Xiaowang Zhang
Differentiating Choices via Commonality for Multiple-Choice Question Answering
Aug 21, 2024
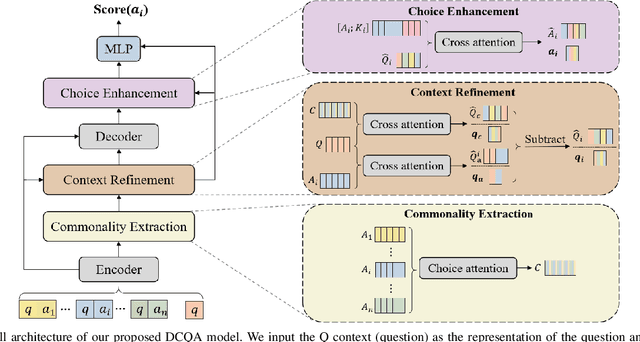
Abstract:Multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) becomes particularly challenging when all choices are relevant to the question and are semantically similar. Yet this setting of MCQA can potentially provide valuable clues for choosing the right answer. Existing models often rank each choice separately, overlooking the context provided by other choices. Specifically, they fail to leverage the semantic commonalities and nuances among the choices for reasoning. In this paper, we propose a novel MCQA model by differentiating choices through identifying and eliminating their commonality, called DCQA. Our model captures token-level attention of each choice to the question, and separates tokens of the question attended to by all the choices (i.e., commonalities) from those by individual choices (i.e., nuances). Using the nuances as refined contexts for the choices, our model can effectively differentiate choices with subtle differences and provide justifications for choosing the correct answer. We conduct comprehensive experiments across five commonly used MCQA benchmarks, demonstrating that DCQA consistently outperforms baseline models. Furthermore, our case study illustrates the effectiveness of the approach in directing the attention of the model to more differentiating features.
SememeLM: A Sememe Knowledge Enhanced Method for Long-tail Relation Representation
Jun 13, 2024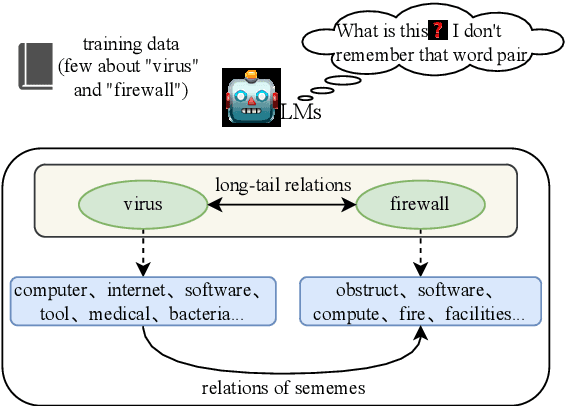
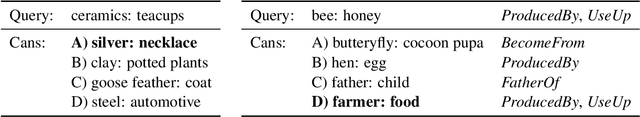
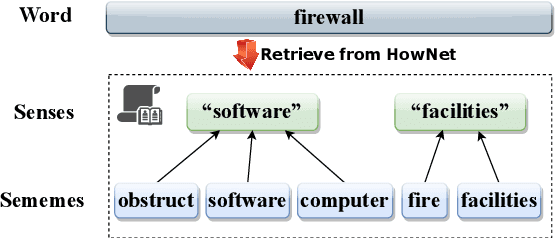
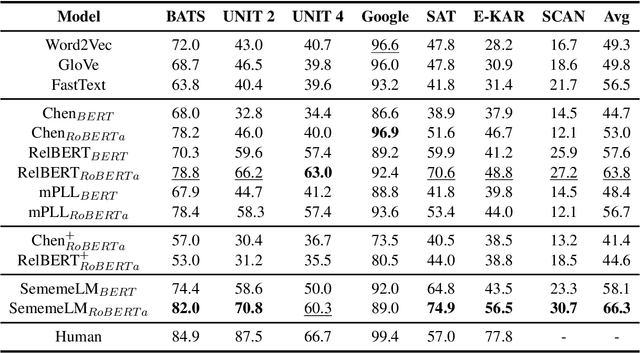
Abstract:Recognizing relations between two words is a fundamental task with the broad applications. Different from extracting relations from text, it is difficult to identify relations among words without their contexts. Especially for long-tail relations, it becomes more difficult due to inadequate semantic features. Existing approaches based on language models (LMs) utilize rich knowledge of LMs to enhance the semantic features of relations. However, they capture uncommon relations while overlooking less frequent but meaningful ones since knowledge of LMs seriously relies on trained data where often represents common relations. On the other hand, long-tail relations are often uncommon in training data. It is interesting but not trivial to use external knowledge to enrich LMs due to collecting corpus containing long-tail relationships is hardly feasible. In this paper, we propose a sememe knowledge enhanced method (SememeLM) to enhance the representation of long-tail relations, in which sememes can break the contextual constraints between wors. Firstly, we present a sememe relation graph and propose a graph encoding method. Moreover, since external knowledge base possibly consisting of massive irrelevant knowledge, the noise is introduced. We propose a consistency alignment module, which aligns the introduced knowledge with LMs, reduces the noise and integrates the knowledge into the language model. Finally, we conducted experiments on word analogy datasets, which evaluates the ability to distinguish relation representations subtle differences, including long-tail relations. Extensive experiments show that our approach outperforms some state-of-the-art methods.
BiSup: Bidirectional Quantization Error Suppression for Large Language Models
May 24, 2024Abstract:As the size and context length of Large Language Models (LLMs) grow, weight-activation quantization has emerged as a crucial technique for efficient deployment of LLMs. Compared to weight-only quantization, weight-activation quantization presents greater challenges due to the presence of outliers in activations. Existing methods have made significant progress by exploring mixed-precision quantization and outlier suppression. However, these methods primarily focus on optimizing the results of single matrix multiplication, neglecting the bidirectional propagation of quantization errors in LLMs. Specifically, errors accumulate vertically within the same token through layers, and diffuse horizontally across different tokens due to self-attention mechanisms. To address this issue, we introduce BiSup, a Bidirectional quantization error Suppression method. By constructing appropriate optimizable parameter spaces, BiSup utilizes a small amount of data for quantization-aware parameter-efficient fine-tuning to suppress the error vertical accumulation. Besides, BiSup employs prompt mixed-precision quantization strategy, which preserves high precision for the key-value cache of system prompts, to mitigate the error horizontal diffusion. Extensive experiments on Llama and Qwen families demonstrate that BiSup can improve performance over two state-of-the-art methods (the average WikiText2 perplexity decreases from 13.26 to 9.41 for Atom and from 14.33 to 7.85 for QuaRot under the W3A3-g128 configuration), further facilitating the practical applications of low-bit weight-activation quantization.
Relative Counterfactual Contrastive Learning for Mitigating Pretrained Stance Bias in Stance Detection
May 16, 2024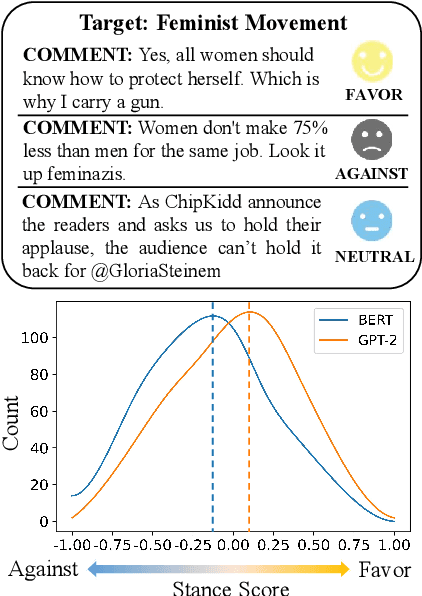
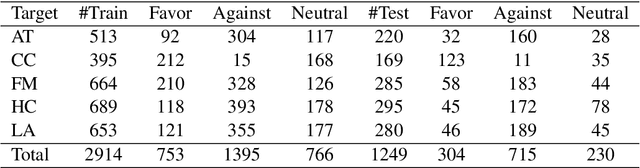
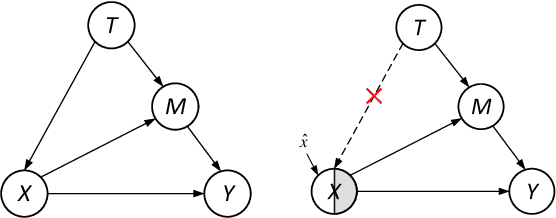
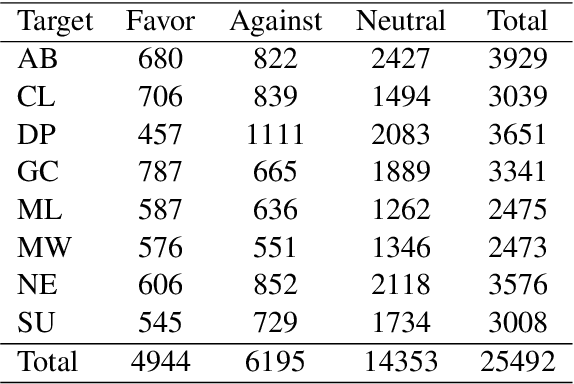
Abstract:Stance detection classifies stance relations (namely, Favor, Against, or Neither) between comments and targets. Pretrained language models (PLMs) are widely used to mine the stance relation to improve the performance of stance detection through pretrained knowledge. However, PLMs also embed ``bad'' pretrained knowledge concerning stance into the extracted stance relation semantics, resulting in pretrained stance bias. It is not trivial to measure pretrained stance bias due to its weak quantifiability. In this paper, we propose Relative Counterfactual Contrastive Learning (RCCL), in which pretrained stance bias is mitigated as relative stance bias instead of absolute stance bias to overtake the difficulty of measuring bias. Firstly, we present a new structural causal model for characterizing complicated relationships among context, PLMs and stance relations to locate pretrained stance bias. Then, based on masked language model prediction, we present a target-aware relative stance sample generation method for obtaining relative bias. Finally, we use contrastive learning based on counterfactual theory to mitigate pretrained stance bias and preserve context stance relation. Experiments show that the proposed method is superior to stance detection and debiasing baselines.
Attribute Simulation for Item Embedding Enhancement in Multi-interest Recommendation
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Although multi-interest recommenders have achieved significant progress in the matching stage, our research reveals that existing models tend to exhibit an under-clustered item embedding space, which leads to a low discernibility between items and hampers item retrieval. This highlights the necessity for item embedding enhancement. However, item attributes, which serve as effective and straightforward side information for enhancement, are either unavailable or incomplete in many public datasets due to the labor-intensive nature of manual annotation tasks. This dilemma raises two meaningful questions: 1. Can we bypass manual annotation and directly simulate complete attribute information from the interaction data? And 2. If feasible, how to simulate attributes with high accuracy and low complexity in the matching stage? In this paper, we first establish an inspiring theoretical feasibility that the item-attribute correlation matrix can be approximated through elementary transformations on the item co-occurrence matrix. Then based on formula derivation, we propose a simple yet effective module, SimEmb (Item Embedding Enhancement via Simulated Attribute), in the multi-interest recommendation of the matching stage to implement our findings. By simulating attributes with the co-occurrence matrix, SimEmb discards the item ID-based embedding and employs the attribute-weighted summation for item embedding enhancement. Comprehensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach notably enhances the clustering of item embedding and significantly outperforms SOTA models with an average improvement of 25.59% on Recall@20.
Function-words Enhanced Attention Networks for Few-Shot Inverse Relation Classification
Apr 26, 2022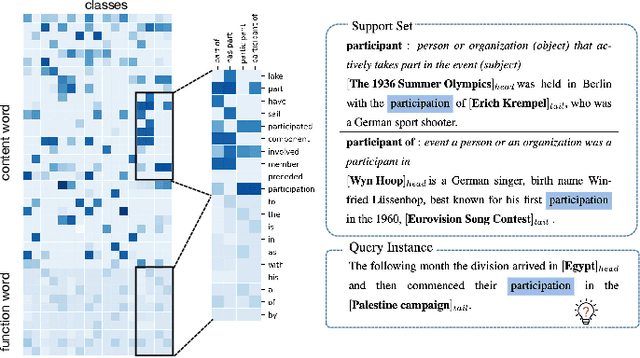
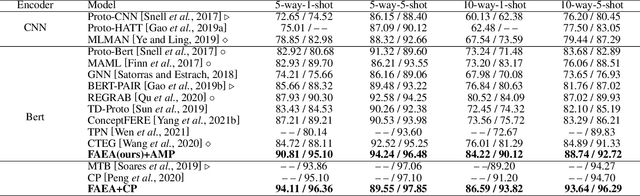
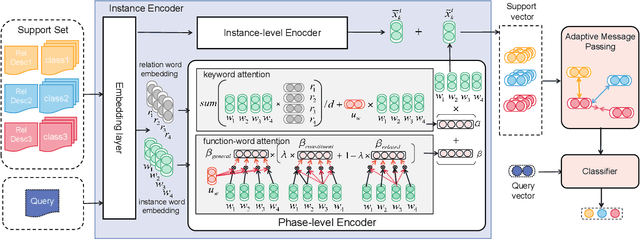
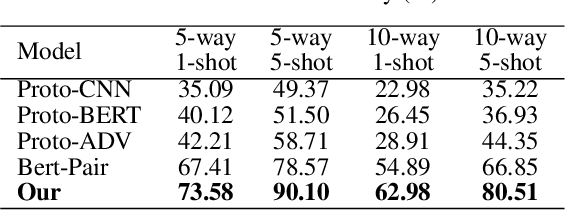
Abstract:The relation classification is to identify semantic relations between two entities in a given text. While existing models perform well for classifying inverse relations with large datasets, their performance is significantly reduced for few-shot learning. In this paper, we propose a function words adaptively enhanced attention framework (FAEA) for few-shot inverse relation classification, in which a hybrid attention model is designed to attend class-related function words based on meta-learning. As the involvement of function words brings in significant intra-class redundancy, an adaptive message passing mechanism is introduced to capture and transfer inter-class differences.We mathematically analyze the negative impact of function words from dot-product measurement, which explains why message passing mechanism effectively reduces the impact. Our experimental results show that FAEA outperforms strong baselines, especially the inverse relation accuracy is improved by 14.33% under 1-shot setting in FewRel1.0.
Learning Disentangled Semantic Representations for Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Transfer in Multilingual Machine Reading Comprehension
Apr 03, 2022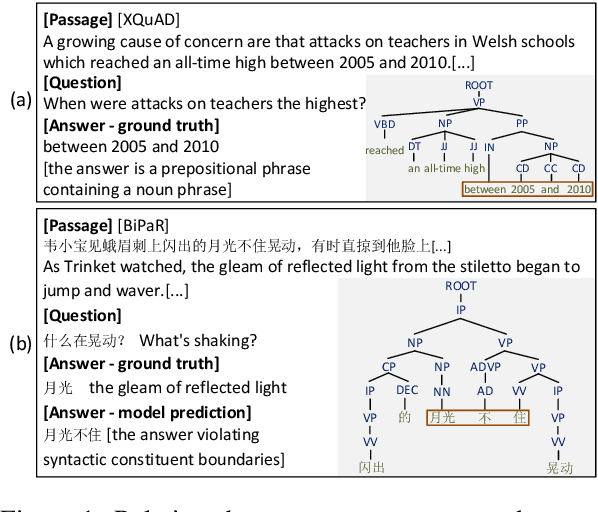
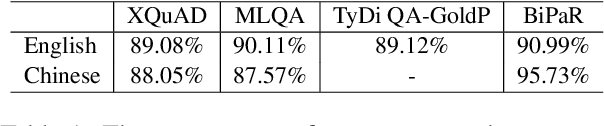
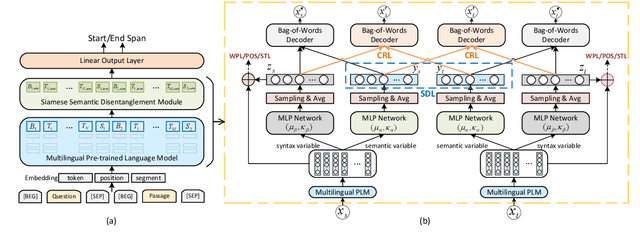
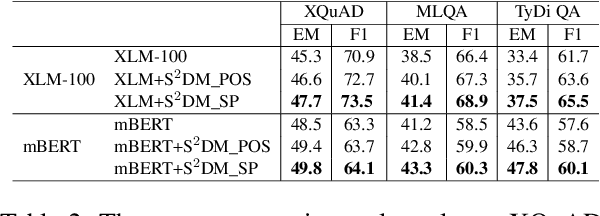
Abstract:Multilingual pre-trained models are able to zero-shot transfer knowledge from rich-resource to low-resource languages in machine reading comprehension (MRC). However, inherent linguistic discrepancies in different languages could make answer spans predicted by zero-shot transfer violate syntactic constraints of the target language. In this paper, we propose a novel multilingual MRC framework equipped with a Siamese Semantic Disentanglement Model (SSDM) to disassociate semantics from syntax in representations learned by multilingual pre-trained models. To explicitly transfer only semantic knowledge to the target language, we propose two groups of losses tailored for semantic and syntactic encoding and disentanglement. Experimental results on three multilingual MRC datasets (i.e., XQuAD, MLQA, and TyDi QA) demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach over models based on mBERT and XLM-100. Code is available at:https://github.com/wulinjuan/SSDM_MRC.
Modeling Global Semantics for Question Answering over Knowledge Bases
Jan 05, 2021



Abstract:Semantic parsing, as an important approach to question answering over knowledge bases (KBQA), transforms a question into the complete query graph for further generating the correct logical query. Existing semantic parsing approaches mainly focus on relations matching with paying less attention to the underlying internal structure of questions (e.g., the dependencies and relations between all entities in a question) to select the query graph. In this paper, we present a relational graph convolutional network (RGCN)-based model gRGCN for semantic parsing in KBQA. gRGCN extracts the global semantics of questions and their corresponding query graphs, including structure semantics via RGCN and relational semantics (label representation of relations between entities) via a hierarchical relation attention mechanism. Experiments evaluated on benchmarks show that our model outperforms off-the-shelf models.
TrQuery: An Embedding-based Framework for Recommanding SPARQL Queries
Jun 16, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, we present an embedding-based framework (TrQuery) for recommending solutions of a SPARQL query, including approximate solutions when exact querying solutions are not available due to incompleteness or inconsistencies of real-world RDF data. Within this framework, embedding is applied to score solutions together with edit distance so that we could obtain more fine-grained recommendations than those recommendations via edit distance. For instance, graphs of two querying solutions with a similar structure can be distinguished in our proposed framework while the edit distance depending on structural difference becomes unable. To this end, we propose a novel score model built on vector space generated in embedding system to compute the similarity between an approximate subgraph matching and a whole graph matching. Finally, we evaluate our approach on large RDF datasets DBpedia and YAGO, and experimental results show that TrQuery exhibits an excellent behavior in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency.
On the satisfiability problem for SPARQL patterns
Jun 01, 2016

Abstract:The satisfiability problem for SPARQL patterns is undecidable in general, since the expressive power of SPARQL 1.0 is comparable with that of the relational algebra. The goal of this paper is to delineate the boundary of decidability of satisfiability in terms of the constraints allowed in filter conditions. The classes of constraints considered are bound-constraints, negated bound-constraints, equalities, nonequalities, constant-equalities, and constant-nonequalities. The main result of the paper can be summarized by saying that, as soon as inconsistent filter conditions can be formed, satisfiability is undecidable. The key insight in each case is to find a way to emulate the set difference operation. Undecidability can then be obtained from a known undecidability result for the algebra of binary relations with union, composition, and set difference. When no inconsistent filter conditions can be formed, satisfiability is efficiently decidable by simple checks on bound variables and on the use of literals. The paper also points out that satisfiability for the so-called `well-designed' patterns can be decided by a check on bound variables and a check for inconsistent filter conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge