Yanxiong Li
Fully Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification Using Expandable Dual-embedding Extractor
Jun 12, 2024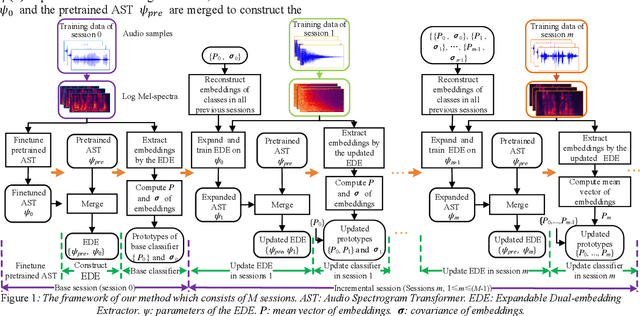
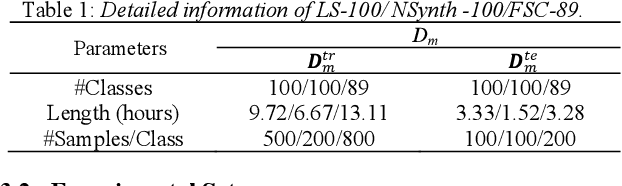
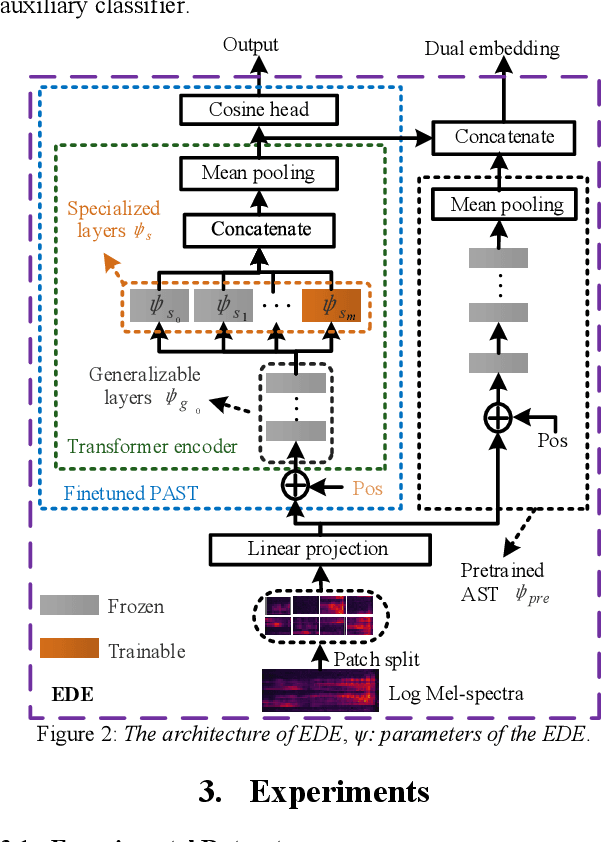
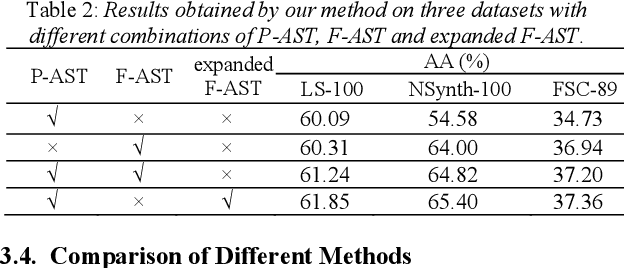
Abstract:It's assumed that training data is sufficient in base session of few-shot class-incremental audio classification. However, it's difficult to collect abundant samples for model training in base session in some practical scenarios due to the data scarcity of some classes. This paper explores a new problem of fully few-shot class-incremental audio classification with few training samples in all sessions. Moreover, we propose a method using expandable dual-embedding extractor to solve it. The proposed model consists of an embedding extractor and an expandable classifier. The embedding extractor consists of a pretrained Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) and a finetuned AST. The expandable classifier consists of prototypes and each prototype represents a class. Experiments are conducted on three datasets (LS-100, NSynth-100 and FSC-89). Results show that our method exceeds seven baseline ones in average accuracy with statistical significance. Code is at: https://github.com/YongjieSi/EDE.
Lightweight Speaker Verification Using Transformation Module with Feature Partition and Fusion
Dec 06, 2023Abstract:Although many efforts have been made on decreasing the model complexity for speaker verification, it is still challenging to deploy speaker verification systems with satisfactory result on low-resource terminals. We design a transformation module that performs feature partition and fusion to implement lightweight speaker verification. The transformation module consists of multiple simple but effective operations, such as convolution, pooling, mean, concatenation, normalization, and element-wise summation. It works in a plug-and-play way, and can be easily implanted into a wide variety of models to reduce the model complexity while maintaining the model error. First, the input feature is split into several low-dimensional feature subsets for decreasing the model complexity. Then, each feature subset is updated by fusing it with the inter-feature-subsets correlational information to enhance its representational capability. Finally, the updated feature subsets are independently fed into the block (one or several layers) of the model for further processing. The features that are output from current block of the model are processed according to the steps above before they are fed into the next block of the model. Experimental data are selected from two public speech corpora (namely VoxCeleb1 and VoxCeleb2). Results show that implanting the transformation module into three models (namely AMCRN, ResNet34, and ECAPA-TDNN) for speaker verification slightly increases the model error and significantly decreases the model complexity. Our proposed method outperforms baseline methods on the whole in memory requirement and computational complexity with lower equal error rate. It also generalizes well across truncated segments with various lengths.
Acoustic Scene Clustering Using Joint Optimization of Deep Embedding Learning and Clustering Iteration
Jun 09, 2023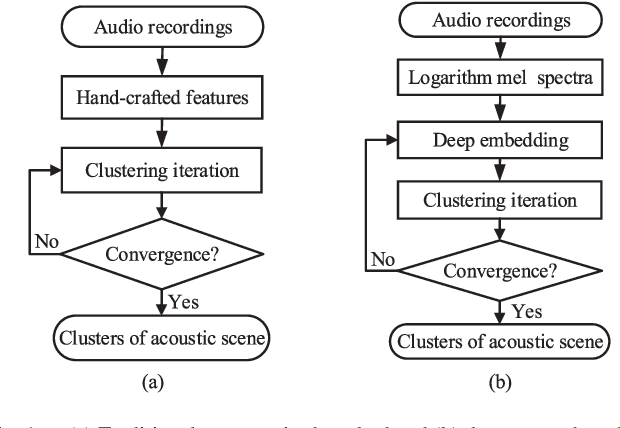
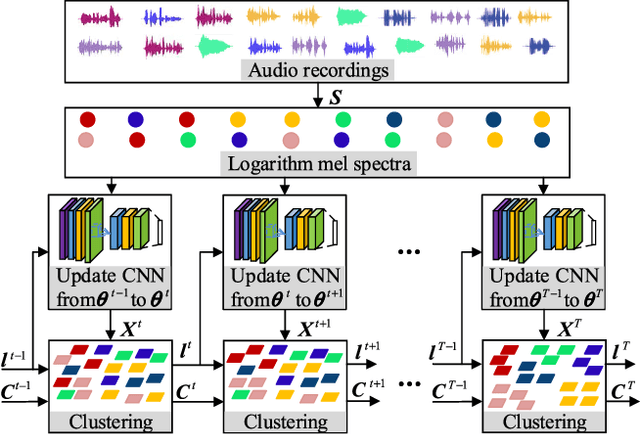
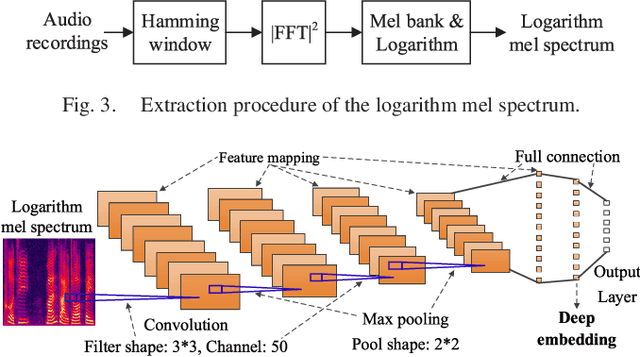
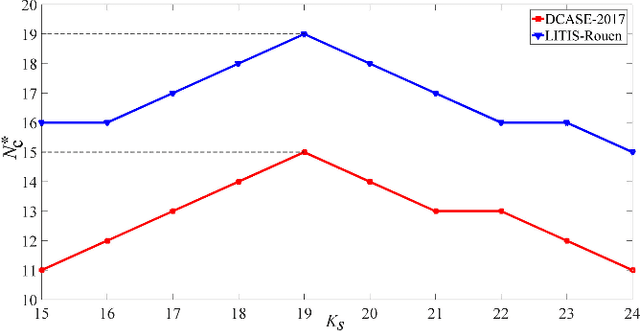
Abstract:Recent efforts have been made on acoustic scene classification in the audio signal processing community. In contrast, few studies have been conducted on acoustic scene clustering, which is a newly emerging problem. Acoustic scene clustering aims at merging the audio recordings of the same class of acoustic scene into a single cluster without using prior information and training classifiers. In this study, we propose a method for acoustic scene clustering that jointly optimizes the procedures of feature learning and clustering iteration. In the proposed method, the learned feature is a deep embedding that is extracted from a deep convolutional neural network (CNN), while the clustering algorithm is the agglomerative hierarchical clustering (AHC). We formulate a unified loss function for integrating and optimizing these two procedures. Various features and methods are compared. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other unsupervised methods in terms of the normalized mutual information and the clustering accuracy. In addition, the deep embedding outperforms many state-of-the-art features.
Domestic Activities Classification from Audio Recordings Using Multi-scale Dilated Depthwise Separable Convolutional Network
Jun 09, 2023



Abstract:Domestic activities classification (DAC) from audio recordings aims at classifying audio recordings into pre-defined categories of domestic activities, which is an effective way for estimation of daily activities performed in home environment. In this paper, we propose a method for DAC from audio recordings using a multi-scale dilated depthwise separable convolutional network (DSCN). The DSCN is a lightweight neural network with small size of parameters and thus suitable to be deployed in portable terminals with limited computing resources. To expand the receptive field with the same size of DSCN's parameters, dilated convolution, instead of normal convolution, is used in the DSCN for further improving the DSCN's performance. In addition, the embeddings of various scales learned by the dilated DSCN are concatenated as a multi-scale embedding for representing property differences among various classes of domestic activities. Evaluated on a public dataset of the Task 5 of the 2018 challenge on Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE-2018), the results show that: both dilated convolution and multi-scale embedding contribute to the performance improvement of the proposed method; and the proposed method outperforms the methods based on state-of-the-art lightweight network in terms of classification accuracy.
Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification Using Stochastic Classifier
Jun 03, 2023



Abstract:It is generally assumed that number of classes is fixed in current audio classification methods, and the model can recognize pregiven classes only. When new classes emerge, the model needs to be retrained with adequate samples of all classes. If new classes continually emerge, these methods will not work well and even infeasible. In this study, we propose a method for fewshot class-incremental audio classification, which continually recognizes new classes and remember old ones. The proposed model consists of an embedding extractor and a stochastic classifier. The former is trained in base session and frozen in incremental sessions, while the latter is incrementally expanded in all sessions. Two datasets (NS-100 and LS-100) are built by choosing samples from audio corpora of NSynth and LibriSpeech, respectively. Results show that our method exceeds four baseline ones in average accuracy and performance dropping rate. Code is at https://github.com/vinceasvp/meta-sc.
Low-Complexity Acoustic Scene Classification Using Data Augmentation and Lightweight ResNet
Jun 03, 2023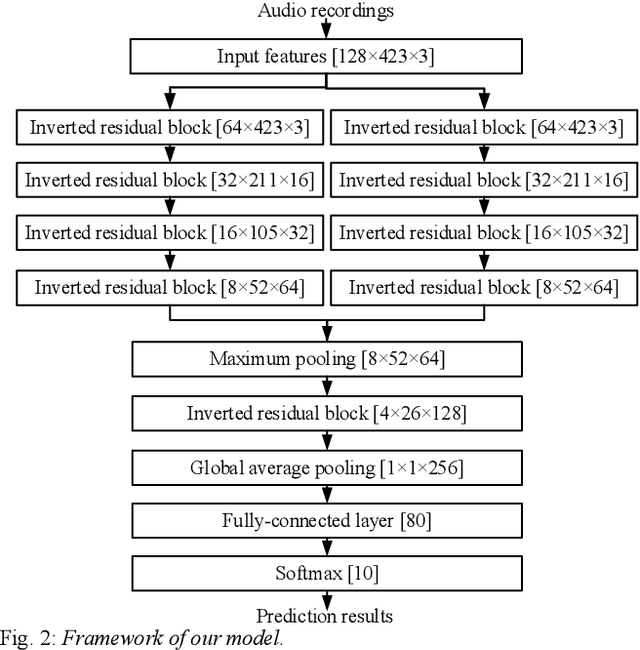
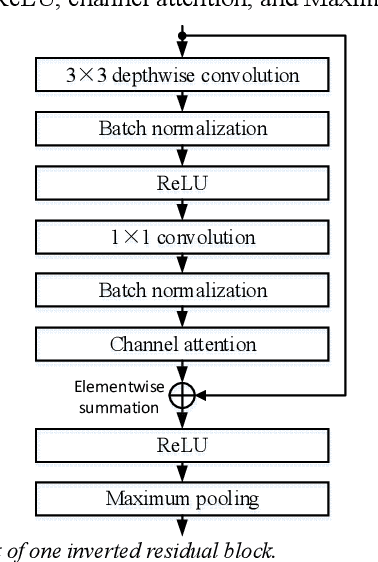
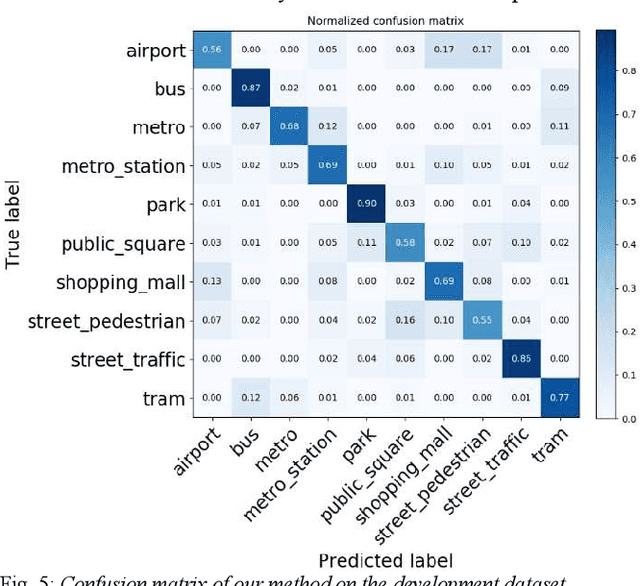
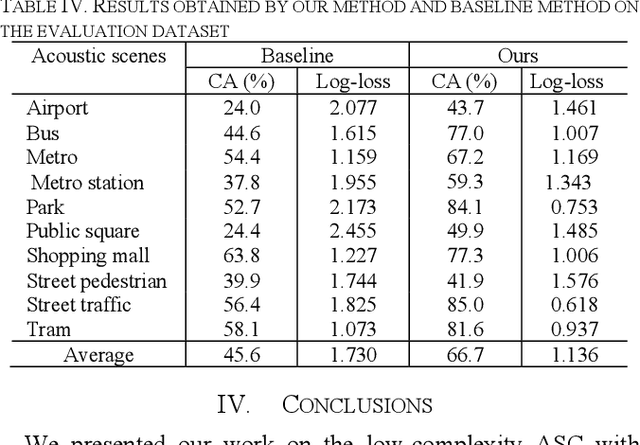
Abstract:We present a work on low-complexity acoustic scene classification (ASC) with multiple devices, namely the subtask A of Task 1 of the DCASE2021 challenge. This subtask focuses on classifying audio samples of multiple devices with a low-complexity model, where two main difficulties need to be overcome. First, the audio samples are recorded by different devices, and there is mismatch of recording devices in audio samples. We reduce the negative impact of the mismatch of recording devices by using some effective strategies, including data augmentation (e.g., mix-up, spectrum correction, pitch shift), usages of multi-patch network structure and channel attention. Second, the model size should be smaller than a threshold (e.g., 128 KB required by the DCASE2021 challenge). To meet this condition, we adopt a ResNet with both depthwise separable convolution and channel attention as the backbone network, and perform model compression. In summary, we propose a low-complexity ASC method using data augmentation and a lightweight ResNet. Evaluated on the official development and evaluation datasets, our method obtains classification accuracy scores of 71.6% and 66.7%, respectively; and obtains Log-loss scores of 1.038 and 1.136, respectively. Our final model size is 110.3 KB which is smaller than the maximum of 128 KB.
Speaker verification using attentive multi-scale convolutional recurrent network
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a speaker verification method by an Attentive Multi-scale Convolutional Recurrent Network (AMCRN). The proposed AMCRN can acquire both local spatial information and global sequential information from the input speech recordings. In the proposed method, logarithm Mel spectrum is extracted from each speech recording and then fed to the proposed AMCRN for learning speaker embedding. Afterwards, the learned speaker embedding is fed to the back-end classifier (such as cosine similarity metric) for scoring in the testing stage. The proposed method is compared with state-of-the-art methods for speaker verification. Experimental data are three public datasets that are selected from two large-scale speech corpora (VoxCeleb1 and VoxCeleb2). Experimental results show that our method exceeds baseline methods in terms of equal error rate and minimal detection cost function, and has advantages over most of baseline methods in terms of computational complexity and memory requirement. In addition, our method generalizes well across truncated speech segments with different durations, and the speaker embedding learned by the proposed AMCRN has stronger generalization ability across two back-end classifiers.
Few-Shot Speaker Identification Using Lightweight Prototypical Network with Feature Grouping and Interaction
May 31, 2023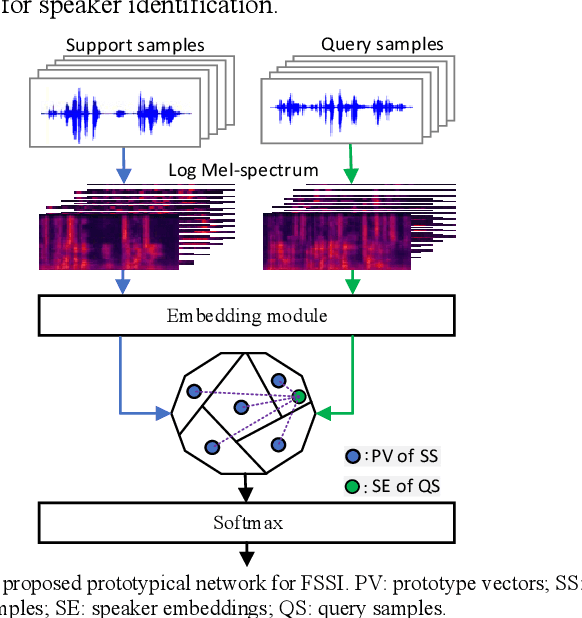
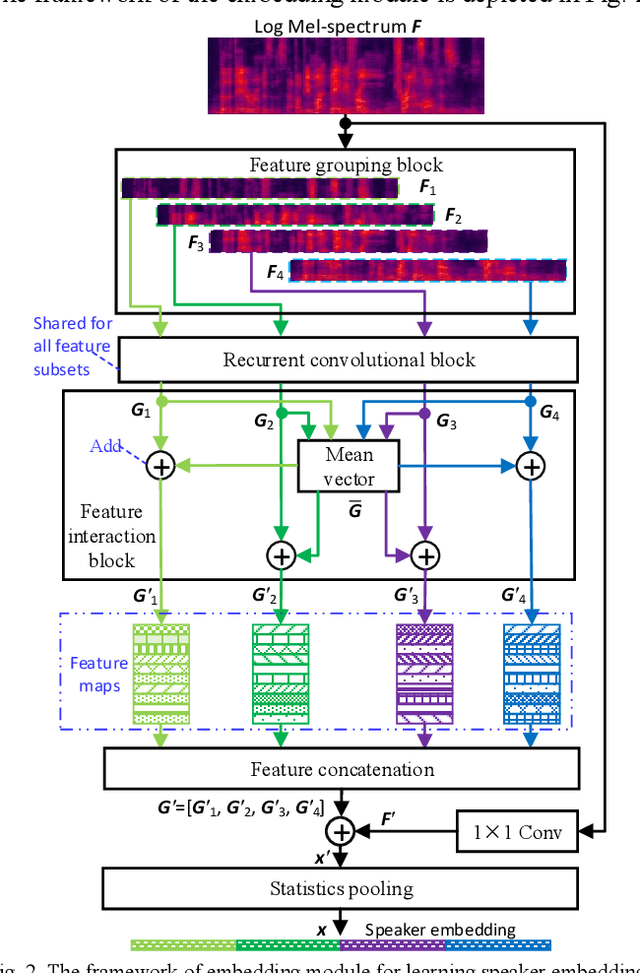
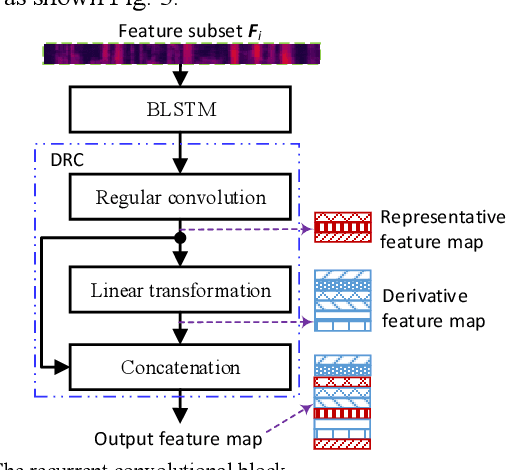

Abstract:Existing methods for few-shot speaker identification (FSSI) obtain high accuracy, but their computational complexities and model sizes need to be reduced for lightweight applications. In this work, we propose a FSSI method using a lightweight prototypical network with the final goal to implement the FSSI on intelligent terminals with limited resources, such as smart watches and smart speakers. In the proposed prototypical network, an embedding module is designed to perform feature grouping for reducing the memory requirement and computational complexity, and feature interaction for enhancing the representational ability of the learned speaker embedding. In the proposed embedding module, audio feature of each speech sample is split into several low-dimensional feature subsets that are transformed by a recurrent convolutional block in parallel. Then, the operations of averaging, addition, concatenation, element-wise summation and statistics pooling are sequentially executed to learn a speaker embedding for each speech sample. The recurrent convolutional block consists of a block of bidirectional long short-term memory, and a block of de-redundancy convolution in which feature grouping and interaction are conducted too. Our method is compared to baseline methods on three datasets that are selected from three public speech corpora (VoxCeleb1, VoxCeleb2, and LibriSpeech). The results show that our method obtains higher accuracy under several conditions, and has advantages over all baseline methods in computational complexity and model size.
Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification Using Dynamically Expanded Classifier with Self-attention Modified Prototypes
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Most existing methods for audio classification assume that the vocabulary of audio classes to be classified is fixed. When novel (unseen) audio classes appear, audio classification systems need to be retrained with abundant labeled samples of all audio classes for recognizing base (initial) and novel audio classes. If novel audio classes continue to appear, the existing methods for audio classification will be inefficient and even infeasible. In this work, we propose a method for few-shot class-incremental audio classification, which can continually recognize novel audio classes without forgetting old ones. The framework of our method mainly consists of two parts: an embedding extractor and a classifier, and their constructions are decoupled. The embedding extractor is the backbone of a ResNet based network, which is frozen after construction by a training strategy using only samples of base audio classes. However, the classifier consisting of prototypes is expanded by a prototype adaptation network with few samples of novel audio classes in incremental sessions. Labeled support samples and unlabeled query samples are used to train the prototype adaptation network and update the classifier, since they are informative for audio classification. Three audio datasets, named NSynth-100, FSC-89 and LS-100 are built by choosing samples from audio corpora of NSynth, FSD-MIX-CLIP and LibriSpeech, respectively. Results show that our method exceeds baseline methods in average accuracy and performance dropping rate. In addition, it is competitive compared to baseline methods in computational complexity and memory requirement. The code for our method is given at https://github.com/vinceasvp/FCAC.
Few-shot Class-incremental Audio Classification Using Adaptively-refined Prototypes
May 29, 2023



Abstract:New classes of sounds constantly emerge with a few samples, making it challenging for models to adapt to dynamic acoustic environments. This challenge motivates us to address the new problem of few-shot class-incremental audio classification. This study aims to enable a model to continuously recognize new classes of sounds with a few training samples of new classes while remembering the learned ones. To this end, we propose a method to generate discriminative prototypes and use them to expand the model's classifier for recognizing sounds of new and learned classes. The model is first trained with a random episodic training strategy, and then its backbone is used to generate the prototypes. A dynamic relation projection module refines the prototypes to enhance their discriminability. Results on two datasets (derived from the corpora of Nsynth and FSD-MIX-CLIPS) show that the proposed method exceeds three state-of-the-art methods in average accuracy and performance dropping rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge