Xiaofei Wen
Diagnosing and Mitigating Modality Interference in Multimodal Large Language Models
May 26, 2025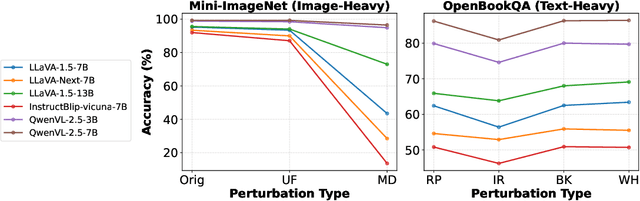
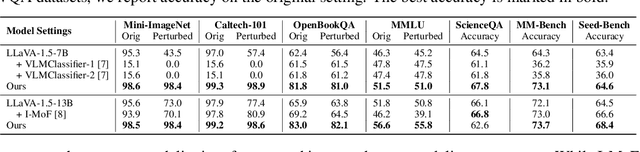
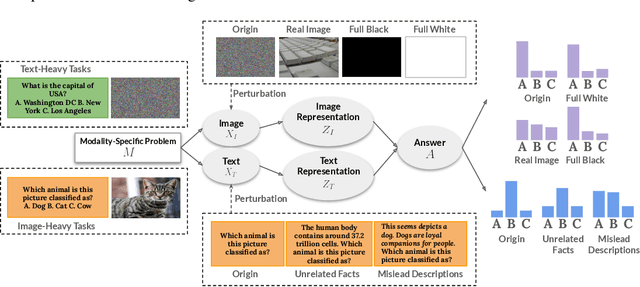
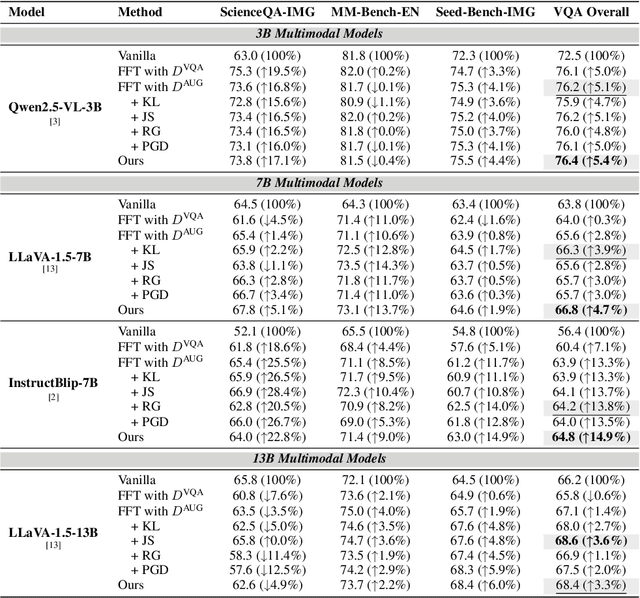
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across tasks, yet they often exhibit difficulty in distinguishing task-relevant from irrelevant signals, particularly in tasks like Visual Question Answering (VQA), which can lead to susceptibility to misleading or spurious inputs. We refer to this broader limitation as the Cross-Modality Competency Problem: the model's inability to fairly evaluate all modalities. This vulnerability becomes more evident in modality-specific tasks such as image classification or pure text question answering, where models are expected to rely solely on one modality. In such tasks, spurious information from irrelevant modalities often leads to significant performance degradation. We refer to this failure as Modality Interference, which serves as a concrete and measurable instance of the cross-modality competency problem. We further design a perturbation-based causal diagnostic experiment to verify and quantify this problem. To mitigate modality interference, we propose a novel framework to fine-tune MLLMs, including perturbation-based data augmentations with both heuristic perturbations and adversarial perturbations via Projected Gradient Descent (PGD), and a consistency regularization strategy applied to model outputs with original and perturbed inputs. Experiments on multiple benchmark datasets (image-heavy, text-heavy, and VQA tasks) and multiple model families with different scales demonstrate significant improvements in robustness and cross-modality competency, indicating our method's effectiveness in boosting unimodal reasoning ability while enhancing performance on multimodal tasks.
ThinkGuard: Deliberative Slow Thinking Leads to Cautious Guardrails
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Ensuring the safety of large language models (LLMs) is critical as they are deployed in real-world applications. Existing guardrails rely on rule-based filtering or single-pass classification, limiting their ability to handle nuanced safety violations. To address this, we propose ThinkGuard, a critique-augmented guardrail model that distills knowledge from high-capacity LLMs by generating structured critiques alongside safety labels. Fine-tuned on critique-augmented data, the captured deliberative thinking ability drastically enhances the guardrail's cautiousness and interpretability. Evaluated on multiple safety benchmarks, ThinkGuard achieves the highest average F1 and AUPRC, outperforming all baselines. Compared to LLaMA Guard 3, ThinkGuard improves accuracy by 16.1% and macro F1 by 27.0%. Moreover, it surpasses label-only fine-tuned models, confirming that structured critiques enhance both classification precision and nuanced safety reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
MetaScientist: A Human-AI Synergistic Framework for Automated Mechanical Metamaterial Design
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:The discovery of novel mechanical metamaterials, whose properties are dominated by their engineered structures rather than chemical composition, is a knowledge-intensive and resource-demanding process. To accelerate the design of novel metamaterials, we present MetaScientist, a human-in-the-loop system that integrates advanced AI capabilities with expert oversight with two primary phases: (1) hypothesis generation, where the system performs complex reasoning to generate novel and scientifically sound hypotheses, supported with domain-specific foundation models and inductive biases retrieved from existing literature; (2) 3D structure synthesis, where a 3D structure is synthesized with a novel 3D diffusion model based on the textual hypothesis and refined it with a LLM-based refinement model to achieve better structure properties. At each phase, domain experts iteratively validate the system outputs, and provide feedback and supplementary materials to ensure the alignment of the outputs with scientific principles and human preferences. Through extensive evaluation from human scientists, MetaScientist is able to deliver novel and valid mechanical metamaterial designs that have the potential to be highly impactful in the metamaterial field.
Personalized Topic Selection Model for Topic-Grounded Dialogue
Jun 04, 2024Abstract:Recently, the topic-grounded dialogue (TGD) system has become increasingly popular as its powerful capability to actively guide users to accomplish specific tasks through topic-guided conversations. Most existing works utilize side information (\eg topics or personas) in isolation to enhance the topic selection ability. However, due to disregarding the noise within these auxiliary information sources and their mutual influence, current models tend to predict user-uninteresting and contextually irrelevant topics. To build user-engaging and coherent dialogue agent, we propose a \textbf{P}ersonalized topic s\textbf{E}lection model for \textbf{T}opic-grounded \textbf{D}ialogue, named \textbf{PETD}, which takes account of the interaction of side information to selectively aggregate such information for more accurately predicting subsequent topics. Specifically, we evaluate the correlation between global topics and personas and selectively incorporate the global topics aligned with user personas. Furthermore, we propose a contrastive learning based persona selector to filter out irrelevant personas under the constraint of lacking pertinent persona annotations. Throughout the selection and generation, diverse relevant side information is considered. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method can generate engaging and diverse responses, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines across various evaluation metrics.
Red Teaming Language Models for Contradictory Dialogues
May 17, 2024



Abstract:Most language models currently available are prone to self-contradiction during dialogues. To mitigate this issue, this study explores a novel contradictory dialogue processing task that aims to detect and modify contradictory statements in a conversation. This task is inspired by research on context faithfulness and dialogue comprehension, which have demonstrated that the detection and understanding of contradictions often necessitate detailed explanations. We develop a dataset comprising contradictory dialogues, in which one side of the conversation contradicts itself. Each dialogue is accompanied by an explanatory label that highlights the location and details of the contradiction. With this dataset, we present a Red Teaming framework for contradictory dialogue processing. The framework detects and attempts to explain the dialogue, then modifies the existing contradictory content using the explanation. Our experiments demonstrate that the framework improves the ability to detect contradictory dialogues and provides valid explanations. Additionally, it showcases distinct capabilities for modifying such dialogues. Our study highlights the importance of the logical inconsistency problem in conversational AI.
Sequential Topic Selection Model with Latent Variable for Topic-Grounded Dialogue
Oct 17, 2022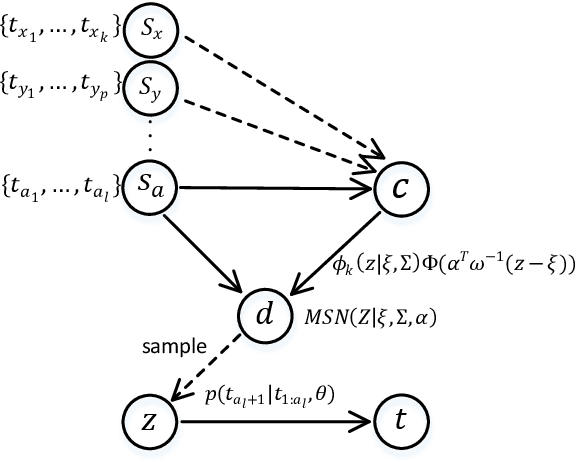
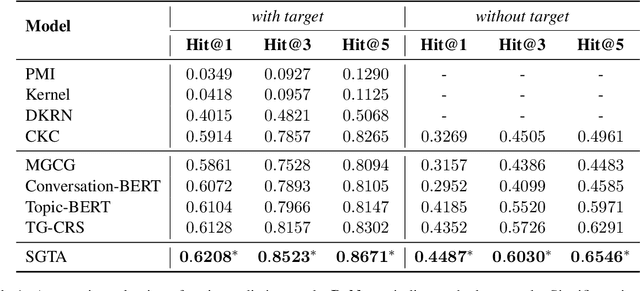
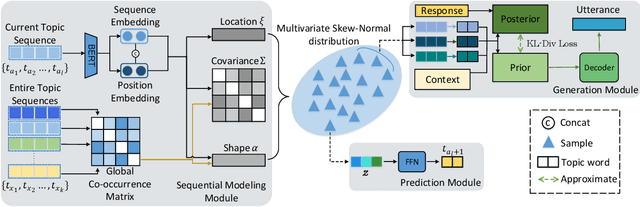
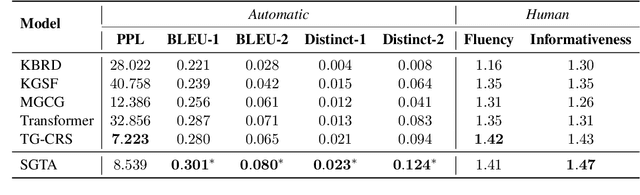
Abstract:Recently, topic-grounded dialogue system has attracted significant attention due to its effectiveness in predicting the next topic to yield better responses via the historical context and given topic sequence. However, almost all existing topic prediction solutions focus on only the current conversation and corresponding topic sequence to predict the next conversation topic, without exploiting other topic-guided conversations which may contain relevant topic-transitions to current conversation. To address the problem, in this paper we propose a novel approach, named Sequential Global Topic Attention (SGTA) to exploit topic transition over all conversations in a subtle way for better modeling post-to-response topic-transition and guiding the response generation to the current conversation. Specifically, we introduce a latent space modeled as a Multivariate Skew-Normal distribution with hybrid kernel functions to flexibly integrate the global-level information with sequence-level information, and predict the topic based on the distribution sampling results. We also leverage a topic-aware prior-posterior approach for secondary selection of predicted topics, which is utilized to optimize the response generation task. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms competitive baselines on prediction and generation tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge