Xiaofan Gui
BatteryML:An Open-source platform for Machine Learning on Battery Degradation
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Battery degradation remains a pivotal concern in the energy storage domain, with machine learning emerging as a potent tool to drive forward insights and solutions. However, this intersection of electrochemical science and machine learning poses complex challenges. Machine learning experts often grapple with the intricacies of battery science, while battery researchers face hurdles in adapting intricate models tailored to specific datasets. Beyond this, a cohesive standard for battery degradation modeling, inclusive of data formats and evaluative benchmarks, is conspicuously absent. Recognizing these impediments, we present BatteryML - a one-step, all-encompass, and open-source platform designed to unify data preprocessing, feature extraction, and the implementation of both traditional and state-of-the-art models. This streamlined approach promises to enhance the practicality and efficiency of research applications. BatteryML seeks to fill this void, fostering an environment where experts from diverse specializations can collaboratively contribute, thus elevating the collective understanding and advancement of battery research.The code for our project is publicly available on GitHub at https://github.com/microsoft/BatteryML.
Learning Intra- and Inter-Cell Differences for Accurate Battery Lifespan Prediction across Diverse Conditions
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:Battery life prediction holds significant practical value for battery research and development. Currently, many data-driven models rely on early electrical signals from specific target batteries to predict their lifespan. A common shortfall is that most existing methods are developed based on specific aging conditions, which not only limits their model's capability but also diminishes their effectiveness in predicting degradation under varied conditions. As a result, these models often miss out on fully benefiting from the rich historical data available under other conditions. Here, to address above, we introduce an approach that explicitly captures differences between electrical signals of a target battery and a reference battery, irrespective of their materials and aging conditions, to forecast the target battery life. Through this inter-cell difference, we not only enhance the feature space but also pave the way for a universal battery life prediction framework. Remarkably, our model that combines the inter- and intra-cell differences shines across diverse conditions, standing out in its efficiency and accuracy using all accessible datasets. An essential application of our approach is its capability to leverage data from older batteries effectively, enabling newer batteries to capitalize on insights gained from past batteries. This work not only enriches the battery data utilization strategy but also sets the stage for smarter battery management system in the future.
UADB: Unsupervised Anomaly Detection Booster
Jun 03, 2023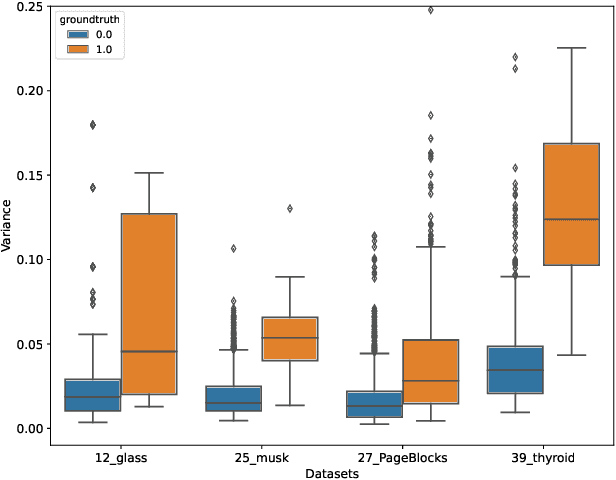
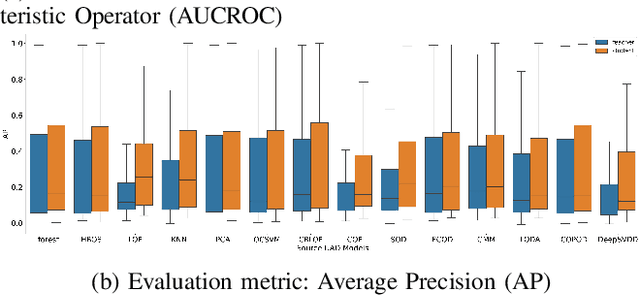
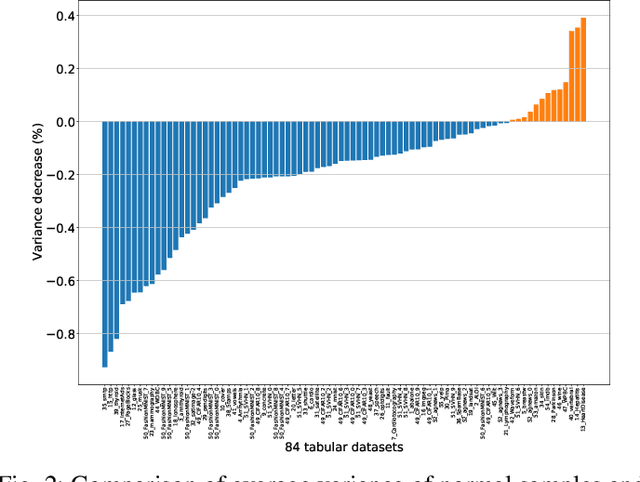
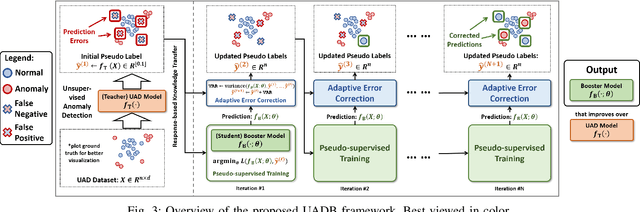
Abstract:Unsupervised Anomaly Detection (UAD) is a key data mining problem owing to its wide real-world applications. Due to the complete absence of supervision signals, UAD methods rely on implicit assumptions about anomalous patterns (e.g., scattered/sparsely/densely clustered) to detect anomalies. However, real-world data are complex and vary significantly across different domains. No single assumption can describe such complexity and be valid in all scenarios. This is also confirmed by recent research that shows no UAD method is omnipotent. Based on above observations, instead of searching for a magic universal winner assumption, we seek to design a general UAD Booster (UADB) that empowers any UAD models with adaptability to different data. This is a challenging task given the heterogeneous model structures and assumptions adopted by existing UAD methods. To achieve this, we dive deep into the UAD problem and find that compared to normal data, anomalies (i) lack clear structure/pattern in feature space, thus (ii) harder to learn by model without a suitable assumption, and finally, leads to (iii) high variance between different learners. In light of these findings, we propose to (i) distill the knowledge of the source UAD model to an imitation learner (booster) that holds no data assumption, then (ii) exploit the variance between them to perform automatic correction, and thus (iii) improve the booster over the original UAD model. We use a neural network as the booster for its strong expressive power as a universal approximator and ability to perform flexible post-hoc tuning. Note that UADB is a model-agnostic framework that can enhance heterogeneous UAD models in a unified way. Extensive experiments on over 80 tabular datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of UADB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge