Xingyu Su
Dynamic Search for Inference-Time Alignment in Diffusion Models
Mar 03, 2025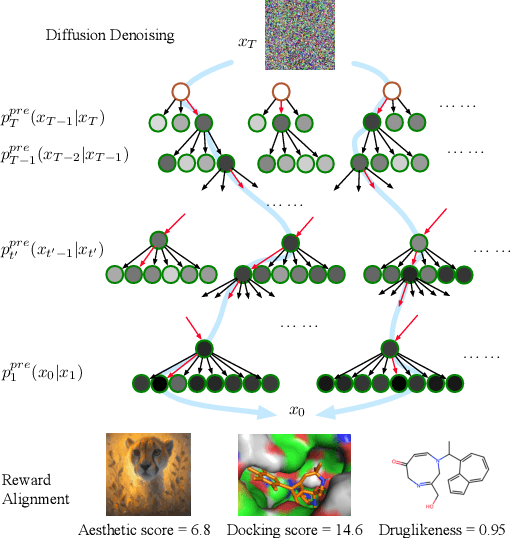
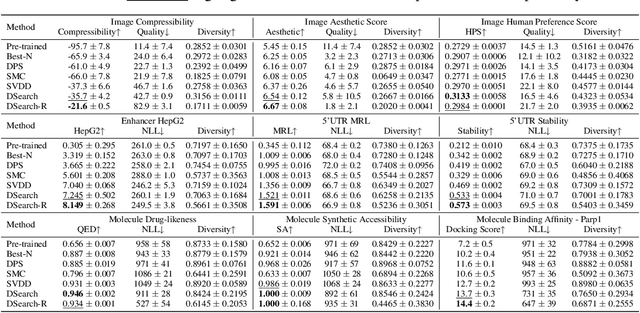
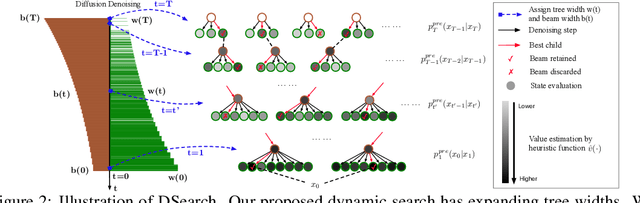
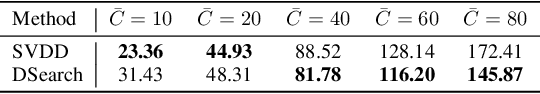
Abstract:Diffusion models have shown promising generative capabilities across diverse domains, yet aligning their outputs with desired reward functions remains a challenge, particularly in cases where reward functions are non-differentiable. Some gradient-free guidance methods have been developed, but they often struggle to achieve optimal inference-time alignment. In this work, we newly frame inference-time alignment in diffusion as a search problem and propose Dynamic Search for Diffusion (DSearch), which subsamples from denoising processes and approximates intermediate node rewards. It also dynamically adjusts beam width and tree expansion to efficiently explore high-reward generations. To refine intermediate decisions, DSearch incorporates adaptive scheduling based on noise levels and a lookahead heuristic function. We validate DSearch across multiple domains, including biological sequence design, molecular optimization, and image generation, demonstrating superior reward optimization compared to existing approaches.
Reward-Guided Iterative Refinement in Diffusion Models at Test-Time with Applications to Protein and DNA Design
Feb 20, 2025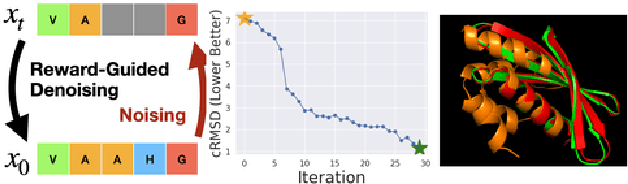
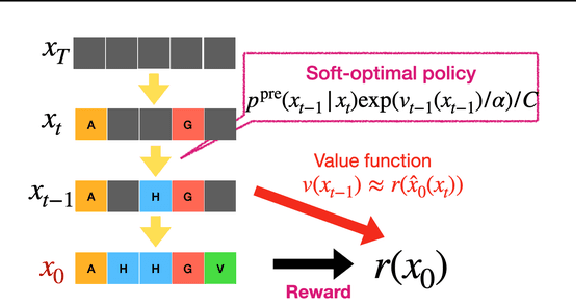
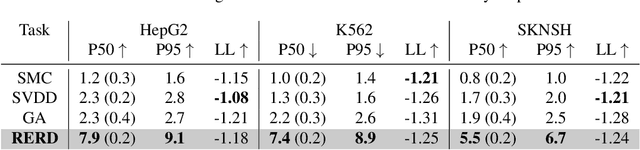
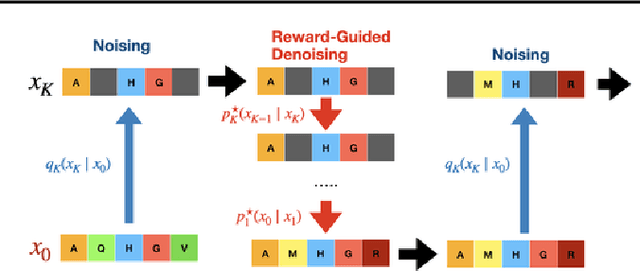
Abstract:To fully leverage the capabilities of diffusion models, we are often interested in optimizing downstream reward functions during inference. While numerous algorithms for reward-guided generation have been recently proposed due to their significance, current approaches predominantly focus on single-shot generation, transitioning from fully noised to denoised states. We propose a novel framework for inference-time reward optimization with diffusion models inspired by evolutionary algorithms. Our approach employs an iterative refinement process consisting of two steps in each iteration: noising and reward-guided denoising. This sequential refinement allows for the gradual correction of errors introduced during reward optimization. Besides, we provide a theoretical guarantee for our framework. Finally, we demonstrate its superior empirical performance in protein and cell-type-specific regulatory DNA design. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/masa-ue/ProDifEvo-Refinement}{https://github.com/masa-ue/ProDifEvo-Refinement}.
Learning to Discover Regulatory Elements for Gene Expression Prediction
Feb 19, 2025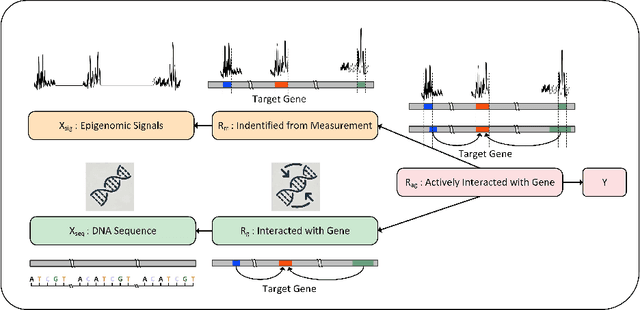
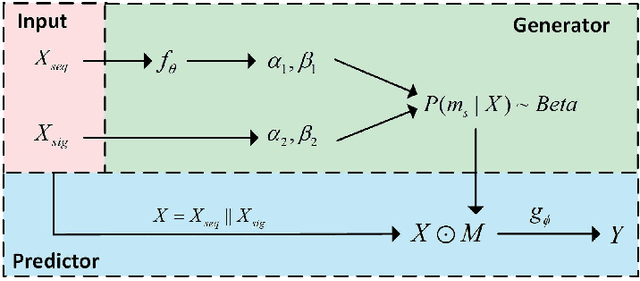
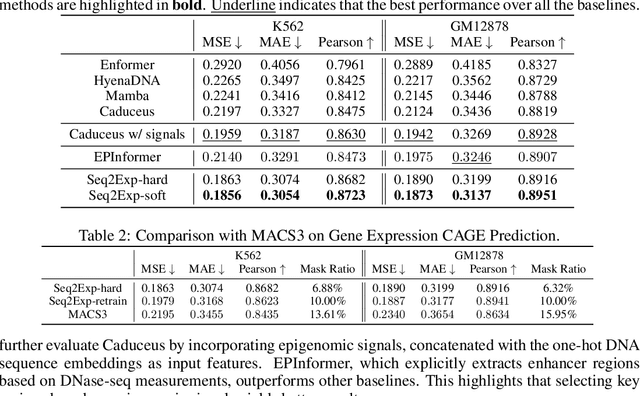
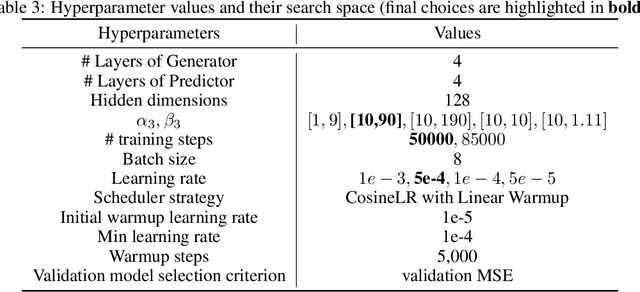
Abstract:We consider the problem of predicting gene expressions from DNA sequences. A key challenge of this task is to find the regulatory elements that control gene expressions. Here, we introduce Seq2Exp, a Sequence to Expression network explicitly designed to discover and extract regulatory elements that drive target gene expression, enhancing the accuracy of the gene expression prediction. Our approach captures the causal relationship between epigenomic signals, DNA sequences and their associated regulatory elements. Specifically, we propose to decompose the epigenomic signals and the DNA sequence conditioned on the causal active regulatory elements, and apply an information bottleneck with the Beta distribution to combine their effects while filtering out non-causal components. Our experiments demonstrate that Seq2Exp outperforms existing baselines in gene expression prediction tasks and discovers influential regions compared to commonly used statistical methods for peak detection such as MACS3. The source code is released as part of the AIRS library (https://github.com/divelab/AIRS/).
PagPassGPT: Pattern Guided Password Guessing via Generative Pretrained Transformer
Apr 07, 2024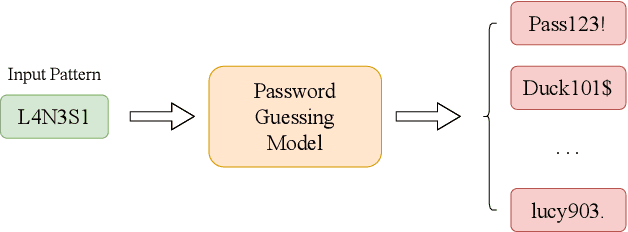
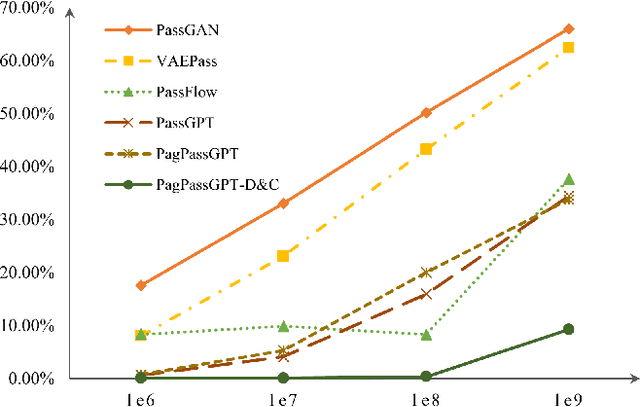
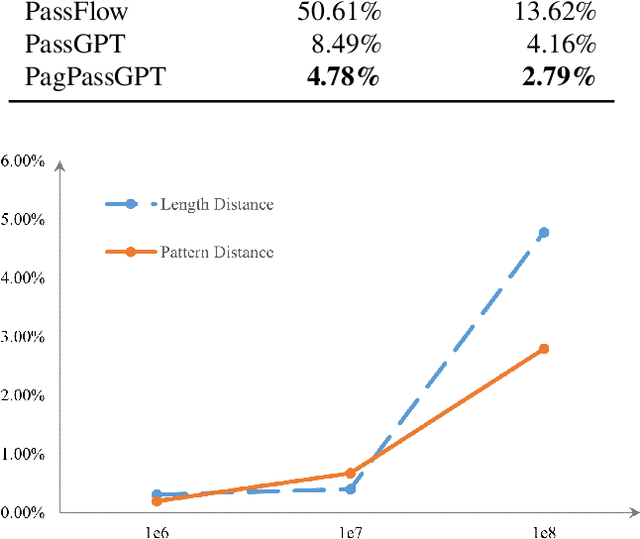
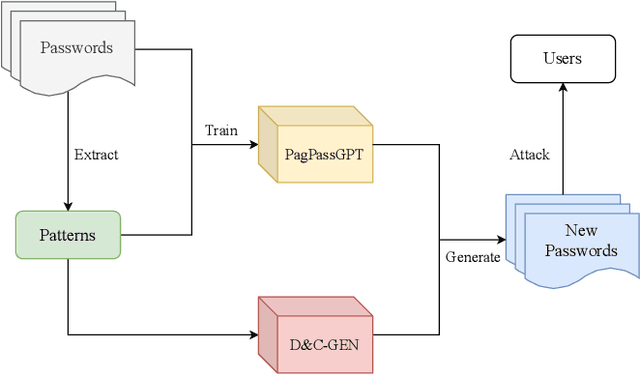
Abstract:Amidst the surge in deep learning-based password guessing models, challenges of generating high-quality passwords and reducing duplicate passwords persist. To address these challenges, we present PagPassGPT, a password guessing model constructed on Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT). It can perform pattern guided guessing by incorporating pattern structure information as background knowledge, resulting in a significant increase in the hit rate. Furthermore, we propose D&C-GEN to reduce the repeat rate of generated passwords, which adopts the concept of a divide-and-conquer approach. The primary task of guessing passwords is recursively divided into non-overlapping subtasks. Each subtask inherits the knowledge from the parent task and predicts succeeding tokens. In comparison to the state-of-the-art model, our proposed scheme exhibits the capability to correctly guess 12% more passwords while producing 25% fewer duplicates.
Arrhenius.jl: A Differentiable Combustion SimulationPackage
Jun 19, 2021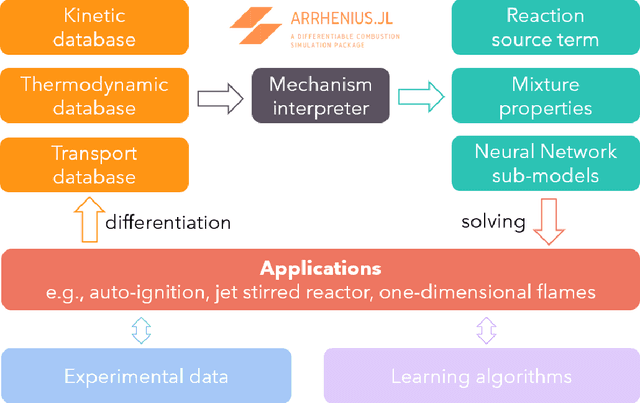
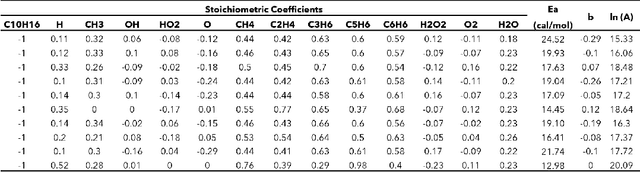
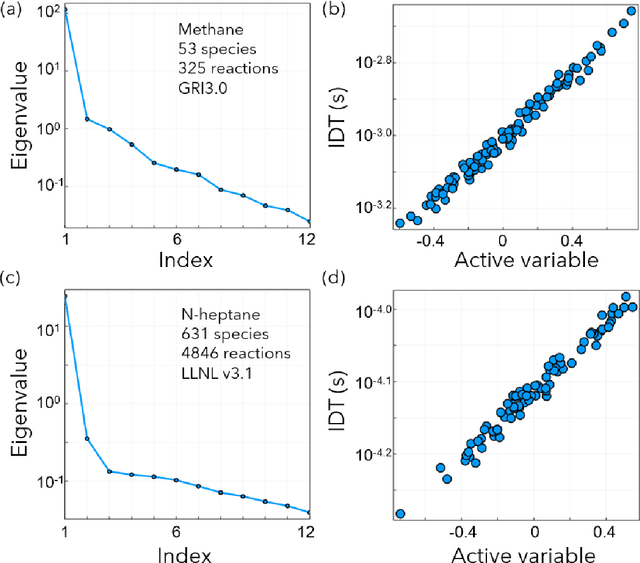
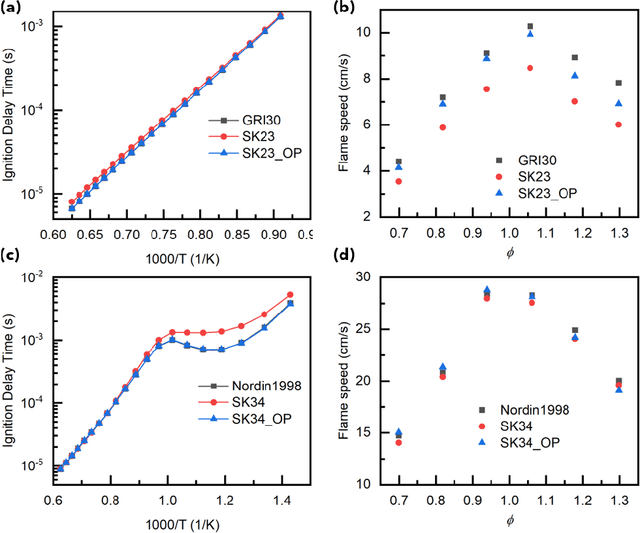
Abstract:Combustion kinetic modeling is an integral part of combustion simulation, and extensive studies have been devoted to developing both high fidelity and computationally affordable models. Despite these efforts, modeling combustion kinetics is still challenging due to the demand for expert knowledge and optimization against experiments, as well as the lack of understanding of the associated uncertainties. Therefore, data-driven approaches that enable efficient discovery and calibration of kinetic models have received much attention in recent years, the core of which is the optimization based on big data. Differentiable programming is a promising approach for learning kinetic models from data by efficiently computing the gradient of objective functions to model parameters. However, it is often challenging to implement differentiable programming in practice. Therefore, it is still not available in widely utilized combustion simulation packages such as CHEMKIN and Cantera. Here, we present a differentiable combustion simulation package leveraging the eco-system in Julia, including DifferentialEquations.jl for solving differential equations, ForwardDiff.jl for auto-differentiation, and Flux.jl for incorporating neural network models into combustion simulations and optimizing neural network models using the state-of-the-art deep learning optimizers. We demonstrate the benefits of differentiable programming in efficient and accurate gradient computations, with applications in uncertainty quantification, kinetic model reduction, data assimilation, and model discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge