Xudong Hong
A surprisal oracle for when every layer counts
Dec 04, 2024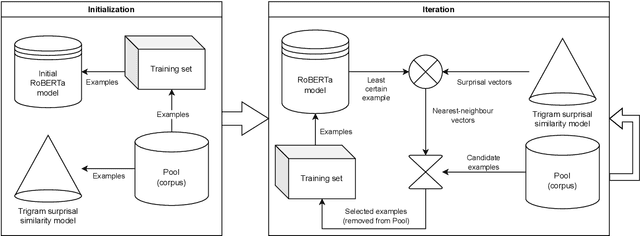
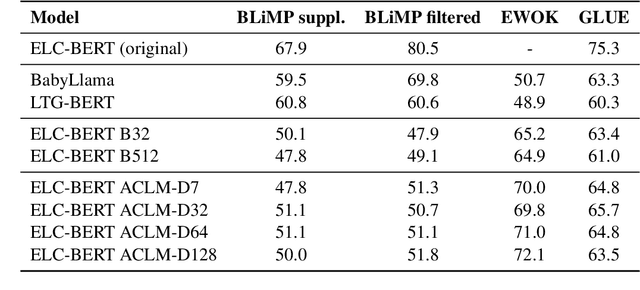
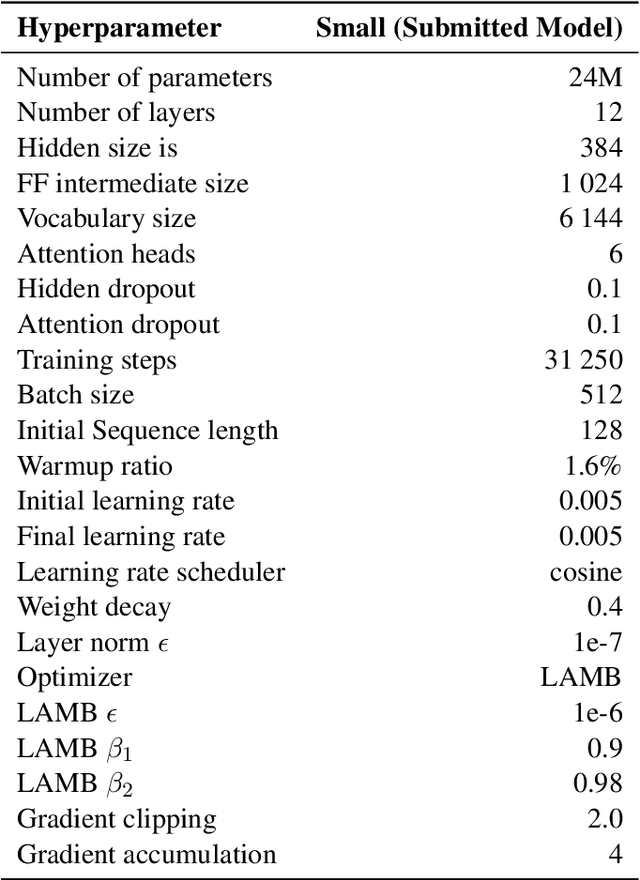
Abstract:Active Curriculum Language Modeling (ACLM; Hong et al., 2023) is a learner directed approach to training a language model. We proposed the original version of this process in our submission to the BabyLM 2023 task, and now we propose an updated ACLM process for the BabyLM 2024 task. ACLM involves an iteratively- and dynamically-constructed curriculum informed over the training process by a model of uncertainty; other training items that are similarly uncertain to a least certain candidate item are prioritized. Our new process improves the similarity model so that it is more dynamic, and we run ACLM over the most successful model from the BabyLM 2023 task: ELC-BERT (Charpentier and Samuel, 2023). We find that while our models underperform on fine-grained grammatical inferences, they outperform the BabyLM 2024 official base-lines on common-sense and world-knowledge tasks. We make our code available at https: //github.com/asayeed/ActiveBaby.
Do large language models and humans have similar behaviors in causal inference with script knowledge?
Nov 13, 2023



Abstract:Recently, large pre-trained language models (LLMs) have demonstrated superior language understanding abilities, including zero-shot causal reasoning. However, it is unclear to what extent their capabilities are similar to human ones. We here study the processing of an event $B$ in a script-based story, which causally depends on a previous event $A$. In our manipulation, event $A$ is stated, negated, or omitted in an earlier section of the text. We first conducted a self-paced reading experiment, which showed that humans exhibit significantly longer reading times when causal conflicts exist ($\neg A \rightarrow B$) than under logical conditions ($A \rightarrow B$). However, reading times remain similar when cause A is not explicitly mentioned, indicating that humans can easily infer event B from their script knowledge. We then tested a variety of LLMs on the same data to check to what extent the models replicate human behavior. Our experiments show that 1) only recent LLMs, like GPT-3 or Vicuna, correlate with human behavior in the $\neg A \rightarrow B$ condition. 2) Despite this correlation, all models still fail to predict that $nil \rightarrow B$ is less surprising than $\neg A \rightarrow B$, indicating that LLMs still have difficulties integrating script knowledge. Our code and collected data set are available at https://github.com/tony-hong/causal-script.
HowToCaption: Prompting LLMs to Transform Video Annotations at Scale
Oct 07, 2023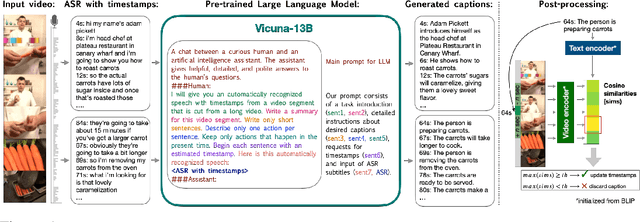
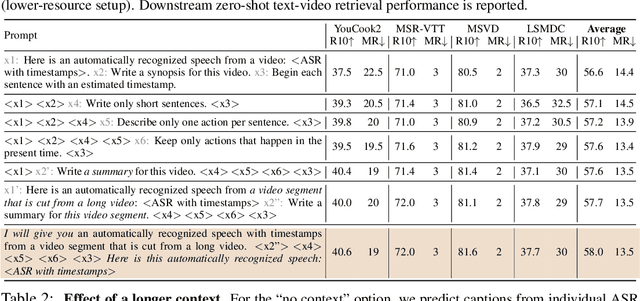


Abstract:Instructional videos are an excellent source for learning multimodal representations by leveraging video-subtitle pairs extracted with automatic speech recognition systems (ASR) from the audio signal in the videos. However, in contrast to human-annotated captions, both speech and subtitles naturally differ from the visual content of the videos and thus provide only noisy supervision for multimodal learning. As a result, large-scale annotation-free web video training data remains sub-optimal for training text-video models. In this work, we propose to leverage the capability of large language models (LLMs) to obtain fine-grained video descriptions aligned with videos. Specifically, we prompt an LLM to create plausible video descriptions based on ASR narrations of the video for a large-scale instructional video dataset. To this end, we introduce a prompting method that is able to take into account a longer text of subtitles, allowing us to capture context beyond a single sentence. To align the captions to the video temporally, we prompt the LLM to generate timestamps for each produced caption based on the subtitles. In this way, we obtain human-style video captions at scale without human supervision. We apply our method to the subtitles of the HowTo100M dataset, creating a new large-scale dataset, HowToCaption. Our evaluation shows that the resulting captions not only significantly improve the performance over many different benchmark datasets for text-video retrieval but also lead to a disentangling of textual narration from the audio, boosting performance in text-video-audio tasks.
Visual Writing Prompts: Character-Grounded Story Generation with Curated Image Sequences
Jan 20, 2023Abstract:Current work on image-based story generation suffers from the fact that the existing image sequence collections do not have coherent plots behind them. We improve visual story generation by producing a new image-grounded dataset, Visual Writing Prompts (VWP). VWP contains almost 2K selected sequences of movie shots, each including 5-10 images. The image sequences are aligned with a total of 12K stories which were collected via crowdsourcing given the image sequences and a set of grounded characters from the corresponding image sequence. Our new image sequence collection and filtering process has allowed us to obtain stories that are more coherent and have more narrativity compared to previous work. We also propose a character-based story generation model driven by coherence as a strong baseline. Evaluations show that our generated stories are more coherent, visually grounded, and have more narrativity than stories generated with the current state-of-the-art model.
Inheritance-guided Hierarchical Assignment for Clinical Automatic Diagnosis
Jan 27, 2021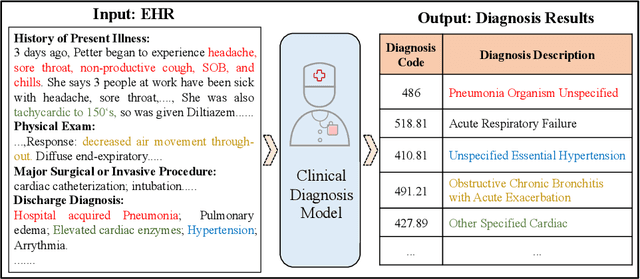
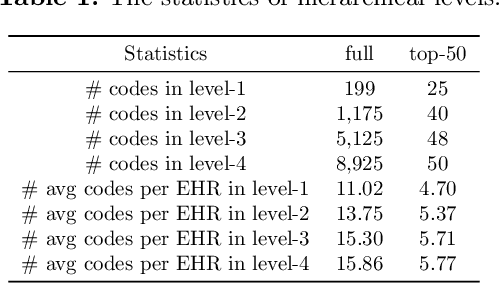
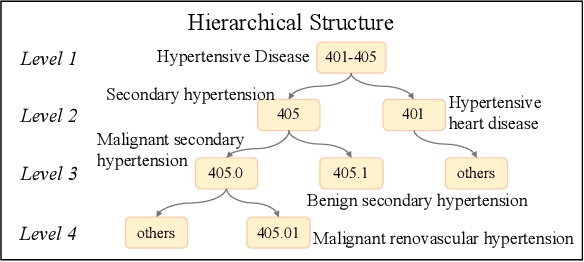
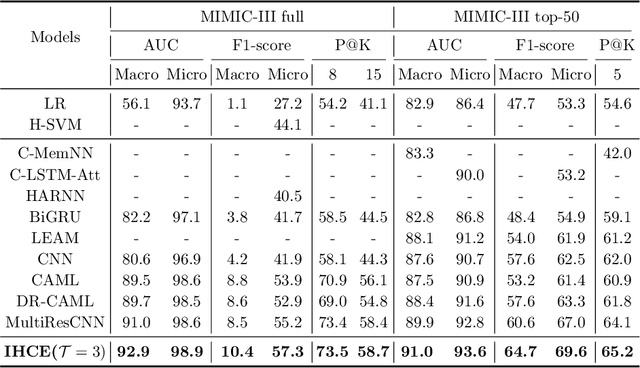
Abstract:Clinical diagnosis, which aims to assign diagnosis codes for a patient based on the clinical note, plays an essential role in clinical decision-making. Considering that manual diagnosis could be error-prone and time-consuming, many intelligent approaches based on clinical text mining have been proposed to perform automatic diagnosis. However, these methods may not achieve satisfactory results due to the following challenges. First, most of the diagnosis codes are rare, and the distribution is extremely unbalanced. Second, existing methods are challenging to capture the correlation between diagnosis codes. Third, the lengthy clinical note leads to the excessive dispersion of key information related to codes. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel framework to combine the inheritance-guided hierarchical assignment and co-occurrence graph propagation for clinical automatic diagnosis. Specifically, we propose a hierarchical joint prediction strategy to address the challenge of unbalanced codes distribution. Then, we utilize graph convolutional neural networks to obtain the correlation and semantic representations of medical ontology. Furthermore, we introduce multi attention mechanisms to extract crucial information. Finally, extensive experiments on MIMIC-III dataset clearly validate the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge