Xuguang Ai
A Federated and Parameter-Efficient Framework for Large Language Model Training in Medicine
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance on medical benchmarks, including question answering and diagnosis. To enable their use in clinical settings, LLMs are typically further adapted through continued pretraining or post-training using clinical data. However, most medical LLMs are trained on data from a single institution, which faces limitations in generalizability and safety in heterogeneous systems. Federated learning (FL) is a promising solution for enabling collaborative model development across healthcare institutions. Yet applying FL to LLMs in medicine remains fundamentally limited. First, conventional FL requires transmitting the full model during each communication round, which becomes impractical for multi-billion-parameter LLMs given the limited computational resources. Second, many FL algorithms implicitly assume data homogeneity, whereas real-world clinical data are highly heterogeneous across patients, diseases, and institutional practices. We introduce the model-agnostic and parameter-efficient federated learning framework for adapting LLMs to medical applications. Fed-MedLoRA transmits only low-rank adapter parameters, reducing communication and computation overhead, while Fed-MedLoRA+ further incorporates adaptive, data-aware aggregation to improve convergence under cross-site heterogeneity. We apply the framework to clinical information extraction (IE), which transforms patient narratives into structured medical entities and relations. Accuracy was assessed across five patient cohorts through comparisons with BERT models, and LLaMA-3 and DeepSeek-R1, GPT-4o models. Evaluation settings included (1) in-domain training and testing, (2) external validation on independent cohorts, and (3) a low-resource new-site adaptation scenario using real-world clinical notes from the Yale New Haven Health System.
EHRNavigator: A Multi-Agent System for Patient-Level Clinical Question Answering over Heterogeneous Electronic Health Records
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Clinical decision-making increasingly relies on timely and context-aware access to patient information within Electronic Health Records (EHRs), yet most existing natural language question-answering (QA) systems are evaluated solely on benchmark datasets, limiting their practical relevance. To overcome this limitation, we introduce EHRNavigator, a multi-agent framework that harnesses AI agents to perform patient-level question answering across heterogeneous and multimodal EHR data. We assessed its performance using both public benchmark and institutional datasets under realistic hospital conditions characterized by diverse schemas, temporal reasoning demands, and multimodal evidence integration. Through quantitative evaluation and clinician-validated chart review, EHRNavigator demonstrated strong generalization, achieving 86% accuracy on real-world cases while maintaining clinically acceptable response times. Overall, these findings confirm that EHRNavigator effectively bridges the gap between benchmark evaluation and clinical deployment, offering a robust, adaptive, and efficient solution for real-world EHR question answering.
Memorization in Large Language Models in Medicine: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Implications
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in medicine. To date, LLMs have been widely applied to tasks such as diagnostic assistance, medical question answering, and clinical information synthesis. However, a key open question remains: to what extent do LLMs memorize medical training data. In this study, we present the first comprehensive evaluation of memorization of LLMs in medicine, assessing its prevalence (how frequently it occurs), characteristics (what is memorized), volume (how much content is memorized), and potential downstream impacts (how memorization may affect medical applications). We systematically analyze common adaptation scenarios: (1) continued pretraining on medical corpora, (2) fine-tuning on standard medical benchmarks, and (3) fine-tuning on real-world clinical data, including over 13,000 unique inpatient records from Yale New Haven Health System. The results demonstrate that memorization is prevalent across all adaptation scenarios and significantly higher than reported in the general domain. Memorization affects both the development and adoption of LLMs in medicine and can be categorized into three types: beneficial (e.g., accurate recall of clinical guidelines and biomedical references), uninformative (e.g., repeated disclaimers or templated medical document language), and harmful (e.g., regeneration of dataset-specific or sensitive clinical content). Based on these findings, we offer practical recommendations to facilitate beneficial memorization that enhances domain-specific reasoning and factual accuracy, minimize uninformative memorization to promote deeper learning beyond surface-level patterns, and mitigate harmful memorization to prevent the leakage of sensitive or identifiable patient information.
Benchmarking Next-Generation Reasoning-Focused Large Language Models in Ophthalmology: A Head-to-Head Evaluation on 5,888 Items
Apr 15, 2025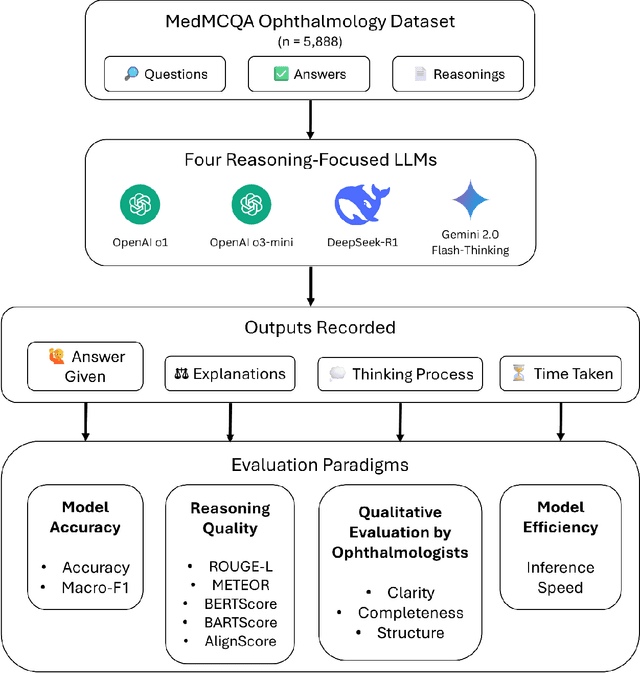
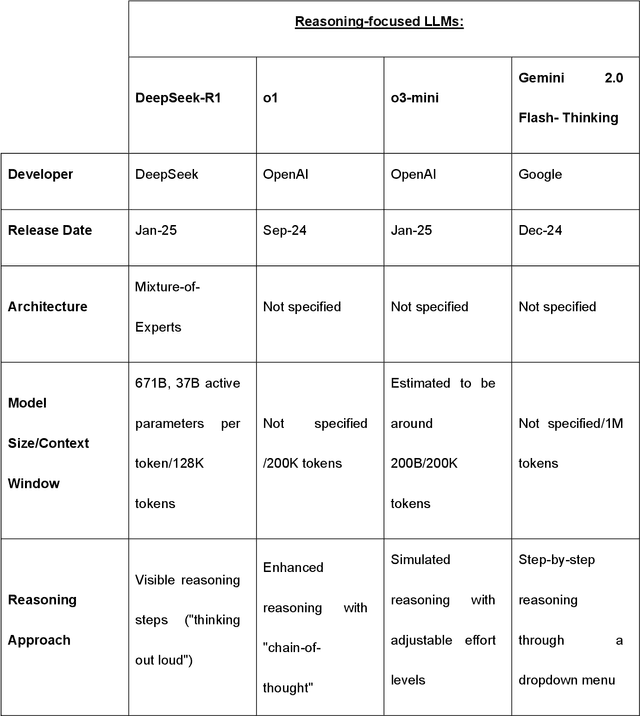
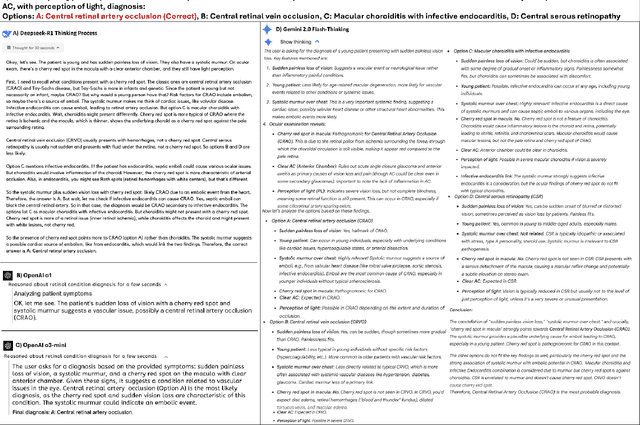
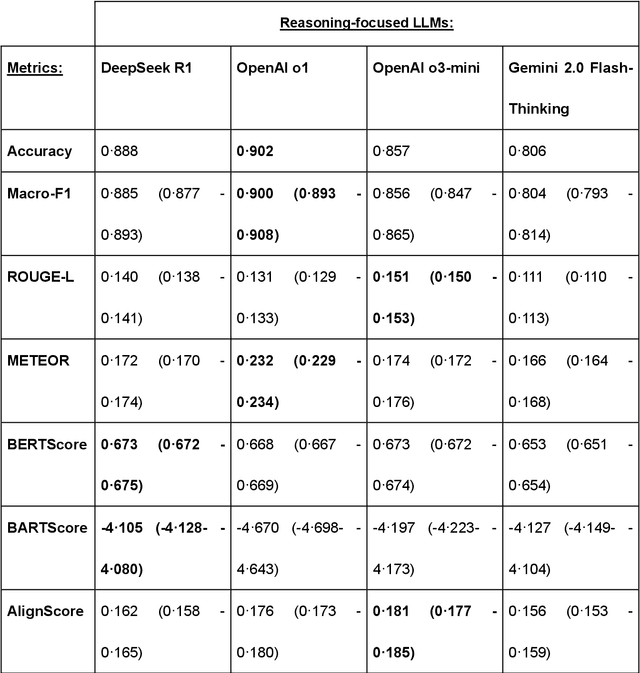
Abstract:Recent advances in reasoning-focused large language models (LLMs) mark a shift from general LLMs toward models designed for complex decision-making, a crucial aspect in medicine. However, their performance in specialized domains like ophthalmology remains underexplored. This study comprehensively evaluated and compared the accuracy and reasoning capabilities of four newly developed reasoning-focused LLMs, namely DeepSeek-R1, OpenAI o1, o3-mini, and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking. Each model was assessed using 5,888 multiple-choice ophthalmology exam questions from the MedMCQA dataset in zero-shot setting. Quantitative evaluation included accuracy, Macro-F1, and five text-generation metrics (ROUGE-L, METEOR, BERTScore, BARTScore, and AlignScore), computed against ground-truth reasonings. Average inference time was recorded for a subset of 100 randomly selected questions. Additionally, two board-certified ophthalmologists qualitatively assessed clarity, completeness, and reasoning structure of responses to differential diagnosis questions.O1 (0.902) and DeepSeek-R1 (0.888) achieved the highest accuracy, with o1 also leading in Macro-F1 (0.900). The performance of models across the text-generation metrics varied: O3-mini excelled in ROUGE-L (0.151), o1 in METEOR (0.232), DeepSeek-R1 and o3-mini tied for BERTScore (0.673), DeepSeek-R1 (-4.105) and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking (-4.127) performed best in BARTScore, while o3-mini (0.181) and o1 (0.176) led AlignScore. Inference time across the models varied, with DeepSeek-R1 being slowest (40.4 seconds) and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking fastest (6.7 seconds). Qualitative evaluation revealed that DeepSeek-R1 and Gemini 2.0 Flash-Thinking tended to provide detailed and comprehensive intermediate reasoning, whereas o1 and o3-mini displayed concise and summarized justifications.
A Benchmark for End-to-End Zero-Shot Biomedical Relation Extraction with LLMs: Experiments with OpenAI Models
Apr 05, 2025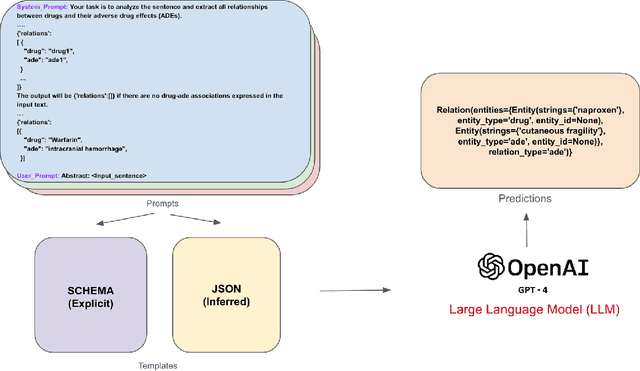
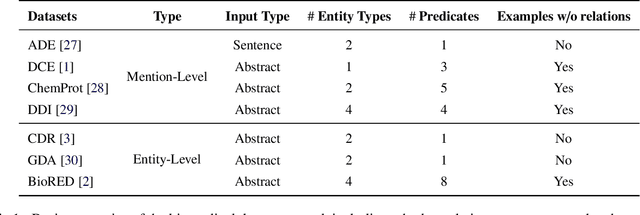
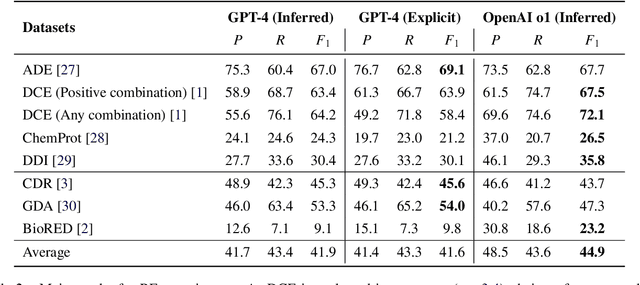
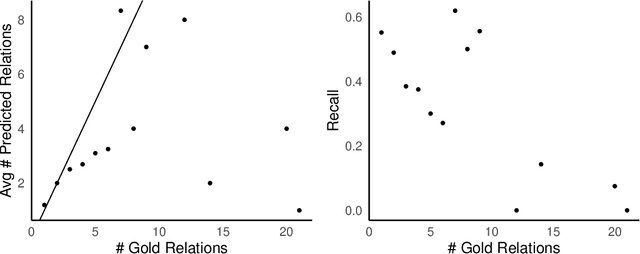
Abstract:Objective: Zero-shot methodology promises to cut down on costs of dataset annotation and domain expertise needed to make use of NLP. Generative large language models trained to align with human goals have achieved high zero-shot performance across a wide variety of tasks. As of yet, it is unclear how well these models perform on biomedical relation extraction (RE). To address this knowledge gap, we explore patterns in the performance of OpenAI LLMs across a diverse sampling of RE tasks. Methods: We use OpenAI GPT-4-turbo and their reasoning model o1 to conduct end-to-end RE experiments on seven datasets. We use the JSON generation capabilities of GPT models to generate structured output in two ways: (1) by defining an explicit schema describing the structure of relations, and (2) using a setting that infers the structure from the prompt language. Results: Our work is the first to study and compare the performance of the GPT-4 and o1 for the end-to-end zero-shot biomedical RE task across a broad array of datasets. We found the zero-shot performances to be proximal to that of fine-tuned methods. The limitations of this approach are that it performs poorly on instances containing many relations and errs on the boundaries of textual mentions. Conclusion: Recent large language models exhibit promising zero-shot capabilities in complex biomedical RE tasks, offering competitive performance with reduced dataset curation and NLP modeling needs at the cost of increased computing, potentially increasing medical community accessibility. Addressing the limitations we identify could further boost reliability. The code, data, and prompts for all our experiments are publicly available: https://github.com/bionlproc/ZeroShotRE
Enhancing Large Language Models with Domain-specific Retrieval Augment Generation: A Case Study on Long-form Consumer Health Question Answering in Ophthalmology
Sep 20, 2024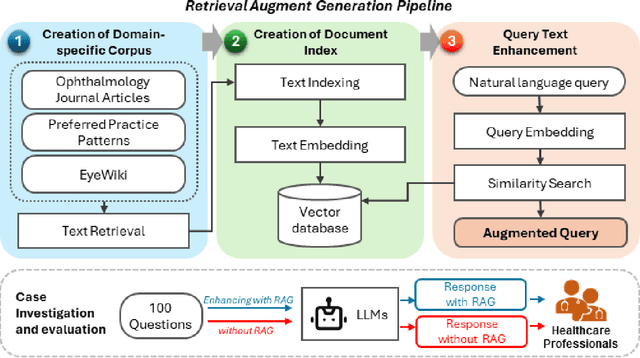
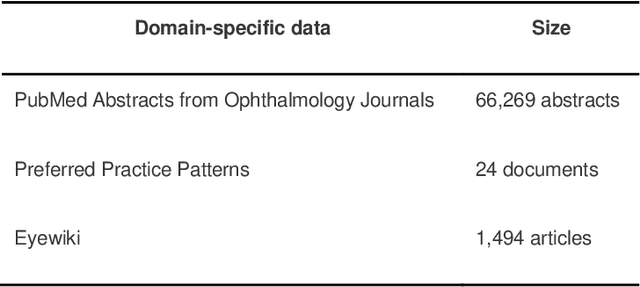
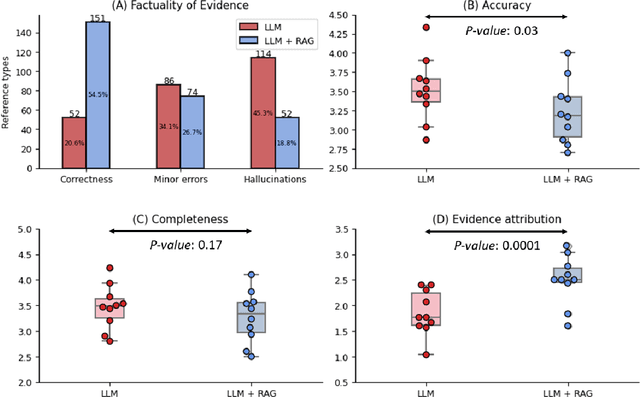

Abstract:Despite the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in medicine, they may generate responses lacking supporting evidence or based on hallucinated evidence. While Retrieval Augment Generation (RAG) is popular to address this issue, few studies implemented and evaluated RAG in downstream domain-specific applications. We developed a RAG pipeline with 70,000 ophthalmology-specific documents that retrieve relevant documents to augment LLMs during inference time. In a case study on long-form consumer health questions, we systematically evaluated the responses including over 500 references of LLMs with and without RAG on 100 questions with 10 healthcare professionals. The evaluation focuses on factuality of evidence, selection and ranking of evidence, attribution of evidence, and answer accuracy and completeness. LLMs without RAG provided 252 references in total. Of which, 45.3% hallucinated, 34.1% consisted of minor errors, and 20.6% were correct. In contrast, LLMs with RAG significantly improved accuracy (54.5% being correct) and reduced error rates (18.8% with minor hallucinations and 26.7% with errors). 62.5% of the top 10 documents retrieved by RAG were selected as the top references in the LLM response, with an average ranking of 4.9. The use of RAG also improved evidence attribution (increasing from 1.85 to 2.49 on a 5-point scale, P<0.001), albeit with slight decreases in accuracy (from 3.52 to 3.23, P=0.03) and completeness (from 3.47 to 3.27, P=0.17). The results demonstrate that LLMs frequently exhibited hallucinated and erroneous evidence in the responses, raising concerns for downstream applications in the medical domain. RAG substantially reduced the proportion of such evidence but encountered challenges.
Comparison of pipeline, sequence-to-sequence, and GPT models for end-to-end relation extraction: experiments with the rare disease use-case
Nov 22, 2023Abstract:End-to-end relation extraction (E2ERE) is an important and realistic application of natural language processing (NLP) in biomedicine. In this paper, we aim to compare three prevailing paradigms for E2ERE using a complex dataset focused on rare diseases involving discontinuous and nested entities. We use the RareDis information extraction dataset to evaluate three competing approaches (for E2ERE): NER $\rightarrow$ RE pipelines, joint sequence to sequence models, and generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models. We use comparable state-of-the-art models and best practices for each of these approaches and conduct error analyses to assess their failure modes. Our findings reveal that pipeline models are still the best, while sequence-to-sequence models are not far behind; GPT models with eight times as many parameters are worse than even sequence-to-sequence models and lose to pipeline models by over 10 F1 points. Partial matches and discontinuous entities caused many NER errors contributing to lower overall E2E performances. We also verify these findings on a second E2ERE dataset for chemical-protein interactions. Although generative LM-based methods are more suitable for zero-shot settings, when training data is available, our results show that it is better to work with more conventional models trained and tailored for E2ERE. More innovative methods are needed to marry the best of the both worlds from smaller encoder-decoder pipeline models and the larger GPT models to improve E2ERE. As of now, we see that well designed pipeline models offer substantial performance gains at a lower cost and carbon footprint for E2ERE. Our contribution is also the first to conduct E2ERE for the RareDis dataset.
End-to-End Models for Chemical-Protein Interaction Extraction: Better Tokenization and Span-Based Pipeline Strategies
Apr 03, 2023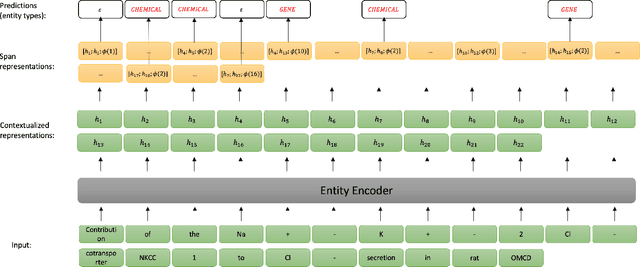
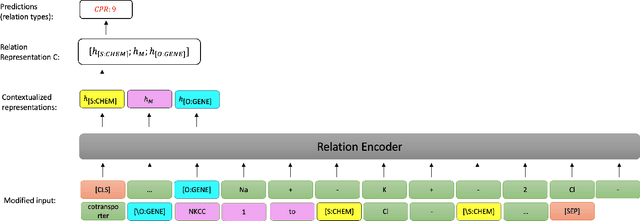
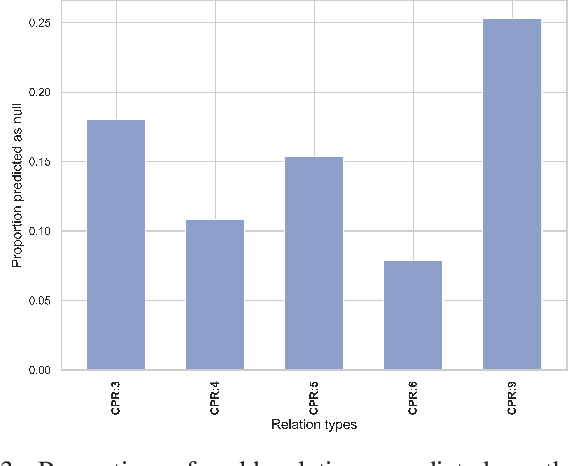
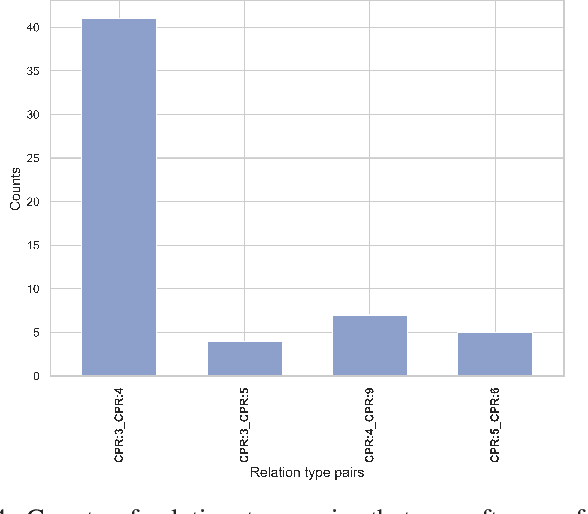
Abstract:End-to-end relation extraction (E2ERE) is an important task in information extraction, more so for biomedicine as scientific literature continues to grow exponentially. E2ERE typically involves identifying entities (or named entity recognition (NER)) and associated relations, while most RE tasks simply assume that the entities are provided upfront and end up performing relation classification. E2ERE is inherently more difficult than RE alone given the potential snowball effect of errors from NER leading to more errors in RE. A complex dataset in biomedical E2ERE is the ChemProt dataset (BioCreative VI, 2017) that identifies relations between chemical compounds and genes/proteins in scientific literature. ChemProt is included in all recent biomedical natural language processing benchmarks including BLUE, BLURB, and BigBio. However, its treatment in these benchmarks and in other separate efforts is typically not end-to-end, with few exceptions. In this effort, we employ a span-based pipeline approach to produce a new state-of-the-art E2ERE performance on the ChemProt dataset, resulting in $> 4\%$ improvement in F1-score over the prior best effort. Our results indicate that a straightforward fine-grained tokenization scheme helps span-based approaches excel in E2ERE, especially with regards to handling complex named entities. Our error analysis also identifies a few key failure modes in E2ERE for ChemProt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge