Xiaofei Liao
FusionANNS: An Efficient CPU/GPU Cooperative Processing Architecture for Billion-scale Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) has emerged as a crucial component of database and AI infrastructure. Ever-increasing vector datasets pose significant challenges in terms of performance, cost, and accuracy for ANNS services. None of modern ANNS systems can address these issues simultaneously. We present FusionANNS, a high-throughput, low-latency, cost-efficient, and high-accuracy ANNS system for billion-scale datasets using SSDs and only one entry-level GPU. The key idea of FusionANNS lies in CPU/GPU collaborative filtering and re-ranking mechanisms, which significantly reduce I/O operations across CPUs, GPU, and SSDs to break through the I/O performance bottleneck. Specifically, we propose three novel designs: (1) multi-tiered indexing to avoid data swapping between CPUs and GPU, (2) heuristic re-ranking to eliminate unnecessary I/Os and computations while guaranteeing high accuracy, and (3) redundant-aware I/O deduplication to further improve I/O efficiency. We implement FusionANNS and compare it with the state-of-the-art SSD-based ANNS system--SPANN and GPU-accelerated in-memory ANNS system--RUMMY. Experimental results show that FusionANNS achieves 1) 9.4-13.1X higher query per second (QPS) and 5.7-8.8X higher cost efficiency compared with SPANN; 2) and 2-4.9X higher QPS and 2.3-6.8X higher cost efficiency compared with RUMMY, while guaranteeing low latency and high accuracy.
GIDN: A Lightweight Graph Inception Diffusion Network for High-efficient Link Prediction
Oct 11, 2022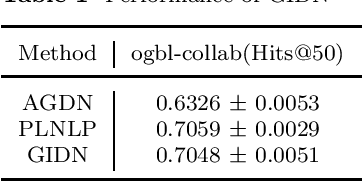
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Graph Inception Diffusion Networks(GIDN) model. This model generalizes graph diffusion in different feature spaces, and uses the inception module to avoid the large amount of computations caused by complex network structures. We evaluate GIDN model on Open Graph Benchmark(OGB) datasets, reached an 11% higher performance than AGDN on ogbl-collab dataset.
Accelerating Backward Aggregation in GCN Training with Execution Path Preparing on GPUs
Apr 06, 2022



Abstract:The emerging Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) has now been widely used in many domains, and it is challenging to improve the efficiencies of applications by accelerating the GCN trainings. For the sparsity nature and exploding scales of input real-world graphs, state-of-the-art GCN training systems (e.g., GNNAdvisor) employ graph processing techniques to accelerate the message exchanging (i.e. aggregations) among the graph vertices. Nevertheless, these systems treat both the aggregation stages of forward and backward propagation phases as all-active graph processing procedures that indiscriminately conduct computation on all vertices of an input graph. In this paper, we first point out that in a GCN training problem with a given training set, the aggregation stages of its backward propagation phase (called as backward aggregations in this paper) can be converted to partially-active graph processing procedures, which conduct computation on only partial vertices of the input graph. By leveraging such a finding, we propose an execution path preparing method that collects and coalesces the data used during backward propagations of GCN training conducted on GPUs. The experimental results show that compared with GNNAdvisor, our approach improves the performance of the backward aggregation of GCN trainings on typical real-world graphs by 1.48x~5.65x. Moreover, the execution path preparing can be conducted either before the training (during preprocessing) or on-the-fly with the training. When used during preprocessing, our approach improves the overall GCN training by 1.05x~1.37x. And when used on-the-fly, our approach improves the overall GCN training by 1.03x~1.35x.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge