Xinfeng Liu
AIDE: Annotation-efficient deep learning for automatic medical image segmentation
Dec 14, 2020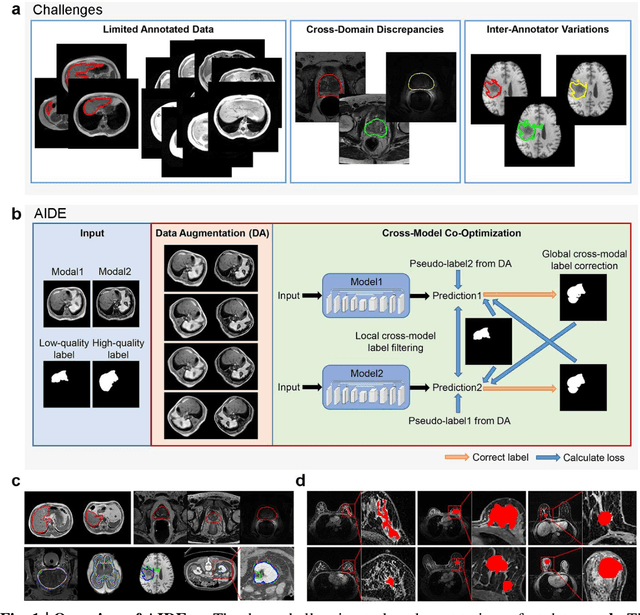
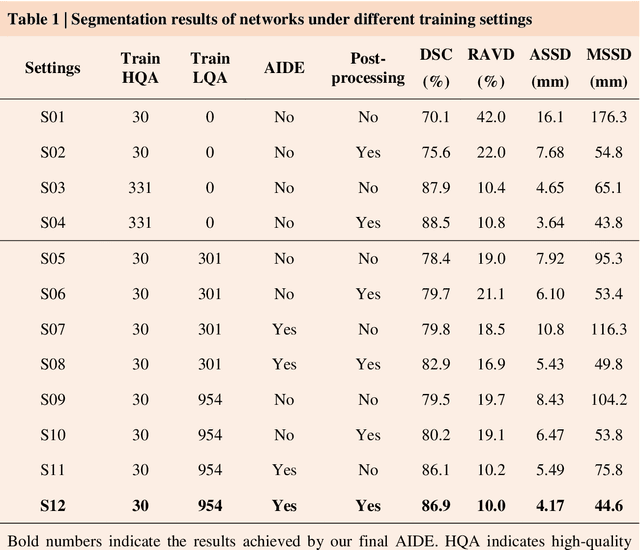
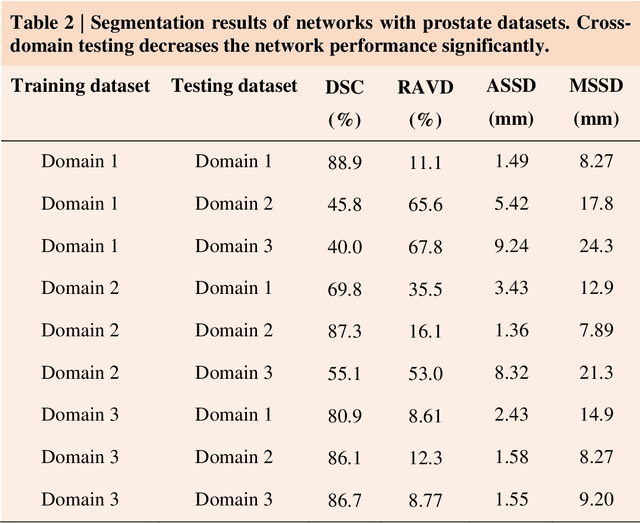
Abstract:Accurate image segmentation is crucial for medical imaging applications. The prevailing deep learning approaches typically rely on very large training datasets with high-quality manual annotations, which are often not available in medical imaging. We introduce Annotation-effIcient Deep lEarning (AIDE) to handle imperfect datasets with an elaborately designed cross-model self-correcting mechanism. AIDE improves the segmentation Dice scores of conventional deep learning models on open datasets possessing scarce or noisy annotations by up to 30%. For three clinical datasets containing 11,852 breast images of 872 patients from three medical centers, AIDE consistently produces segmentation maps comparable to those generated by the fully supervised counterparts as well as the manual annotations of independent radiologists by utilizing only 10% training annotations. Such a 10-fold improvement of efficiency in utilizing experts' labels has the potential to promote a wide range of biomedical applications.
Multi-task MR Imaging with Iterative Teacher Forcing and Re-weighted Deep Learning
Nov 27, 2020
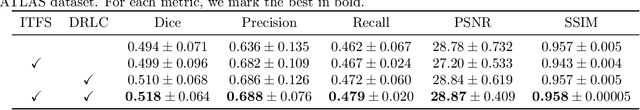

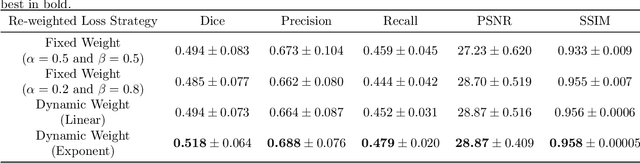
Abstract:Noises, artifacts, and loss of information caused by the magnetic resonance (MR) reconstruction may compromise the final performance of the downstream applications. In this paper, we develop a re-weighted multi-task deep learning method to learn prior knowledge from the existing big dataset and then utilize them to assist simultaneous MR reconstruction and segmentation from the under-sampled k-space data. The multi-task deep learning framework is equipped with two network sub-modules, which are integrated and trained by our designed iterative teacher forcing scheme (ITFS) under the dynamic re-weighted loss constraint (DRLC). The ITFS is designed to avoid error accumulation by injecting the fully-sampled data into the training process. The DRLC is proposed to dynamically balance the contributions from the reconstruction and segmentation sub-modules so as to co-prompt the multi-task accuracy. The proposed method has been evaluated on two open datasets and one in vivo in-house dataset and compared to six state-of-the-art methods. Results show that the proposed method possesses encouraging capabilities for simultaneous and accurate MR reconstruction and segmentation.
A coarse-to-fine framework for unsupervised multi-contrast MR image deformable registration with dual consistency constraint
Aug 06, 2020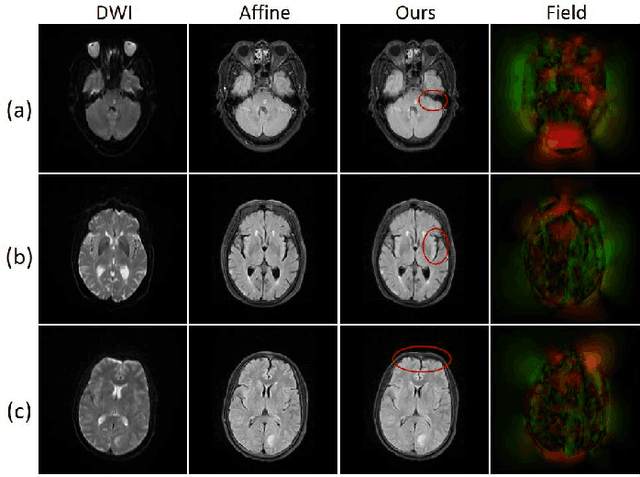
Abstract:Multi-contrast magnetic resonance (MR) image registration is essential in the clinic to achieve fast and accurate imaging-based disease diagnosis and treatment planning. Nevertheless, the efficiency and performance of the existing registration algorithms can still be improved. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised learning-based framework to achieve accurate and efficient multi-contrast MR image registrations. Specifically, an end-to-end coarse-to-fine network architecture consisting of affine and deformable transformations is designed to get rid of both the multi-step iteration process and the complex image preprocessing operations. Furthermore, a dual consistency constraint and a new prior knowledge-based loss function are developed to enhance the registration performances. The proposed method has been evaluated on a clinical dataset that consists of 555 cases, with encouraging performances achieved. Compared to the commonly utilized registration methods, including Voxelmorph, SyN, and LDDMM, the proposed method achieves the best registration performance with a Dice score of 0.826 in identifying stroke lesions. More robust performance in low-signal areas is also observed. With regards to the registration speed, our method is about 17 times faster than the most competitive method of SyN when testing on a same CPU.
CLCI-Net: Cross-Level fusion and Context Inference Networks for Lesion Segmentation of Chronic Stroke
Jul 17, 2019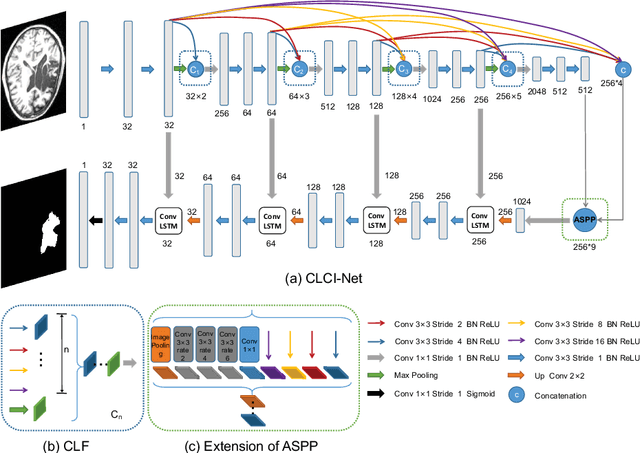
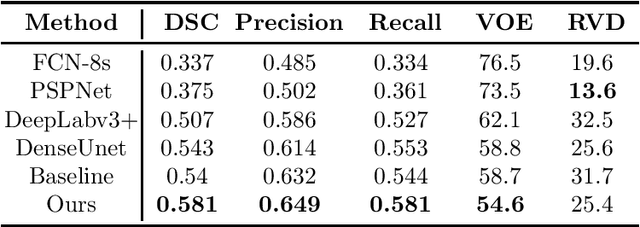
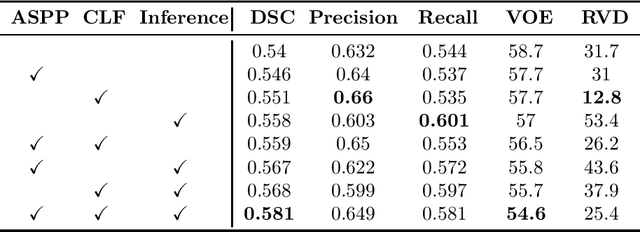
Abstract:Segmenting stroke lesions from T1-weighted MR images is of great value for large-scale stroke rehabilitation neuroimaging analyses. Nevertheless, there are great challenges with this task, such as large range of stroke lesion scales and the tissue intensity similarity. The famous encoder-decoder convolutional neural network, which although has made great achievements in medical image segmentation areas, may fail to address these challenges due to the insufficient uses of multi-scale features and context information. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a Cross-Level fusion and Context Inference Network (CLCI-Net) for the chronic stroke lesion segmentation from T1-weighted MR images. Specifically, a Cross-Level feature Fusion (CLF) strategy was developed to make full use of different scale features across different levels; Extending Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) with CLF, we have enriched multi-scale features to handle the different lesion sizes; In addition, convolutional long short-term memory (ConvLSTM) is employed to infer context information and thus capture fine structures to address the intensity similarity issue. The proposed approach was evaluated on an open-source dataset, the Anatomical Tracings of Lesions After Stroke (ATLAS) with the results showing that our network outperforms five state-of-the-art methods. We make our code and models available at https://github.com/YH0517/CLCI_Net.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge