Xianjing Han
PetalView: Fine-grained Location and Orientation Extraction of Street-view Images via Cross-view Local Search with Supplementary Materials
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:Satellite-based street-view information extraction by cross-view matching refers to a task that extracts the location and orientation information of a given street-view image query by using one or multiple geo-referenced satellite images. Recent work has initiated a new research direction to find accurate information within a local area covered by one satellite image centered at a location prior (e.g., from GPS). It can be used as a standalone solution or complementary step following a large-scale search with multiple satellite candidates. However, these existing works require an accurate initial orientation (angle) prior (e.g., from IMU) and/or do not efficiently search through all possible poses. To allow efficient search and to give accurate prediction regardless of the existence or the accuracy of the angle prior, we present PetalView extractors with multi-scale search. The PetalView extractors give semantically meaningful features that are equivalent across two drastically different views, and the multi-scale search strategy efficiently inspects the satellite image from coarse to fine granularity to provide sub-meter and sub-degree precision extraction. Moreover, when an angle prior is given, we propose a learnable prior angle mixer to utilize this information. Our method obtains the best performance on the VIGOR dataset and successfully improves the performance on KITTI dataset test 1 set with the recall within 1 meter (r@1m) for location estimation to 68.88% and recall within 1 degree (r@1d) 21.10% when no angle prior is available, and with angle prior achieves stable estimations at r@1m and r@1d above 70% and 21%, up to a 40-degree noise level.
* This paper has been accepted by ACM Multimedia 2023. This version contains additional supplementary materials
Hierarchical Deep Residual Reasoning for Temporal Moment Localization
Oct 31, 2021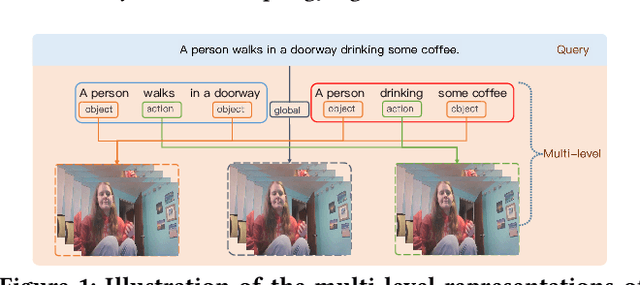
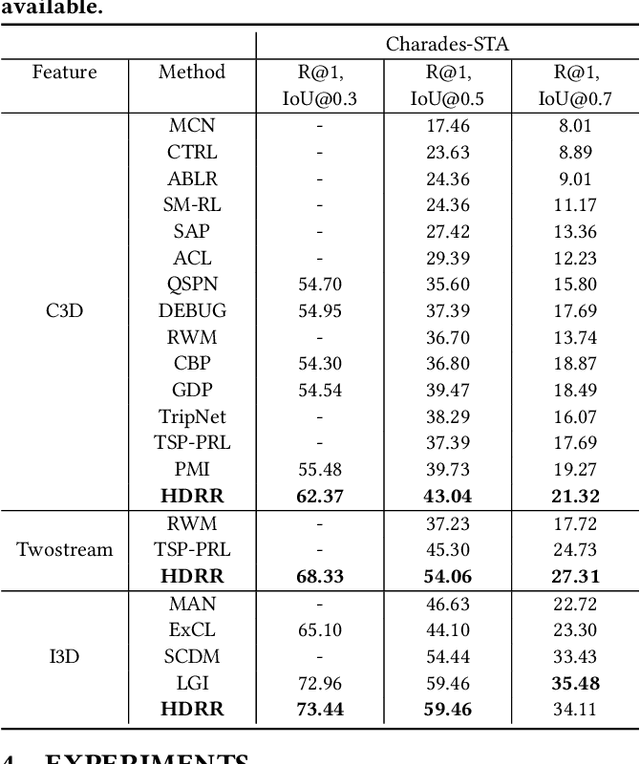
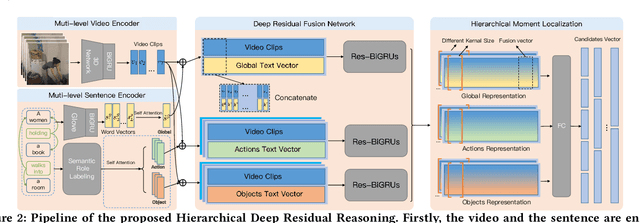
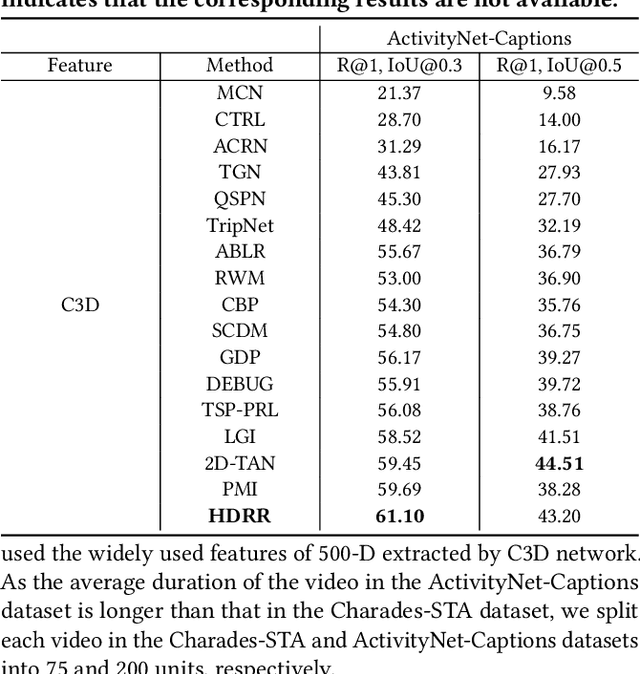
Abstract:Temporal Moment Localization (TML) in untrimmed videos is a challenging task in the field of multimedia, which aims at localizing the start and end points of the activity in the video, described by a sentence query. Existing methods mainly focus on mining the correlation between video and sentence representations or investigating the fusion manner of the two modalities. These works mainly understand the video and sentence coarsely, ignoring the fact that a sentence can be understood from various semantics, and the dominant words affecting the moment localization in the semantics are the action and object reference. Toward this end, we propose a Hierarchical Deep Residual Reasoning (HDRR) model, which decomposes the video and sentence into multi-level representations with different semantics to achieve a finer-grained localization. Furthermore, considering that videos with different resolution and sentences with different length have different difficulty in understanding, we design the simple yet effective Res-BiGRUs for feature fusion, which is able to grasp the useful information in a self-adapting manner. Extensive experiments conducted on Charades-STA and ActivityNet-Captions datasets demonstrate the superiority of our HDRR model compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
Multi-Modal Interaction Graph Convolutional Network for Temporal Language Localization in Videos
Oct 12, 2021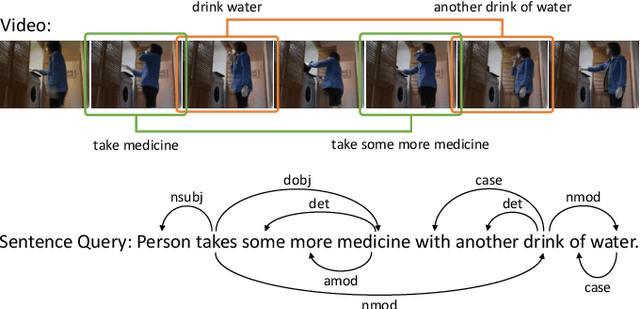
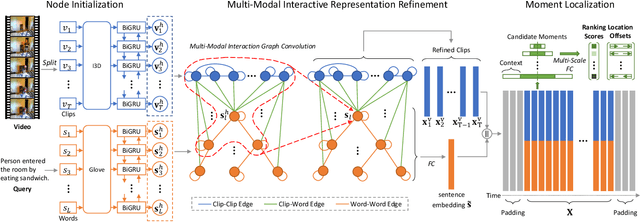
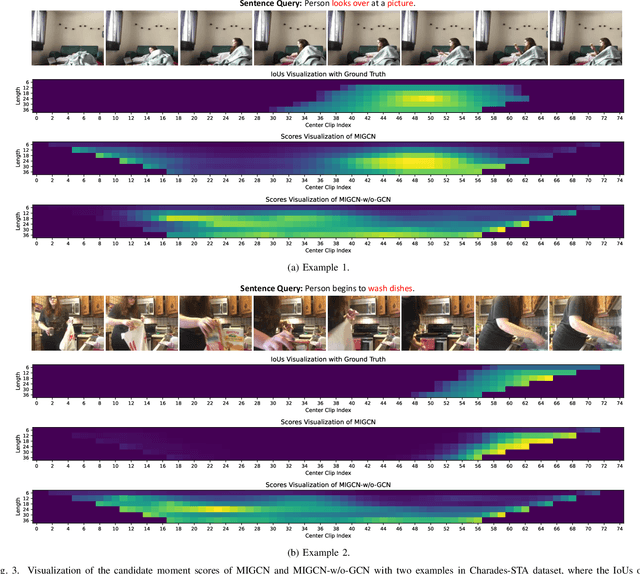

Abstract:This paper focuses on tackling the problem of temporal language localization in videos, which aims to identify the start and end points of a moment described by a natural language sentence in an untrimmed video. However, it is non-trivial since it requires not only the comprehensive understanding of the video and sentence query, but also the accurate semantic correspondence capture between them. Existing efforts are mainly centered on exploring the sequential relation among video clips and query words to reason the video and sentence query, neglecting the other intra-modal relations (e.g., semantic similarity among video clips and syntactic dependency among the query words). Towards this end, in this work, we propose a Multi-modal Interaction Graph Convolutional Network (MIGCN), which jointly explores the complex intra-modal relations and inter-modal interactions residing in the video and sentence query to facilitate the understanding and semantic correspondence capture of the video and sentence query. In addition, we devise an adaptive context-aware localization method, where the context information is taken into the candidate moments and the multi-scale fully connected layers are designed to rank and adjust the boundary of the generated coarse candidate moments with different lengths. Extensive experiments on Charades-STA and ActivityNet datasets demonstrate the promising performance and superior efficiency of our model.
* Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
Neural Compatibility Modeling with Attentive Knowledge Distillation
Apr 17, 2018
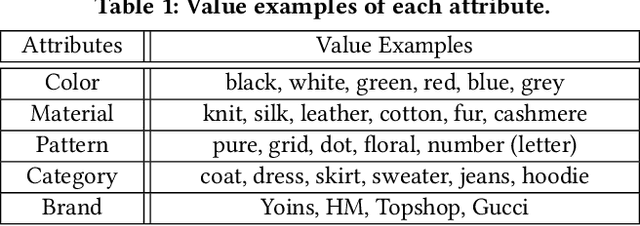

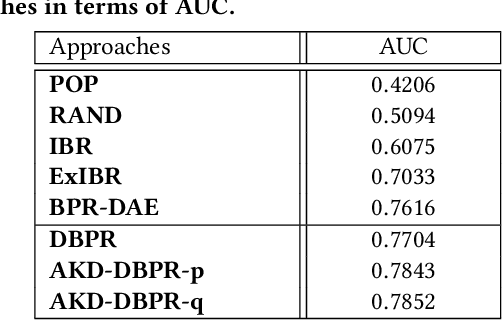
Abstract:Recently, the booming fashion sector and its huge potential benefits have attracted tremendous attention from many research communities. In particular, increasing research efforts have been dedicated to the complementary clothing matching as matching clothes to make a suitable outfit has become a daily headache for many people, especially those who do not have the sense of aesthetics. Thanks to the remarkable success of neural networks in various applications such as image classification and speech recognition, the researchers are enabled to adopt the data-driven learning methods to analyze fashion items. Nevertheless, existing studies overlook the rich valuable knowledge (rules) accumulated in fashion domain, especially the rules regarding clothing matching. Towards this end, in this work, we shed light on complementary clothing matching by integrating the advanced deep neural networks and the rich fashion domain knowledge. Considering that the rules can be fuzzy and different rules may have different confidence levels to different samples, we present a neural compatibility modeling scheme with attentive knowledge distillation based on the teacher-student network scheme. Extensive experiments on the real-world dataset show the superiority of our model over several state-of-the-art baselines. Based upon the comparisons, we observe certain fashion insights that add value to the fashion matching study. As a byproduct, we released the codes, and involved parameters to benefit other researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge