Xinran Xu
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
Robust Uncertainty Estimation under Distribution Shift via Difference Reconstruction
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Estimating uncertainty in deep learning models is critical for reliable decision-making in high-stakes applications such as medical imaging. Prior research has established that the difference between an input sample and its reconstructed version produced by an auxiliary model can serve as a useful proxy for uncertainty. However, directly comparing reconstructions with the original input is degraded by information loss and sensitivity to superficial details, which limits its effectiveness. In this work, we propose Difference Reconstruction Uncertainty Estimation (DRUE), a method that mitigates this limitation by reconstructing inputs from two intermediate layers and measuring the discrepancy between their outputs as the uncertainty score. To evaluate uncertainty estimation in practice, we follow the widely used out-of-distribution (OOD) detection paradigm, where in-distribution (ID) training data are compared against datasets with increasing domain shift. Using glaucoma detection as the ID task, we demonstrate that DRUE consistently achieves superior AUC and AUPR across multiple OOD datasets, highlighting its robustness and reliability under distribution shift. This work provides a principled and effective framework for enhancing model reliability in uncertain environments.
PLawBench: A Rubric-Based Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs in Real-World Legal Practice
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to legal domain-specific tasks, evaluating their ability to perform legal work in real-world settings has become essential. However, existing legal benchmarks rely on simplified and highly standardized tasks, failing to capture the ambiguity, complexity, and reasoning demands of real legal practice. Moreover, prior evaluations often adopt coarse, single-dimensional metrics and do not explicitly assess fine-grained legal reasoning. To address these limitations, we introduce PLawBench, a Practical Law Benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs in realistic legal practice scenarios. Grounded in real-world legal workflows, PLawBench models the core processes of legal practitioners through three task categories: public legal consultation, practical case analysis, and legal document generation. These tasks assess a model's ability to identify legal issues and key facts, perform structured legal reasoning, and generate legally coherent documents. PLawBench comprises 850 questions across 13 practical legal scenarios, with each question accompanied by expert-designed evaluation rubrics, resulting in approximately 12,500 rubric items for fine-grained assessment. Using an LLM-based evaluator aligned with human expert judgments, we evaluate 10 state-of-the-art LLMs. Experimental results show that none achieves strong performance on PLawBench, revealing substantial limitations in the fine-grained legal reasoning capabilities of current LLMs and highlighting important directions for future evaluation and development of legal LLMs. Data is available at: https://github.com/skylenage/PLawbench.
Evaluation of Large Language Models in Legal Applications: Challenges, Methods, and Future Directions
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are being increasingly integrated into legal applications, including judicial decision support, legal practice assistance, and public-facing legal services. While LLMs show strong potential in handling legal knowledge and tasks, their deployment in real-world legal settings raises critical concerns beyond surface-level accuracy, involving the soundness of legal reasoning processes and trustworthy issues such as fairness and reliability. Systematic evaluation of LLM performance in legal tasks has therefore become essential for their responsible adoption. This survey identifies key challenges in evaluating LLMs for legal tasks grounded in real-world legal practice. We analyze the major difficulties involved in assessing LLM performance in the legal domain, including outcome correctness, reasoning reliability, and trustworthiness. Building on these challenges, we review and categorize existing evaluation methods and benchmarks according to their task design, datasets, and evaluation metrics. We further discuss the extent to which current approaches address these challenges, highlight their limitations, and outline future research directions toward more realistic, reliable, and legally grounded evaluation frameworks for LLMs in legal domains.
Seer: Online Context Learning for Fast Synchronous LLM Reinforcement Learning
Nov 18, 2025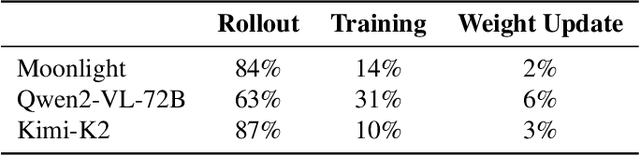
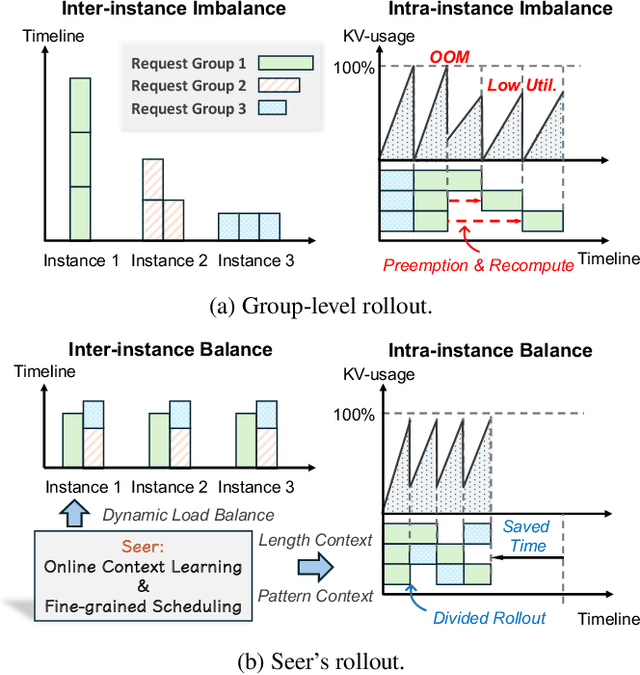
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) has become critical for advancing modern Large Language Models (LLMs), yet existing synchronous RL systems face severe performance bottlenecks. The rollout phase, which dominates end-to-end iteration time, suffers from substantial long-tail latency and poor resource utilization due to inherent workload imbalance. We present Seer, a novel online context learning system that addresses these challenges by exploiting previously overlooked similarities in output lengths and generation patterns among requests sharing the same prompt. Seer introduces three key techniques: divided rollout for dynamic load balancing, context-aware scheduling, and adaptive grouped speculative decoding. Together, these mechanisms substantially reduce long-tail latency and improve resource efficiency during rollout. Evaluations on production-grade RL workloads demonstrate that Seer improves end-to-end rollout throughput by 74% to 97% and reduces long-tail latency by 75% to 93% compared to state-of-the-art synchronous RL systems, significantly accelerating RL training iterations.
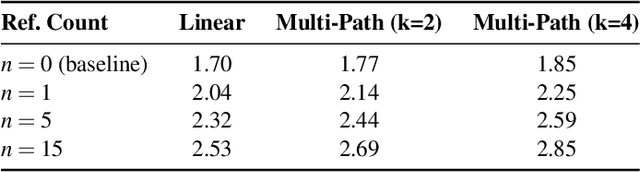
Kimi Linear: An Expressive, Efficient Attention Architecture
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce Kimi Linear, a hybrid linear attention architecture that, for the first time, outperforms full attention under fair comparisons across various scenarios -- including short-context, long-context, and reinforcement learning (RL) scaling regimes. At its core lies Kimi Delta Attention (KDA), an expressive linear attention module that extends Gated DeltaNet with a finer-grained gating mechanism, enabling more effective use of limited finite-state RNN memory. Our bespoke chunkwise algorithm achieves high hardware efficiency through a specialized variant of the Diagonal-Plus-Low-Rank (DPLR) transition matrices, which substantially reduces computation compared to the general DPLR formulation while remaining more consistent with the classical delta rule. We pretrain a Kimi Linear model with 3B activated parameters and 48B total parameters, based on a layerwise hybrid of KDA and Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA). Our experiments show that with an identical training recipe, Kimi Linear outperforms full MLA with a sizeable margin across all evaluated tasks, while reducing KV cache usage by up to 75% and achieving up to 6 times decoding throughput for a 1M context. These results demonstrate that Kimi Linear can be a drop-in replacement for full attention architectures with superior performance and efficiency, including tasks with longer input and output lengths. To support further research, we open-source the KDA kernel and vLLM implementations, and release the pre-trained and instruction-tuned model checkpoints.
Kimi K2: Open Agentic Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025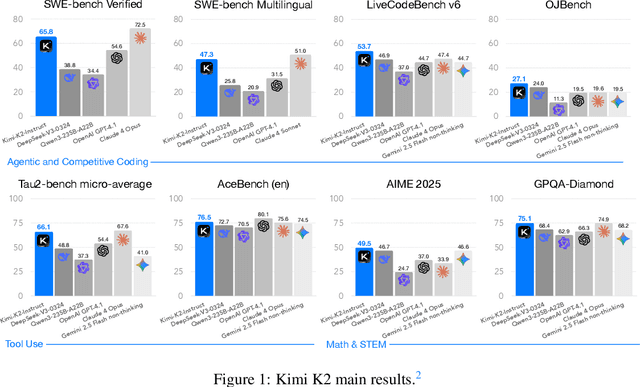
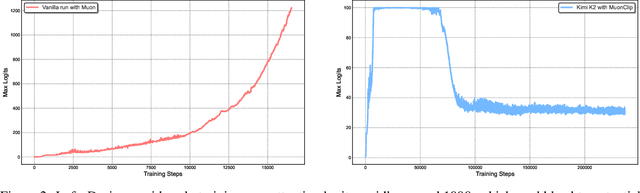
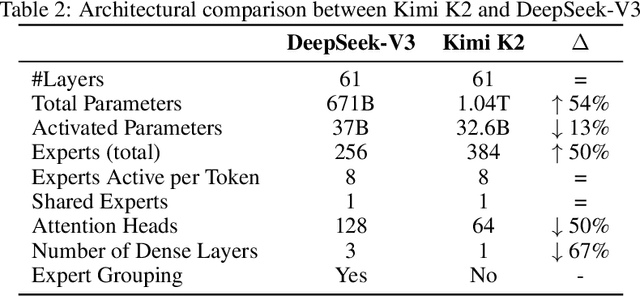
Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) large language model with 32 billion activated parameters and 1 trillion total parameters. We propose the MuonClip optimizer, which improves upon Muon with a novel QK-clip technique to address training instability while enjoying the advanced token efficiency of Muon. Based on MuonClip, K2 was pre-trained on 15.5 trillion tokens with zero loss spike. During post-training, K2 undergoes a multi-stage post-training process, highlighted by a large-scale agentic data synthesis pipeline and a joint reinforcement learning (RL) stage, where the model improves its capabilities through interactions with real and synthetic environments. Kimi K2 achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source non-thinking models, with strengths in agentic capabilities. Notably, K2 obtains 66.1 on Tau2-Bench, 76.5 on ACEBench (En), 65.8 on SWE-Bench Verified, and 47.3 on SWE-Bench Multilingual -- surpassing most open and closed-sourced baselines in non-thinking settings. It also exhibits strong capabilities in coding, mathematics, and reasoning tasks, with a score of 53.7 on LiveCodeBench v6, 49.5 on AIME 2025, 75.1 on GPQA-Diamond, and 27.1 on OJBench, all without extended thinking. These results position Kimi K2 as one of the most capable open-source large language models to date, particularly in software engineering and agentic tasks. We release our base and post-trained model checkpoints to facilitate future research and applications of agentic intelligence.
Kimi-Audio Technical Report
Apr 25, 2025



Abstract:We present Kimi-Audio, an open-source audio foundation model that excels in audio understanding, generation, and conversation. We detail the practices in building Kimi-Audio, including model architecture, data curation, training recipe, inference deployment, and evaluation. Specifically, we leverage a 12.5Hz audio tokenizer, design a novel LLM-based architecture with continuous features as input and discrete tokens as output, and develop a chunk-wise streaming detokenizer based on flow matching. We curate a pre-training dataset that consists of more than 13 million hours of audio data covering a wide range of modalities including speech, sound, and music, and build a pipeline to construct high-quality and diverse post-training data. Initialized from a pre-trained LLM, Kimi-Audio is continual pre-trained on both audio and text data with several carefully designed tasks, and then fine-tuned to support a diverse of audio-related tasks. Extensive evaluation shows that Kimi-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance on a range of audio benchmarks including speech recognition, audio understanding, audio question answering, and speech conversation. We release the codes, model checkpoints, as well as the evaluation toolkits in https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-Audio.
WMKA-Net: A Weighted Multi-Kernel Attention NetworkMethod for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Apr 21, 2025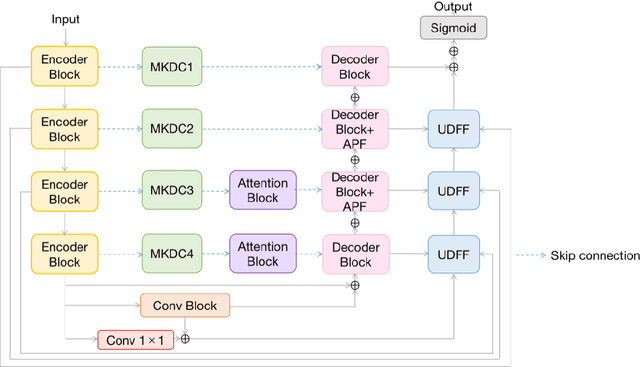

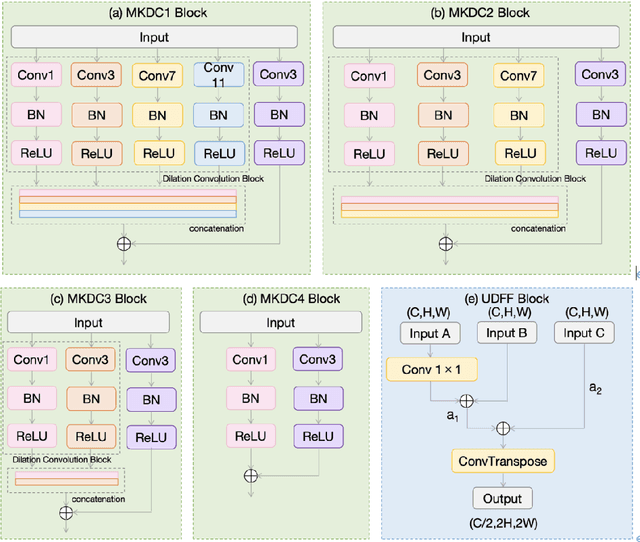
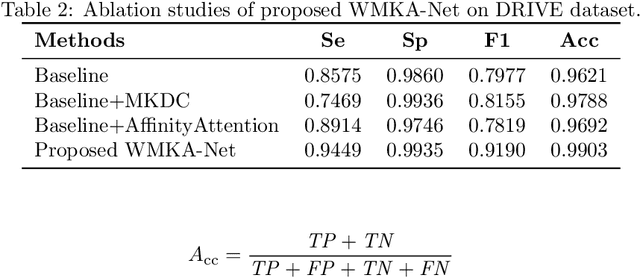
Abstract:We propose a novel retinal vessel segmentation network, the Weighted Multi-Kernel Attention Network (WMKA-Net), which aims to address the issues of insufficient multiscale feature capture, loss of contextual information, and noise sensitivity in retinal vessel segmentation. WMKA-Net significantly improves the segmentation performance of small vessels and low-contrast regions by integrating several innovative components, including the MultiKernelFeature Fusion Module (MKDC), the Progressive Feature Weighting Fusion Strategy (UDFF), and the Attention Mechanism Module (AttentionBlock). The MKDC module employs multiscale parallel convolutional kernels to extract vessel characteristics, thereby enhancing the ability to capture complex vascular structures. The UDFF strategy optimizes the transmission of feature information by weighted fusion of high- and low-level features. The AttentionBlock highlights key regions and suppresses noise interference through the attention mechanism. Experimental results demonstrate that WMKA-Net achieves excellent segmentation performance in multiple public datasets, particularly in segmentation of small vessels and processing of pathological regions. This work provides a robust and efficient new method for segmentation of the retinal vessel.
Muon is Scalable for LLM Training
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Recently, the Muon optimizer based on matrix orthogonalization has demonstrated strong results in training small-scale language models, but the scalability to larger models has not been proven. We identify two crucial techniques for scaling up Muon: (1) adding weight decay and (2) carefully adjusting the per-parameter update scale. These techniques allow Muon to work out-of-the-box on large-scale training without the need of hyper-parameter tuning. Scaling law experiments indicate that Muon achieves $\sim\!2\times$ computational efficiency compared to AdamW with compute optimal training. Based on these improvements, we introduce Moonlight, a 3B/16B-parameter Mixture-of-Expert (MoE) model trained with 5.7T tokens using Muon. Our model improves the current Pareto frontier, achieving better performance with much fewer training FLOPs compared to prior models. We open-source our distributed Muon implementation that is memory optimal and communication efficient. We also release the pretrained, instruction-tuned, and intermediate checkpoints to support future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge