Xiaobing Chen
FLEX-MoE: Federated Mixture-of-Experts with Load-balanced Expert Assignment
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models enable scalable neural networks through conditional computation. However, their deployment with federated learning (FL) faces two critical challenges: 1) resource-constrained edge devices cannot store full expert sets, and 2) non-IID data distributions cause severe expert load imbalance that degrades model performance. To this end, we propose \textbf{FLEX-MoE}, a novel federated MoE framework that jointly optimizes expert assignment and load balancing under limited client capacity. Specifically, our approach introduces client-expert fitness scores that quantify the expert suitability for local datasets through training feedback, and employs an optimization-based algorithm to maximize client-expert specialization while enforcing balanced expert utilization system-wide. Unlike existing greedy methods that focus solely on personalization while ignoring load imbalance, our FLEX-MoE is capable of addressing the expert utilization skew, which is particularly severe in FL settings with heterogeneous data. Our comprehensive experiments on three different datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed FLEX-MoE, together with its ability to maintain balanced expert utilization across diverse resource-constrained scenarios.
Pruning and Malicious Injection: A Retraining-Free Backdoor Attack on Transformer Models
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:Transformer models have demonstrated exceptional performance and have become indispensable in computer vision (CV) and natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, recent studies reveal that transformers are susceptible to backdoor attacks. Prior backdoor attack methods typically rely on retraining with clean data or altering the model architecture, both of which can be resource-intensive and intrusive. In this paper, we propose Head-wise Pruning and Malicious Injection (HPMI), a novel retraining-free backdoor attack on transformers that does not alter the model's architecture. Our approach requires only a small subset of the original data and basic knowledge of the model architecture, eliminating the need for retraining the target transformer. Technically, HPMI works by pruning the least important head and injecting a pre-trained malicious head to establish the backdoor. We provide a rigorous theoretical justification demonstrating that the implanted backdoor resists detection and removal by state-of-the-art defense techniques, under reasonable assumptions. Experimental evaluations across multiple datasets further validate the effectiveness of HPMI, showing that it 1) incurs negligible clean accuracy loss, 2) achieves at least 99.55% attack success rate, and 3) bypasses four advanced defense mechanisms. Additionally, relative to state-of-the-art retraining-dependent attacks, HPMI achieves greater concealment and robustness against diverse defense strategies, while maintaining minimal impact on clean accuracy.
Enhancing Time Series Forecasting via Multi-Level Text Alignment with LLMs
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:The adaptation of large language models (LLMs) to time series forecasting poses unique challenges, as time series data is continuous in nature, while LLMs operate on discrete tokens. Despite the success of LLMs in natural language processing (NLP) and other structured domains, aligning time series data with language-based representations while maintaining both predictive accuracy and interpretability remains a significant hurdle. Existing methods have attempted to reprogram time series data into text-based forms, but these often fall short in delivering meaningful, interpretable results. In this paper, we propose a multi-level text alignment framework for time series forecasting using LLMs that not only improves prediction accuracy but also enhances the interpretability of time series representations. Our method decomposes time series into trend, seasonal, and residual components, which are then reprogrammed into component-specific text representations. We introduce a multi-level alignment mechanism, where component-specific embeddings are aligned with pre-trained word tokens, enabling more interpretable forecasts. Experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art models in accuracy while providing good interpretability.
DualGFL: Federated Learning with a Dual-Level Coalition-Auction Game
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Despite some promising results in federated learning using game-theoretical methods, most existing studies mainly employ a one-level game in either a cooperative or competitive environment, failing to capture the complex dynamics among participants in practice. To address this issue, we propose DualGFL, a novel Federated Learning framework with a Dual-level Game in cooperative-competitive environments. DualGFL includes a lower-level hedonic game where clients form coalitions and an upper-level multi-attribute auction game where coalitions bid for training participation. At the lower-level DualGFL, we introduce a new auction-aware utility function and propose a Pareto-optimal partitioning algorithm to find a Pareto-optimal partition based on clients' preference profiles. At the upper-level DualGFL, we formulate a multi-attribute auction game with resource constraints and derive equilibrium bids to maximize coalitions' winning probabilities and profits. A greedy algorithm is proposed to maximize the utility of the central server. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate DualGFL's effectiveness in improving both server utility and client utility.
ScaleCert: Scalable Certified Defense against Adversarial Patches with Sparse Superficial Layers
Nov 04, 2021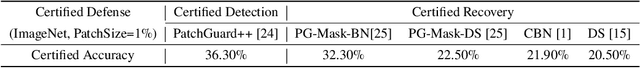
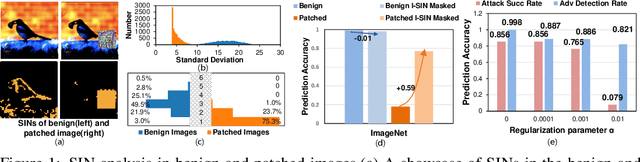
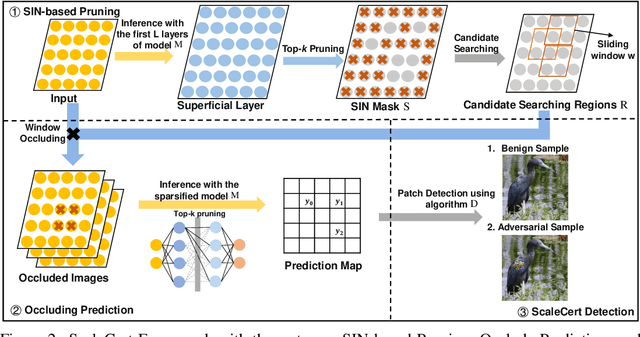
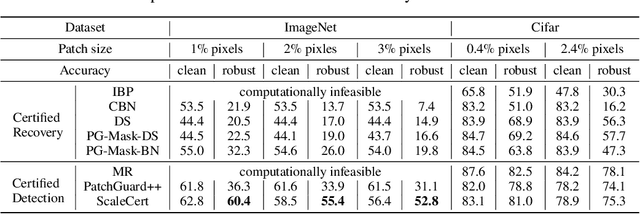
Abstract:Adversarial patch attacks that craft the pixels in a confined region of the input images show their powerful attack effectiveness in physical environments even with noises or deformations. Existing certified defenses towards adversarial patch attacks work well on small images like MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets, but achieve very poor certified accuracy on higher-resolution images like ImageNet. It is urgent to design both robust and effective defenses against such a practical and harmful attack in industry-level larger images. In this work, we propose the certified defense methodology that achieves high provable robustness for high-resolution images and largely improves the practicality for real adoption of the certified defense. The basic insight of our work is that the adversarial patch intends to leverage localized superficial important neurons (SIN) to manipulate the prediction results. Hence, we leverage the SIN-based DNN compression techniques to significantly improve the certified accuracy, by reducing the adversarial region searching overhead and filtering the prediction noises. Our experimental results show that the certified accuracy is increased from 36.3% (the state-of-the-art certified detection) to 60.4% on the ImageNet dataset, largely pushing the certified defenses for practical use.
Pinpointing the Memory Behaviors of DNN Training
Apr 01, 2021



Abstract:The training of deep neural networks (DNNs) is usually memory-hungry due to the limited device memory capacity of DNN accelerators. Characterizing the memory behaviors of DNN training is critical to optimize the device memory pressures. In this work, we pinpoint the memory behaviors of each device memory block of GPU during training by instrumenting the memory allocators of the runtime system. Our results show that the memory access patterns of device memory blocks are stable and follow an iterative fashion. These observations are useful for the future optimization of memory-efficient training from the perspective of raw memory access patterns.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge