Wucheng Wang
Acoustic Scene Clustering Using Joint Optimization of Deep Embedding Learning and Clustering Iteration
Jun 09, 2023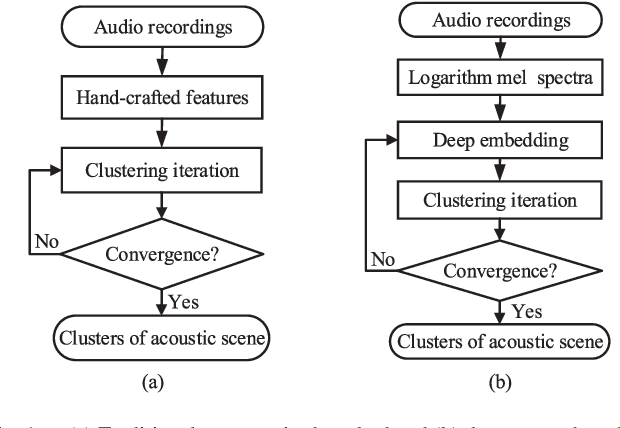
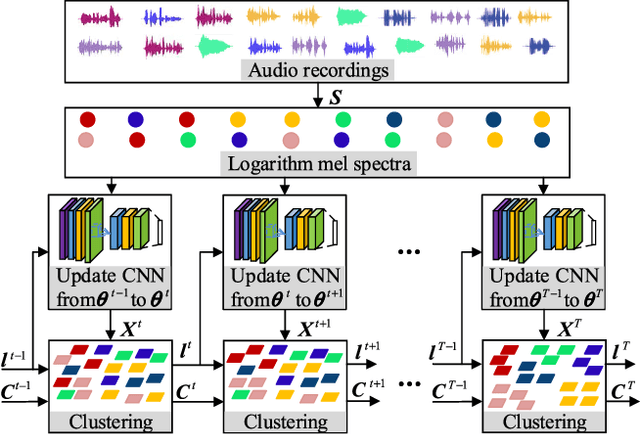
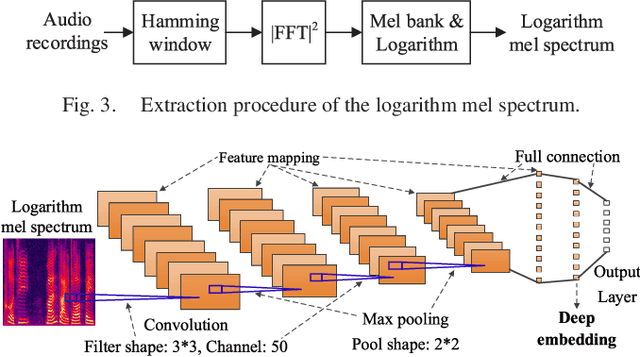
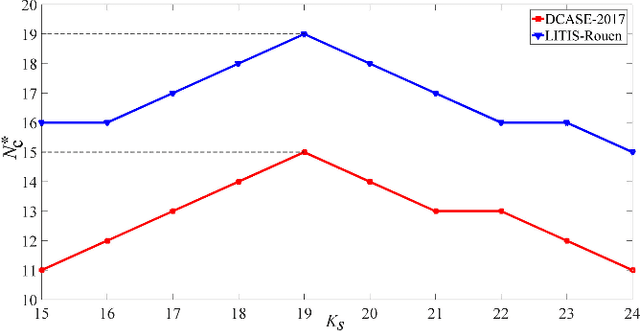
Abstract:Recent efforts have been made on acoustic scene classification in the audio signal processing community. In contrast, few studies have been conducted on acoustic scene clustering, which is a newly emerging problem. Acoustic scene clustering aims at merging the audio recordings of the same class of acoustic scene into a single cluster without using prior information and training classifiers. In this study, we propose a method for acoustic scene clustering that jointly optimizes the procedures of feature learning and clustering iteration. In the proposed method, the learned feature is a deep embedding that is extracted from a deep convolutional neural network (CNN), while the clustering algorithm is the agglomerative hierarchical clustering (AHC). We formulate a unified loss function for integrating and optimizing these two procedures. Various features and methods are compared. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other unsupervised methods in terms of the normalized mutual information and the clustering accuracy. In addition, the deep embedding outperforms many state-of-the-art features.
Few-Shot Speaker Identification Using Depthwise Separable Convolutional Network with Channel Attention
Apr 24, 2022



Abstract:Although few-shot learning has attracted much attention from the fields of image and audio classification, few efforts have been made on few-shot speaker identification. In the task of few-shot learning, overfitting is a tough problem mainly due to the mismatch between training and testing conditions. In this paper, we propose a few-shot speaker identification method which can alleviate the overfitting problem. In the proposed method, the model of a depthwise separable convolutional network with channel attention is trained with a prototypical loss function. Experimental datasets are extracted from three public speech corpora: Aishell-2, VoxCeleb1 and TORGO. Experimental results show that the proposed method exceeds state-of-the-art methods for few-shot speaker identification in terms of accuracy and F-score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge