, we devise a message passing framework that integrates a score-based minimum mean squared error (MMSE) denoiser for compressive image recovery. This framework is firmly rooted in Bayesian formalism, in which state evolution (SE) equations accurately predict its asymptotic performance. Experiments on the FFHQ dataset demonstrate that our method strikes a significantly better performance-complexity tradeoff than conventional message passing, regularized linear regression, and score-based posterior sampling baselines. Remarkably, our method typically requires less than 20 neural function evaluations (NFEs) to converge.
Traversing Distortion-Perception Tradeoff using a Single Score-Based Generative Model
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:The distortion-perception (DP) tradeoff reveals a fundamental conflict between distortion metrics (e.g., MSE and PSNR) and perceptual quality. Recent research has increasingly concentrated on evaluating denoising algorithms within the DP framework. However, existing algorithms either prioritize perceptual quality by sacrificing acceptable distortion, or focus on minimizing MSE for faithful restoration. When the goal shifts or noisy measurements vary, adapting to different points on the DP plane needs retraining or even re-designing the model. Inspired by recent advances in solving inverse problems using score-based generative models, we explore the potential of flexibly and optimally traversing DP tradeoffs using a single pre-trained score-based model. Specifically, we introduce a variance-scaled reverse diffusion process and theoretically characterize the marginal distribution. We then prove that the proposed sample process is an optimal solution to the DP tradeoff for conditional Gaussian distribution. Experimental results on two-dimensional and image datasets illustrate that a single score network can effectively and flexibly traverse the DP tradeoff for general denoising problems.
Joint Coverage and Electromagnetic Field Exposure Analysis in Downlink and Uplink for RIS-assisted Networks
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have shown the potential to improve signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) related coverage, especially at high-frequency communications. However, assessing electromagnetic filed exposure (EMFE) and establishing EMFE regulations in RIS-assisted large-scale networks are still open issues. This paper proposes a framework to characterize SINR and EMFE in such networks for downlink and uplink scenarios. Particularly, we carefully consider the association rule with the presence of RISs, accurate antenna pattern at base stations (BSs), fading model, and power control mechanism at mobile devices in the system model. Under the proposed framework, we derive the marginal and joint distributions of SINR and EMFE in downlink and uplink, respectively. The first moment of EMFE is also provided. Additionally, we design the compliance distance (CD) between a BS/RIS and a user to comply with the EMFE regulations. To facilitate efficient identification, we further provide approximate closed-form expressions for CDs. From numerical results of the marginal distributions, we find that in the downlink scenario, deploying RISs may not always be beneficial, as the improved SINR comes at the cost of increased EMFE. However, in the uplink scenario, RIS deployment is promising to enhance coverage while still maintaining EMFE compliance. By simultaneously evaluating coverage and compliance metrics through joint distributions, we demonstrate the feasibility of RISs in improving uplink and downlink performance. Insights from this framework can contribute to establishing EMFE guidelines and achieving a balance between coverage and compliance when deploying RISs.
FedMABA: Towards Fair Federated Learning through Multi-Armed Bandits Allocation
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:The increasing concern for data privacy has driven the rapid development of federated learning (FL), a privacy-preserving collaborative paradigm. However, the statistical heterogeneity among clients in FL results in inconsistent performance of the server model across various clients. Server model may show favoritism towards certain clients while performing poorly for others, heightening the challenge of fairness. In this paper, we reconsider the inconsistency in client performance distribution and introduce the concept of adversarial multi-armed bandit to optimize the proposed objective with explicit constraints on performance disparities. Practically, we propose a novel multi-armed bandit-based allocation FL algorithm (FedMABA) to mitigate performance unfairness among diverse clients with different data distributions. Extensive experiments, in different Non-I.I.D. scenarios, demonstrate the exceptional performance of FedMABA in enhancing fairness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge